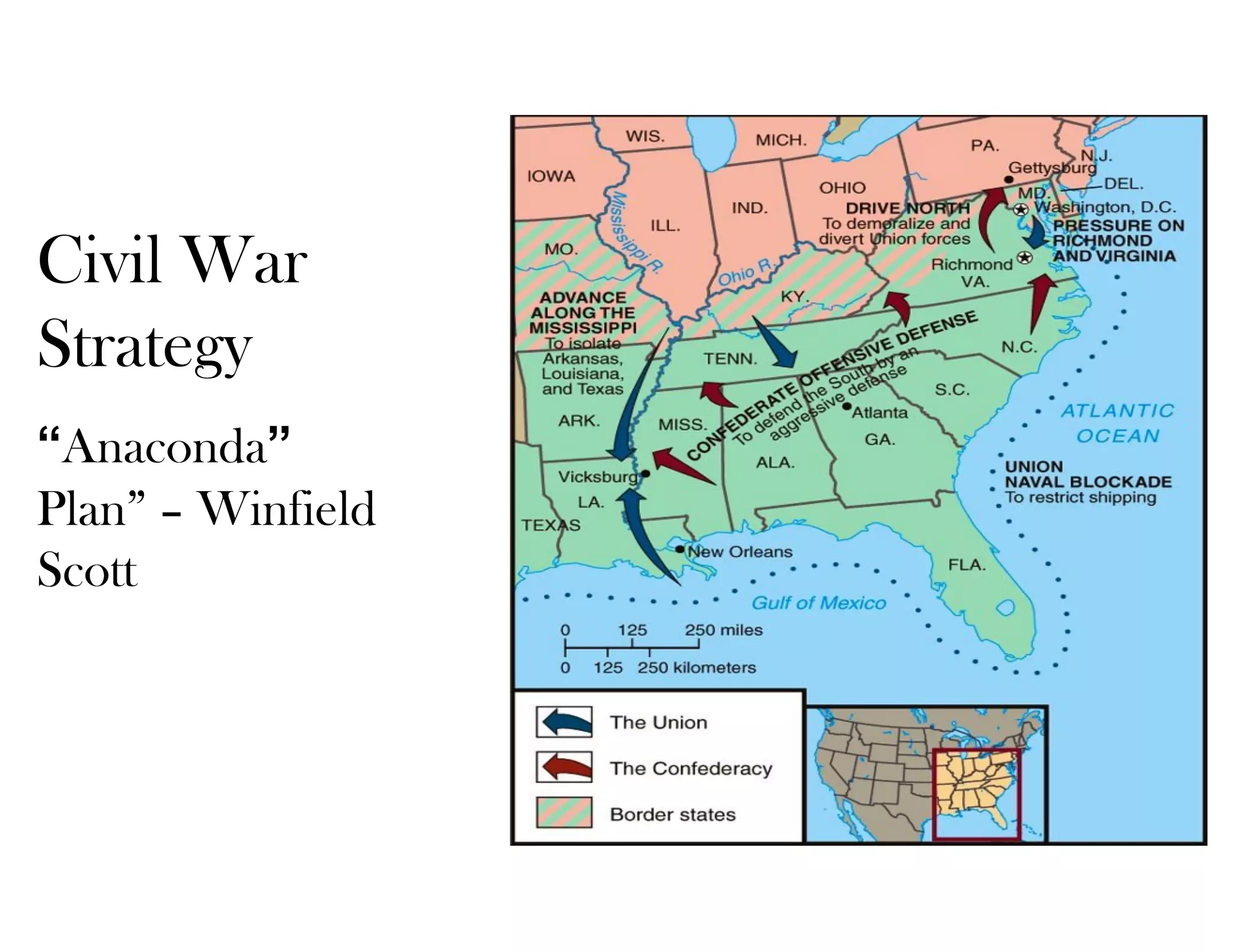
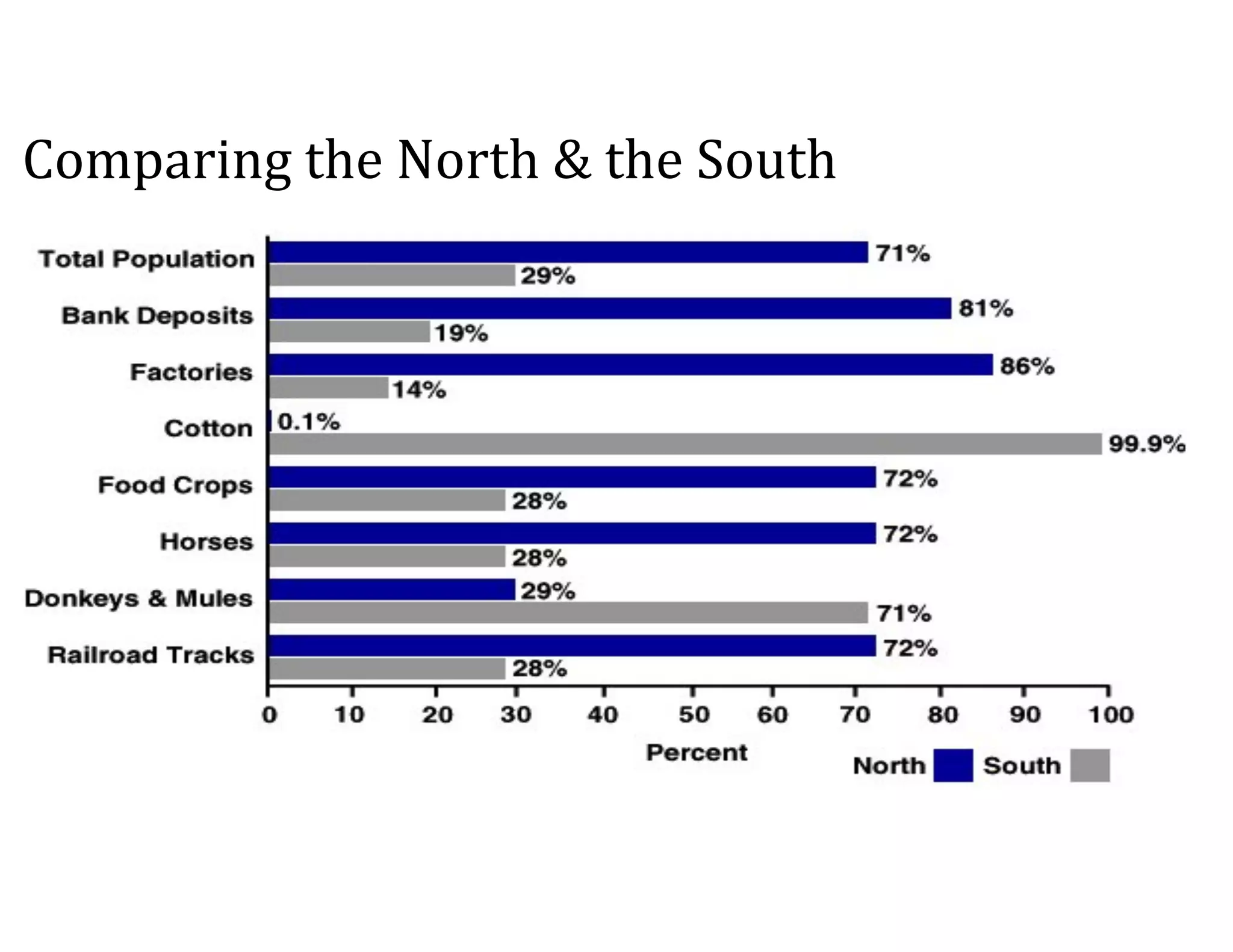
