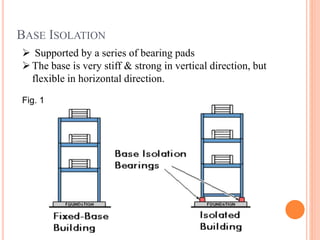
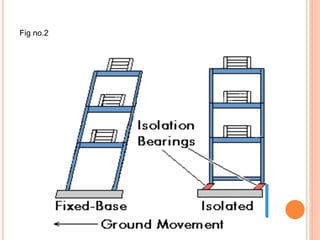
This document discusses techniques for making buildings earthquake resistant. It covers base isolation, which involves supporting a building on bearing pads to allow flexibility during earthquakes. It also discusses energy dissipation devices like friction dampers, metallic dampers, and viscoelastic dampers that can absorb seismic energy. The document provides details on how each technique works and their advantages, such as reducing displacement and maintaining structural performance during earthquakes. It concludes that base isolation and friction dampers are commonly used techniques for earthquake-resistant construction.