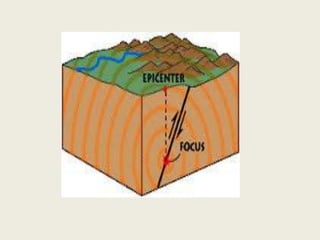
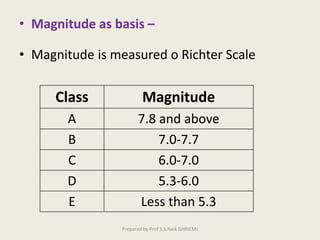
The document discusses earthquakes, including defining them as vibrations induced in the earth's crust due to internal or external causes. It describes seismology as the science dealing with studying earthquakes. Key terms are defined, such as the focus or hypocenter being the point of origin below the surface, and the epicenter being the point above the focus. Different types of seismic waves - P, S, and L waves - are described. Earthquakes are classified based on depth, magnitude using the Richter scale, and causes. Causes include tectonic plate movements and volcanic eruptions. Effects are shaking, landslides, fires, tsunamis, and impact on humans, rivers and seas. Design of earthquake