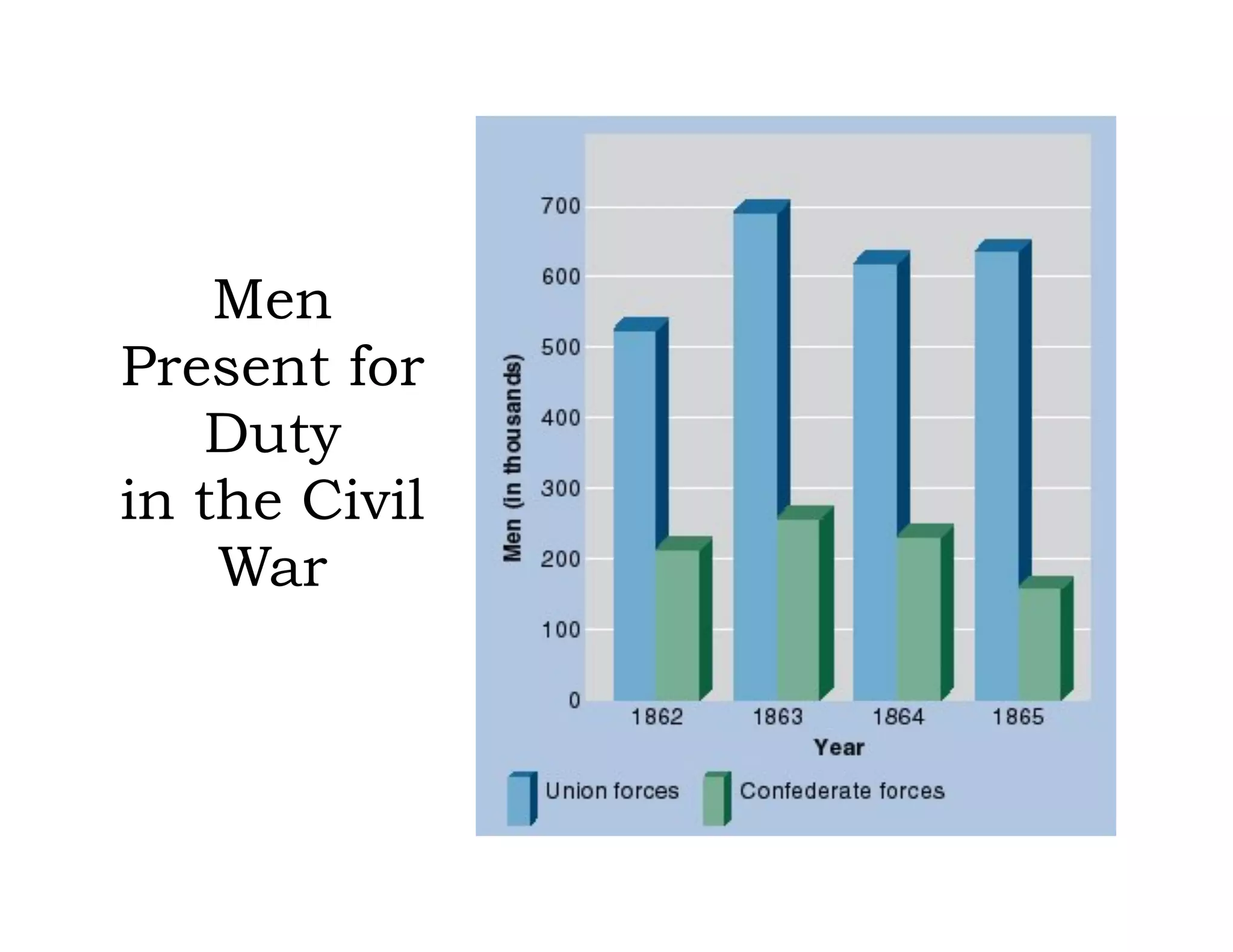
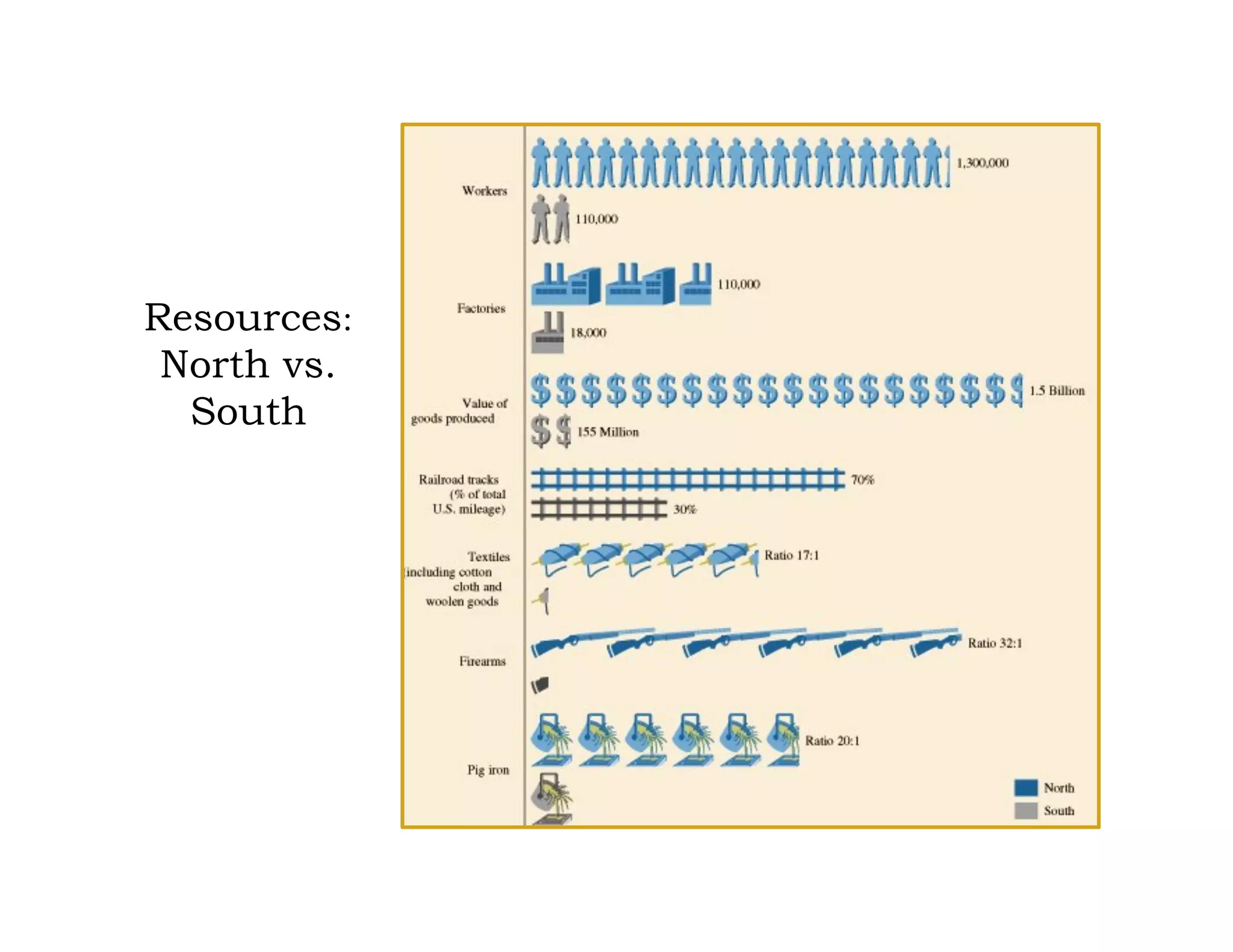
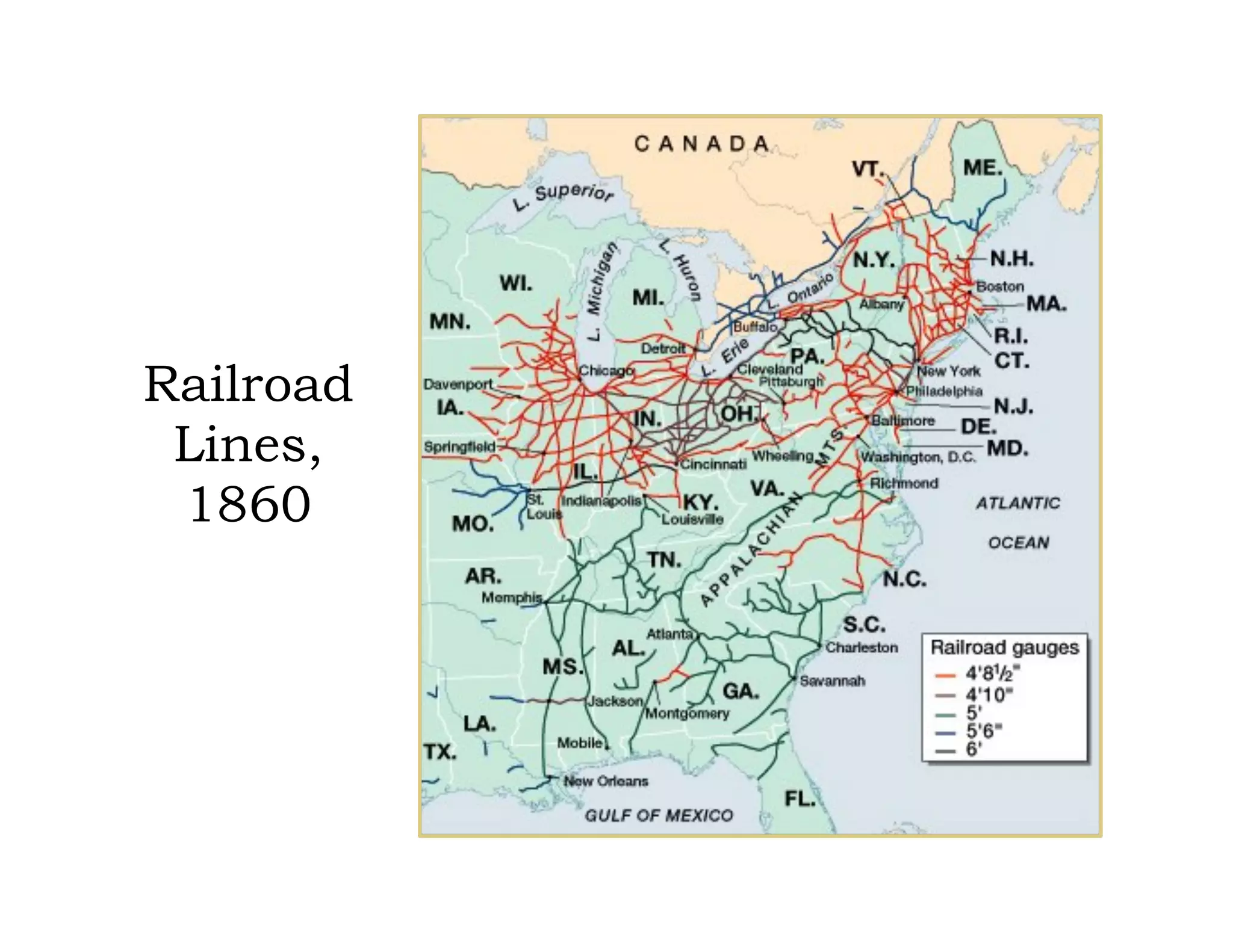
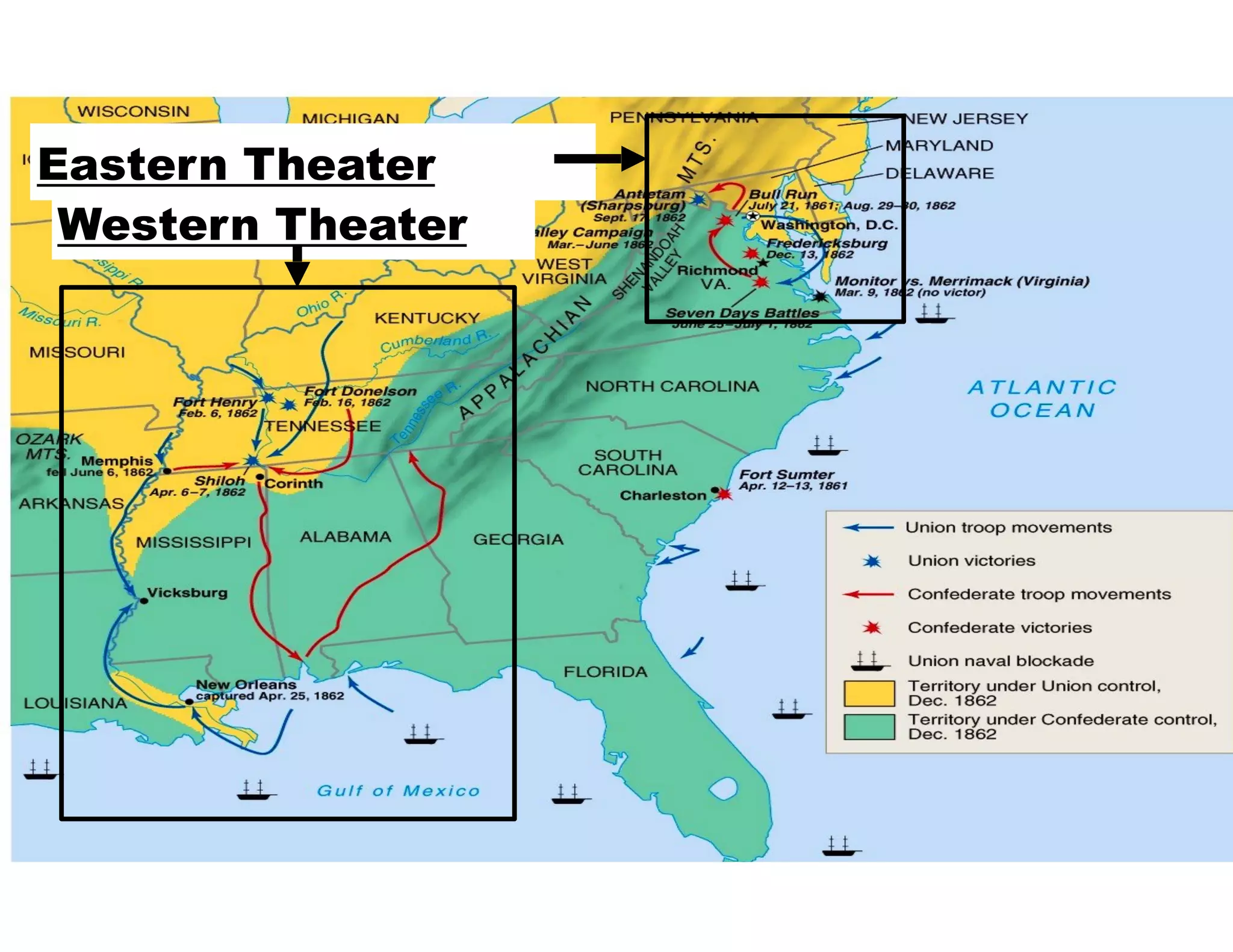
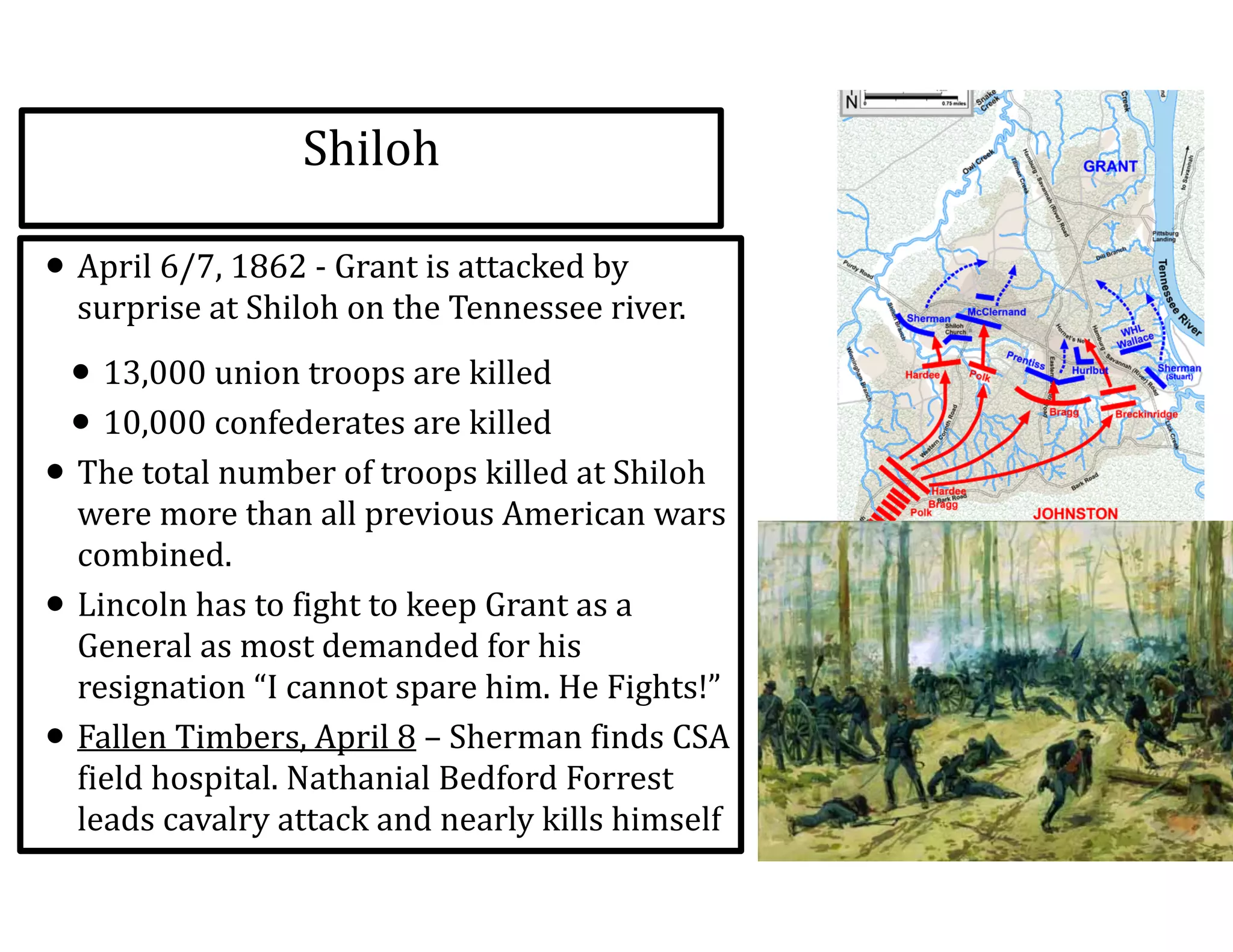
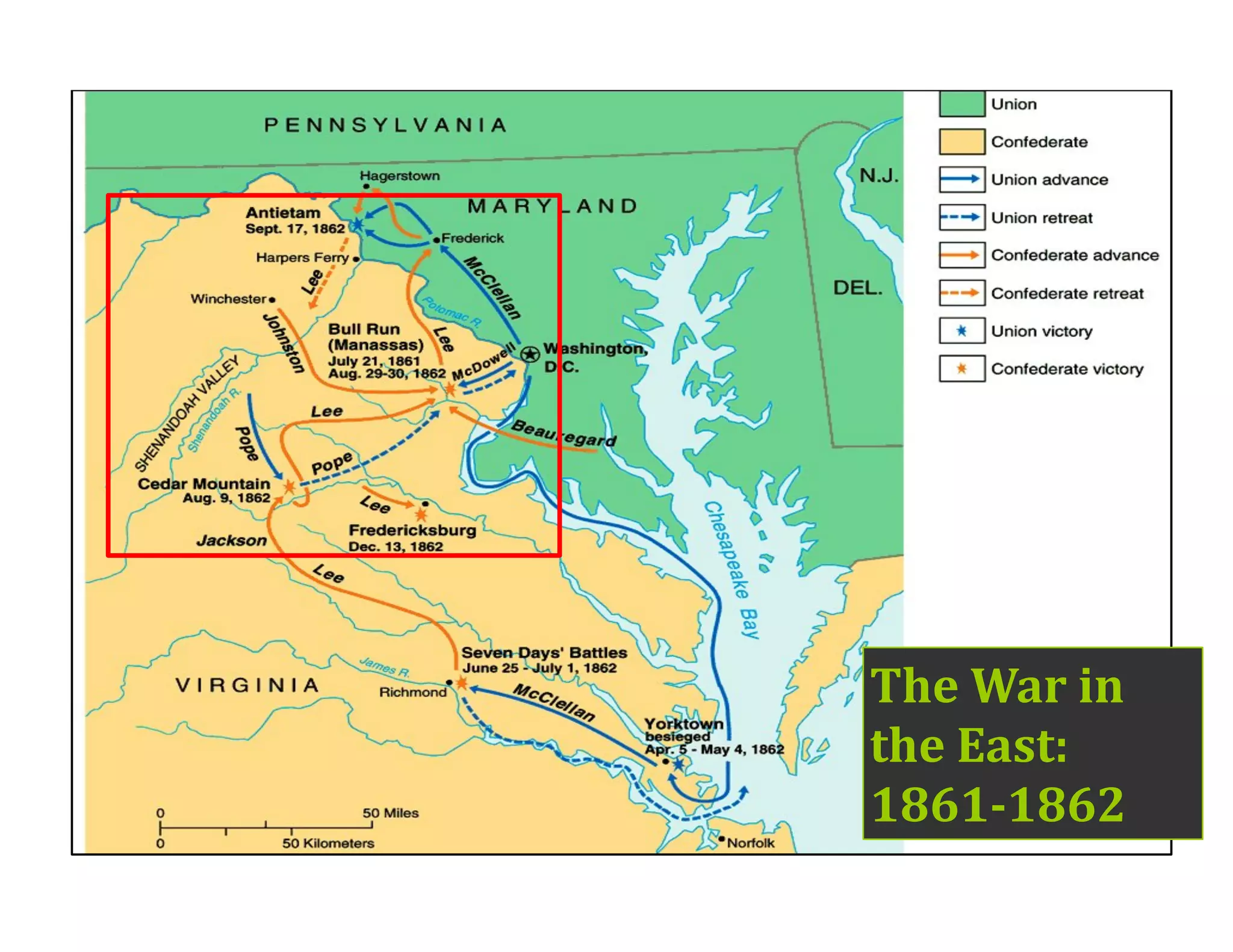
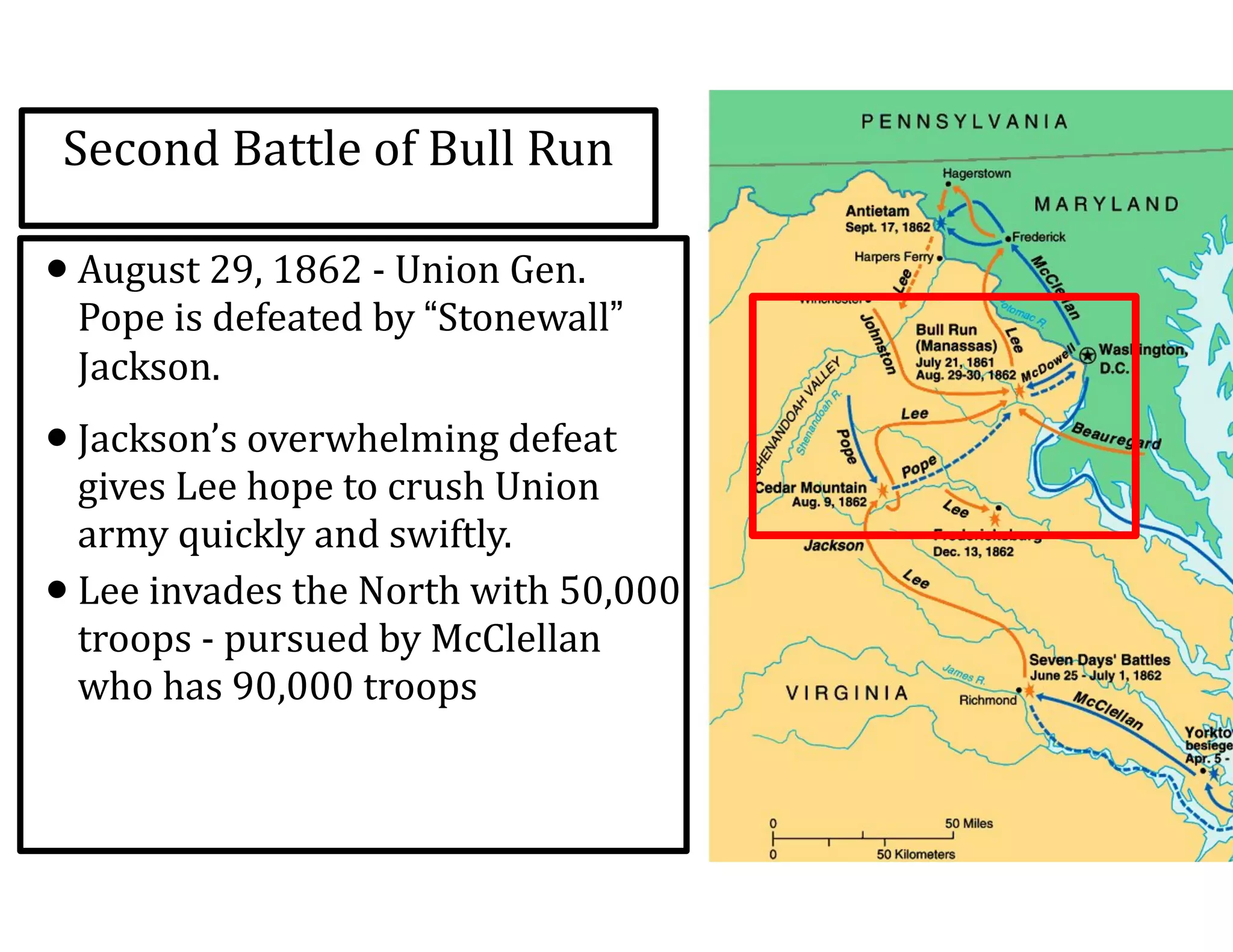
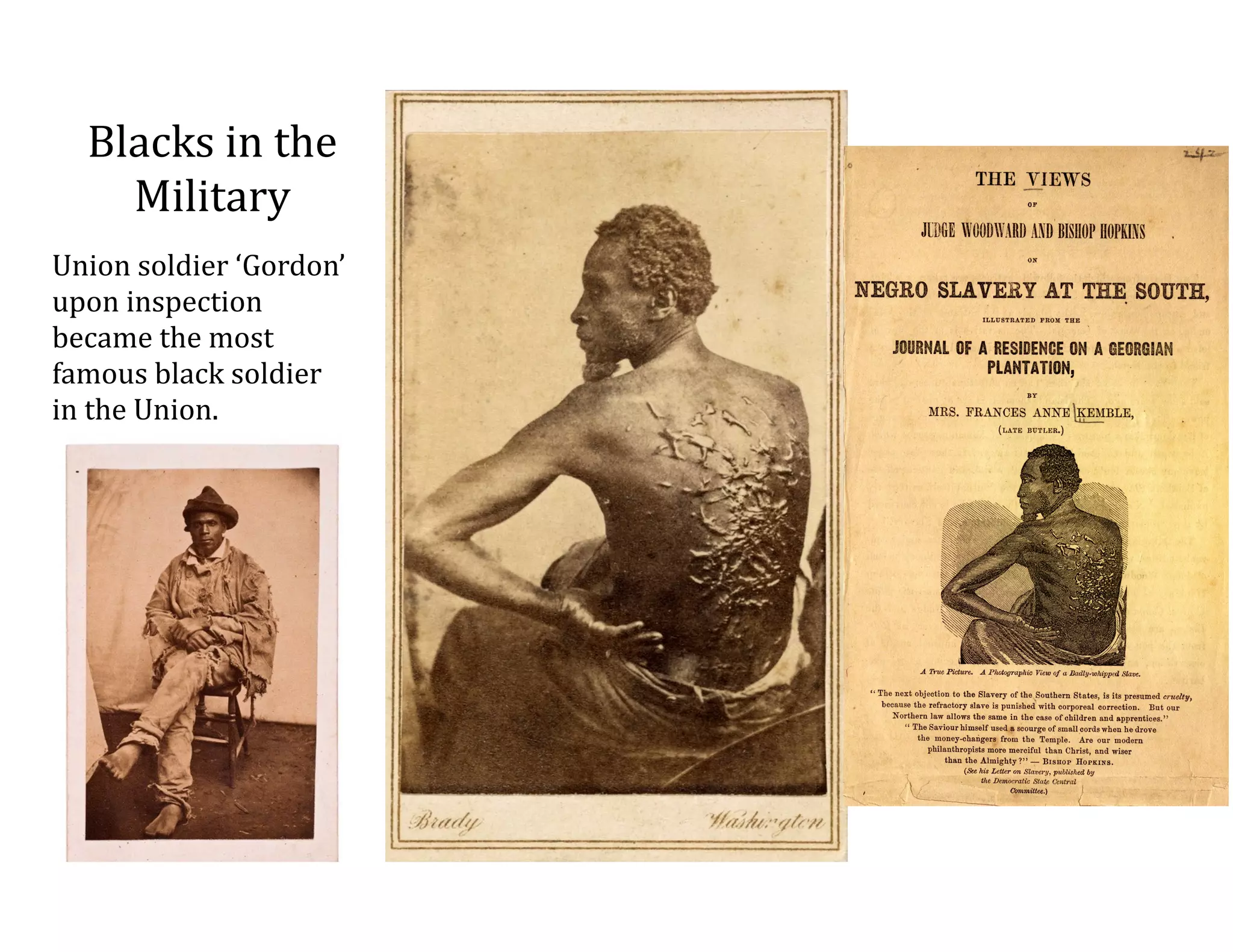
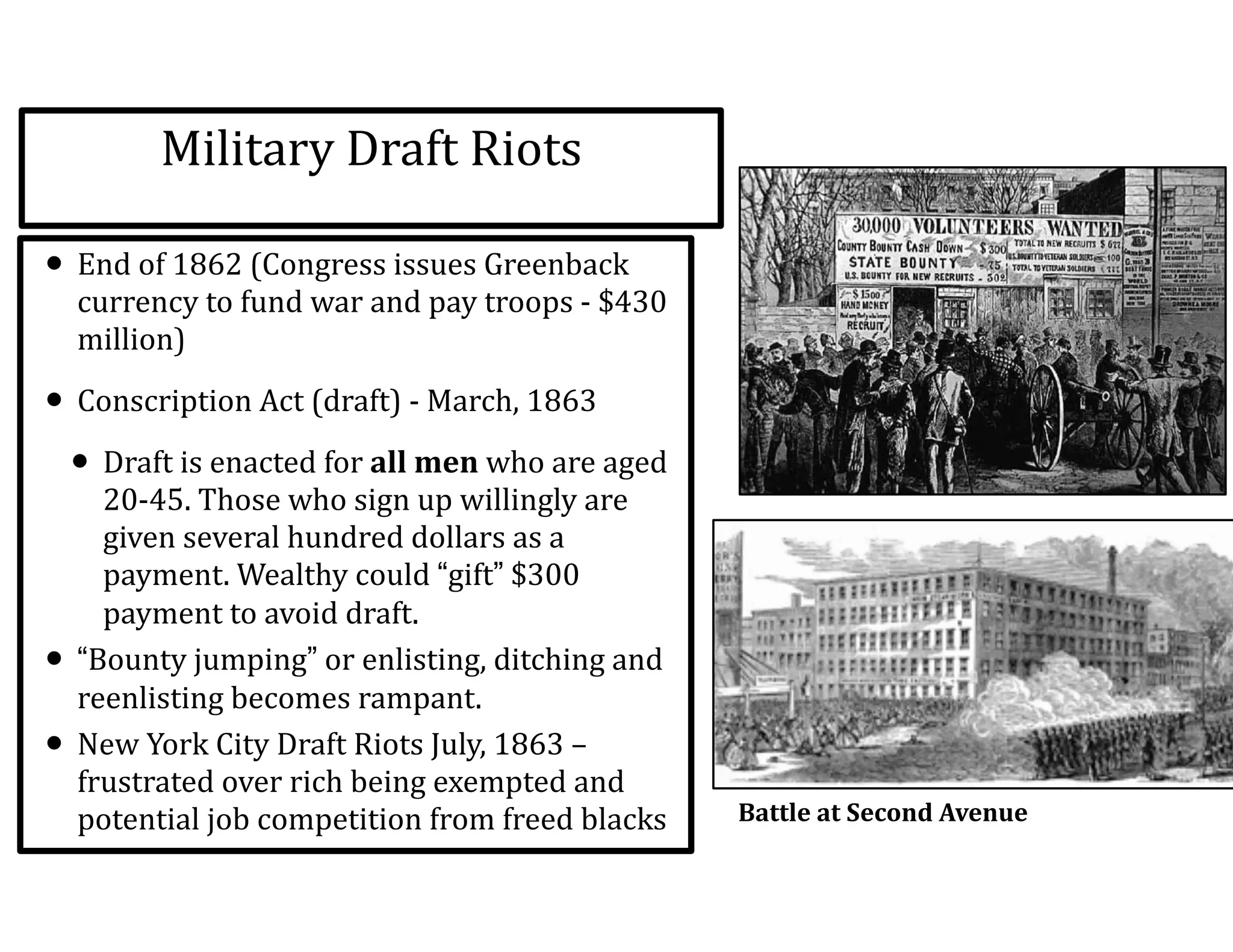
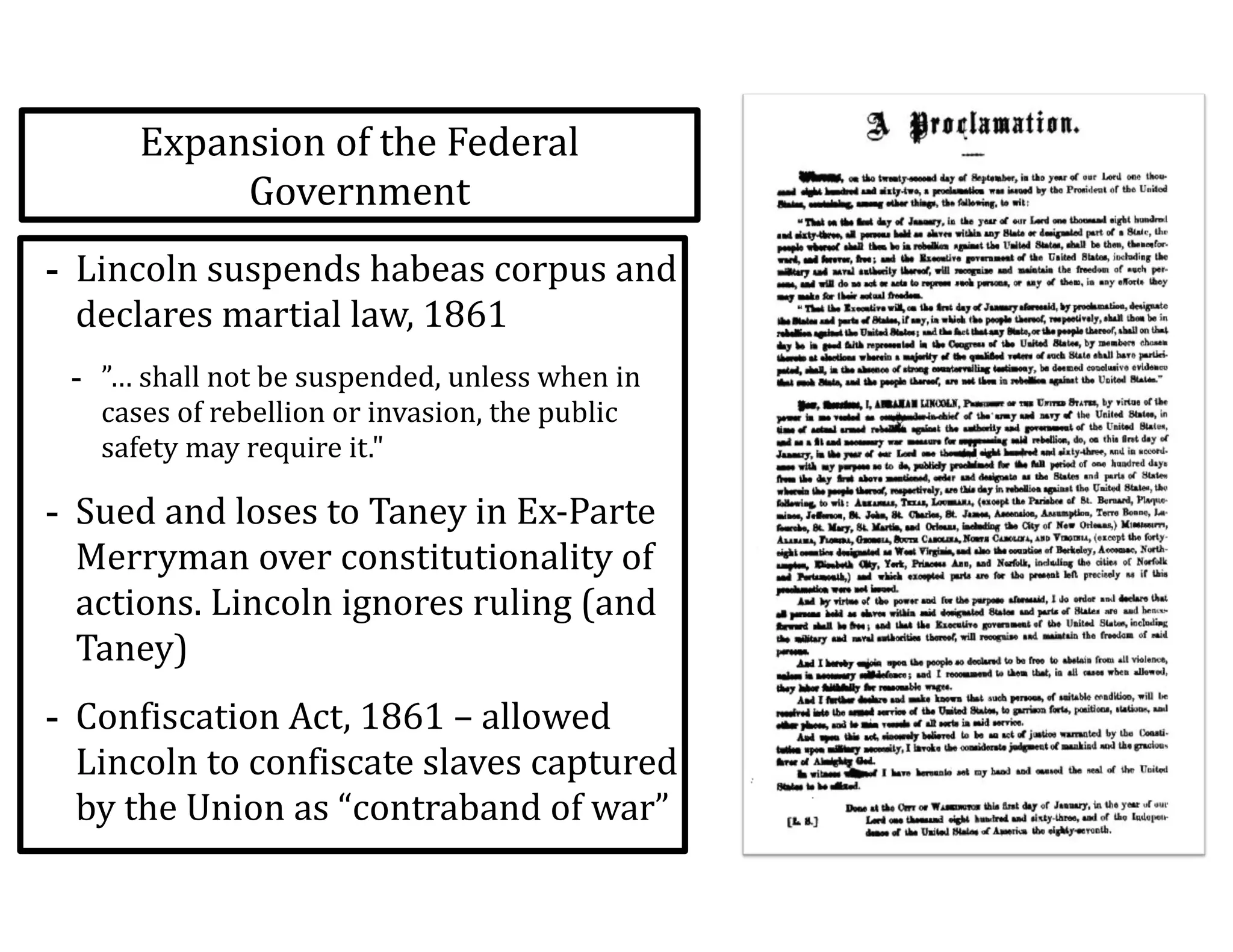
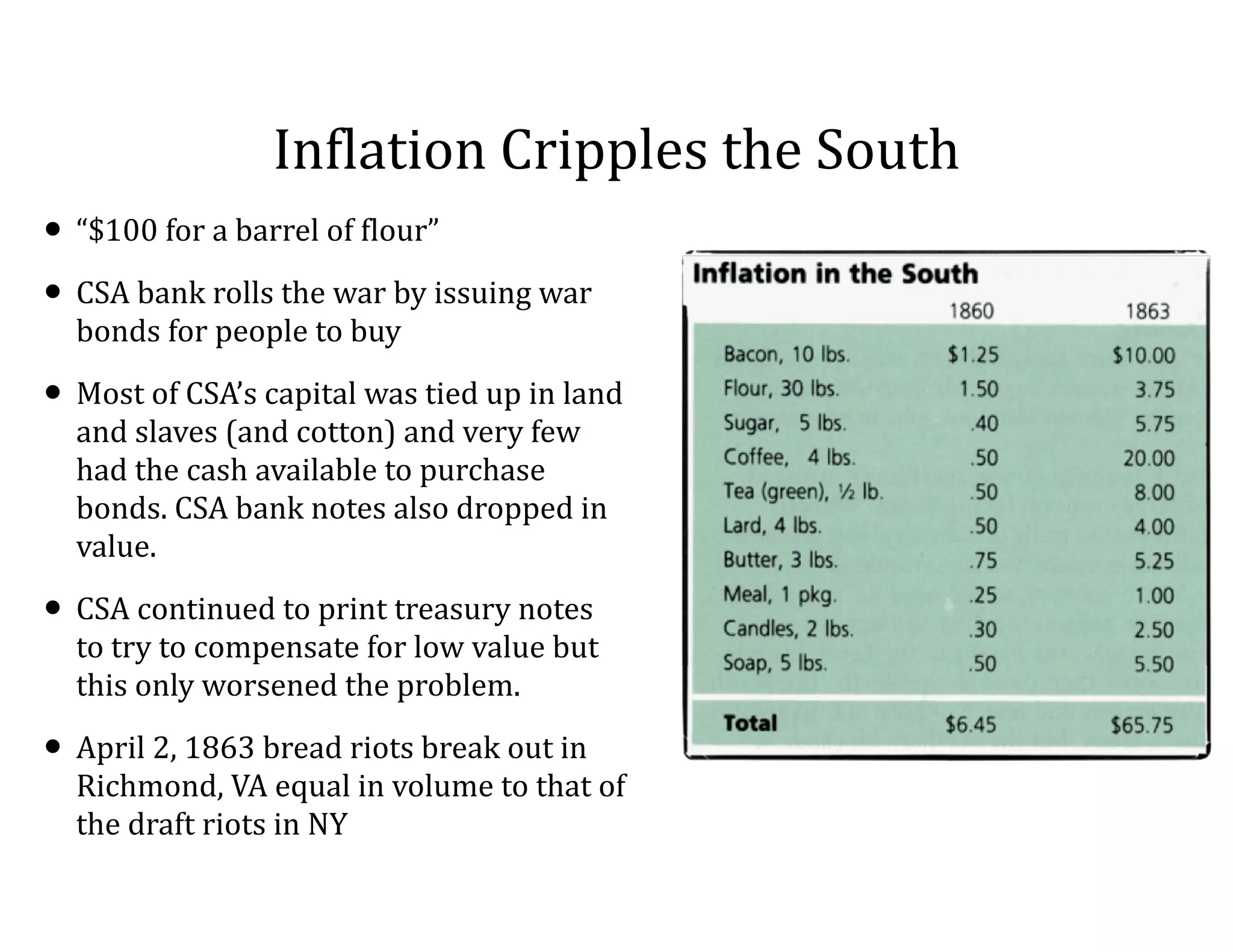
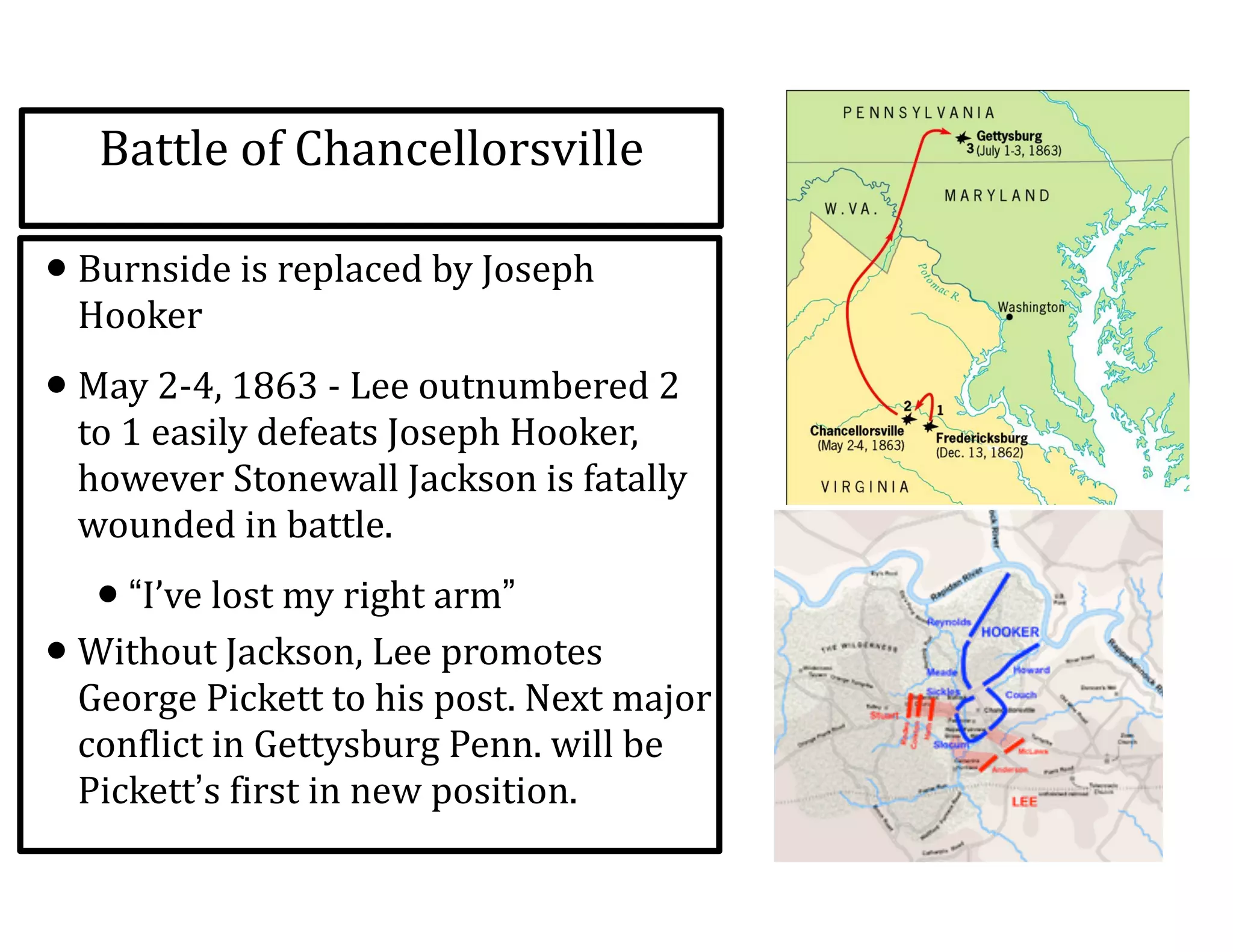
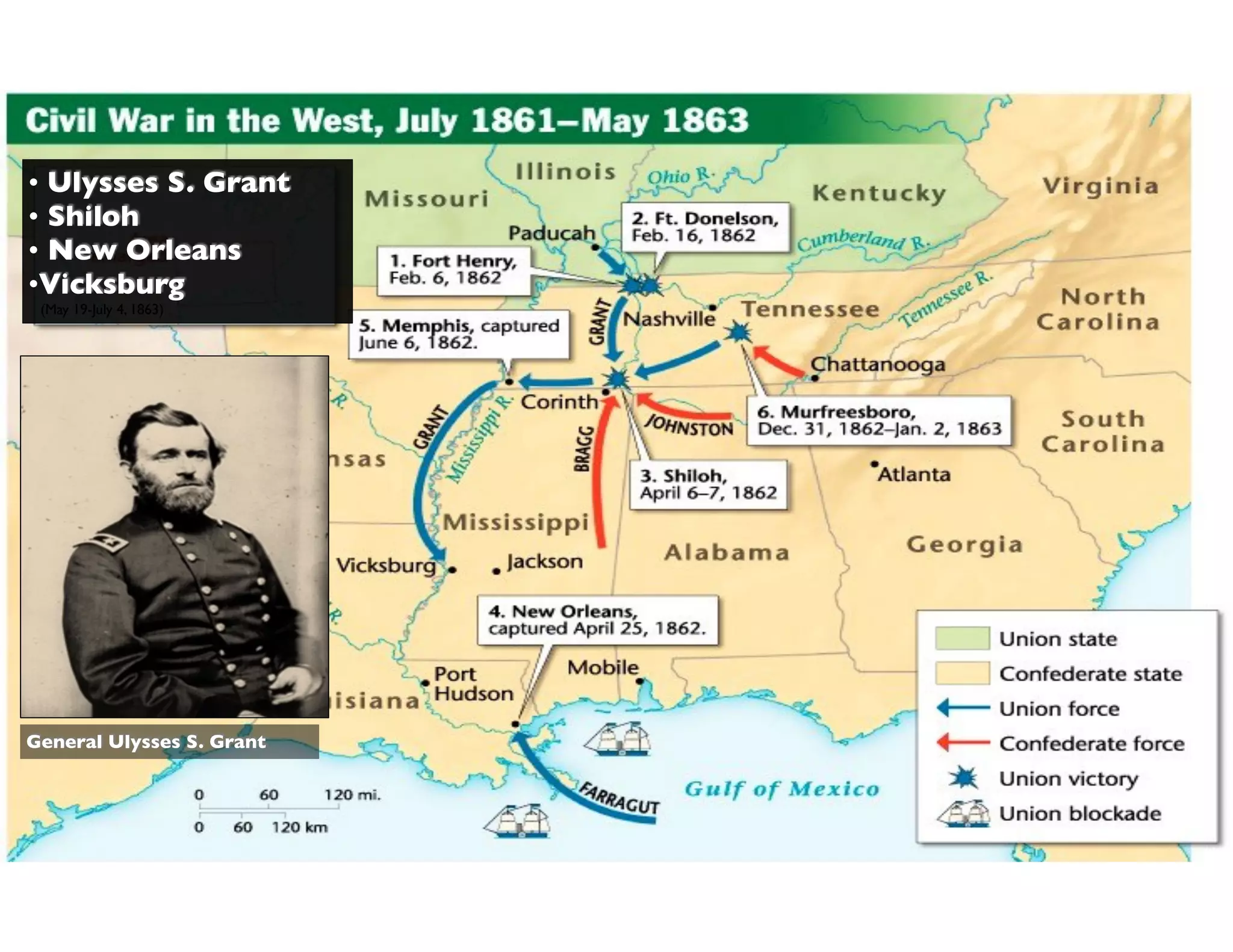
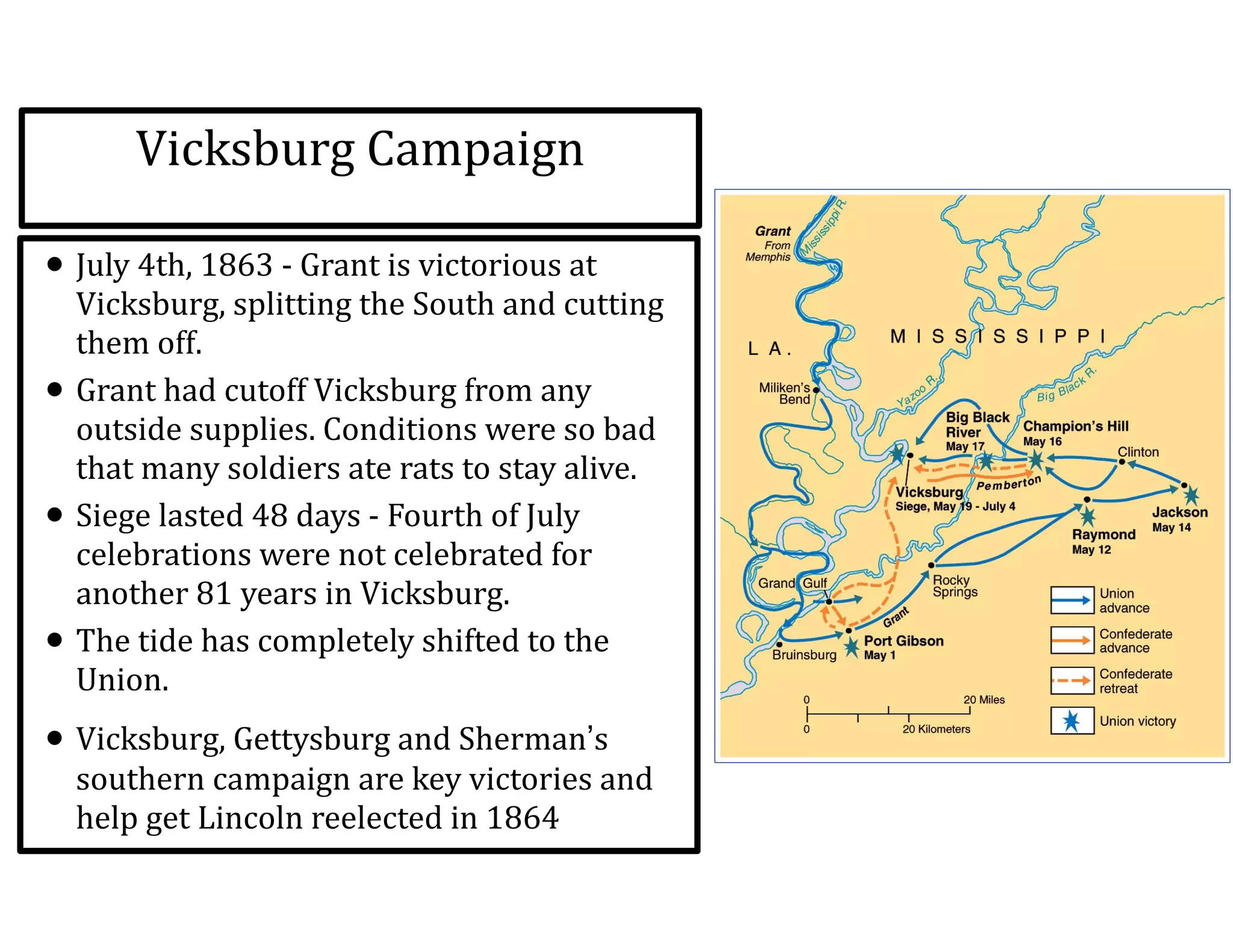
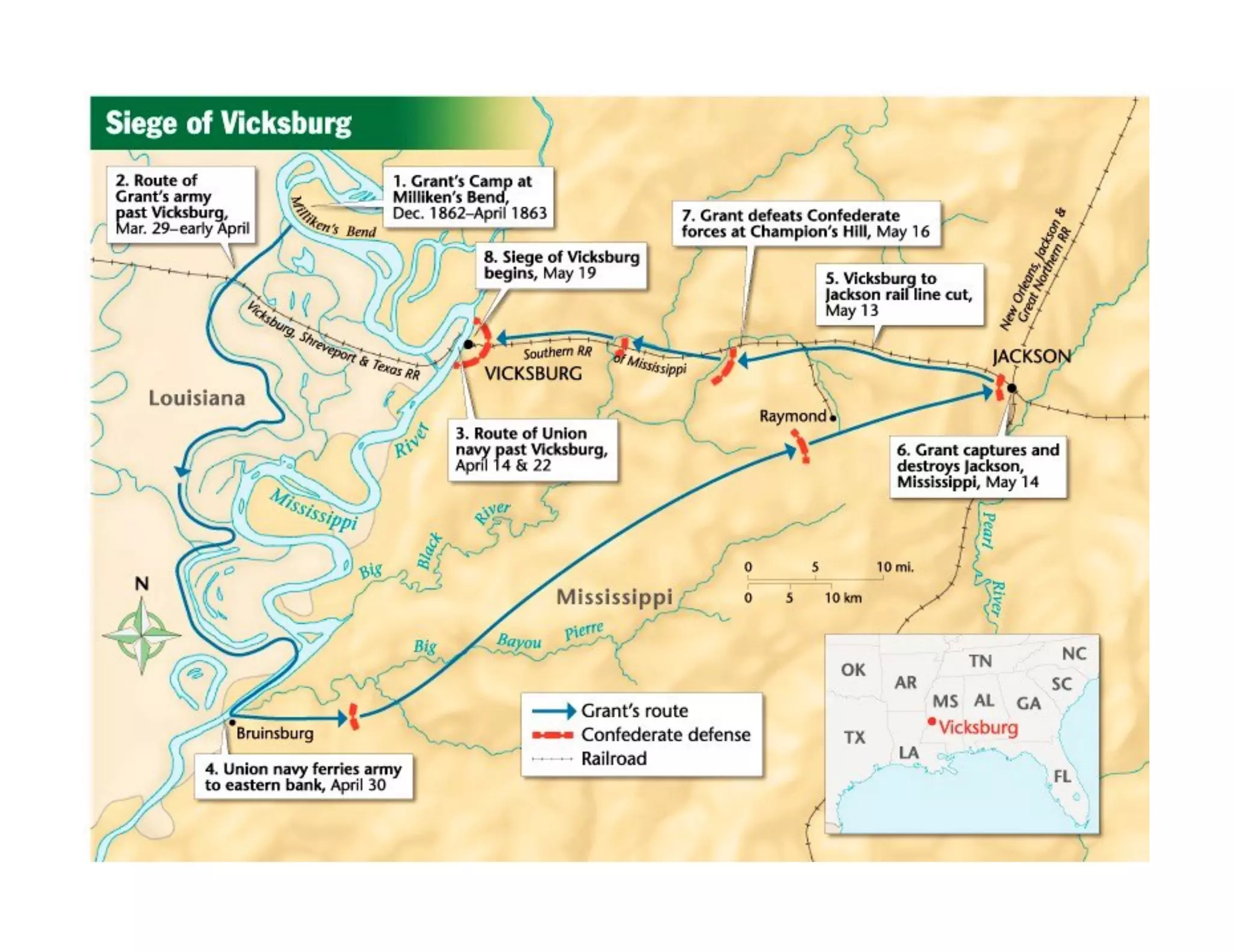
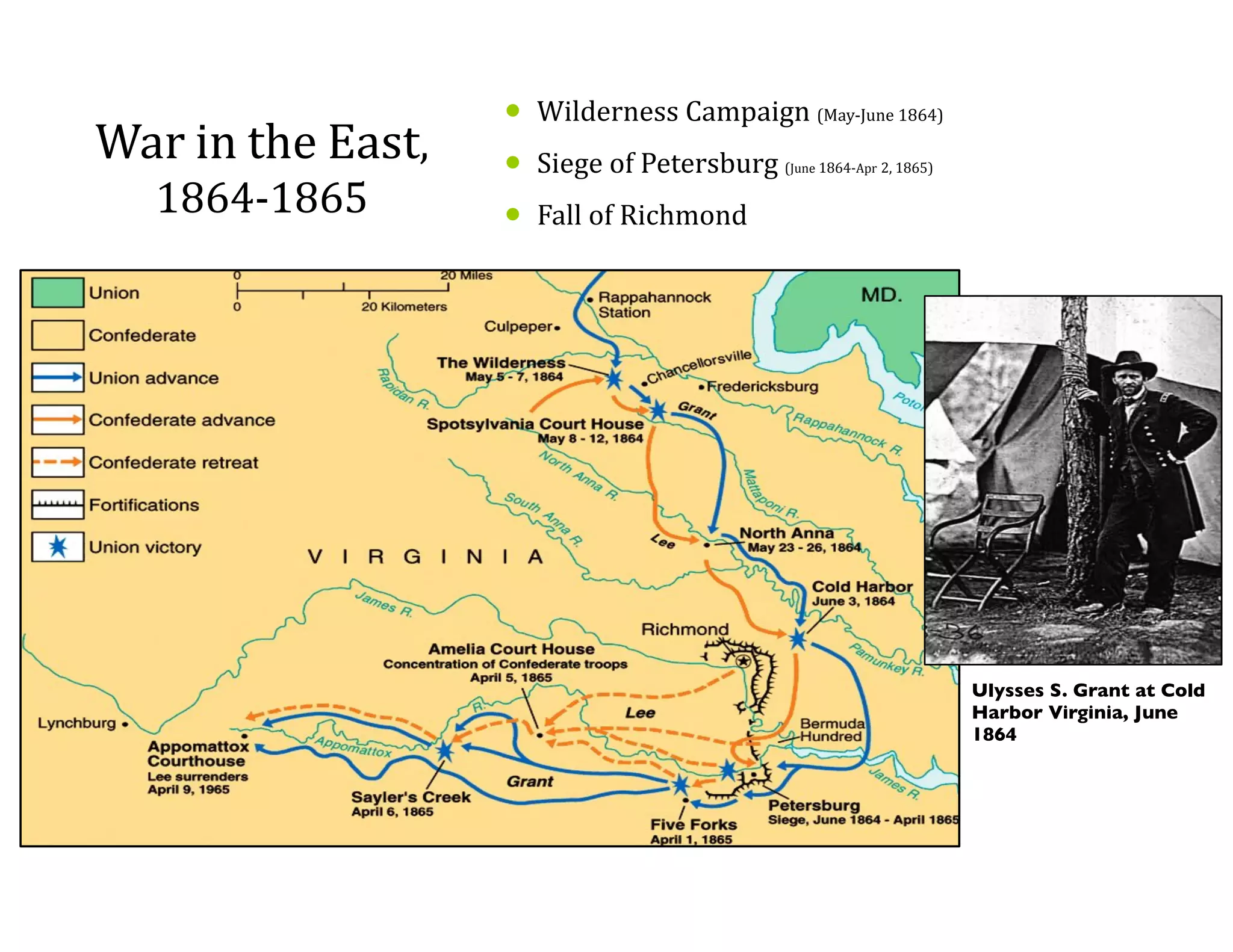
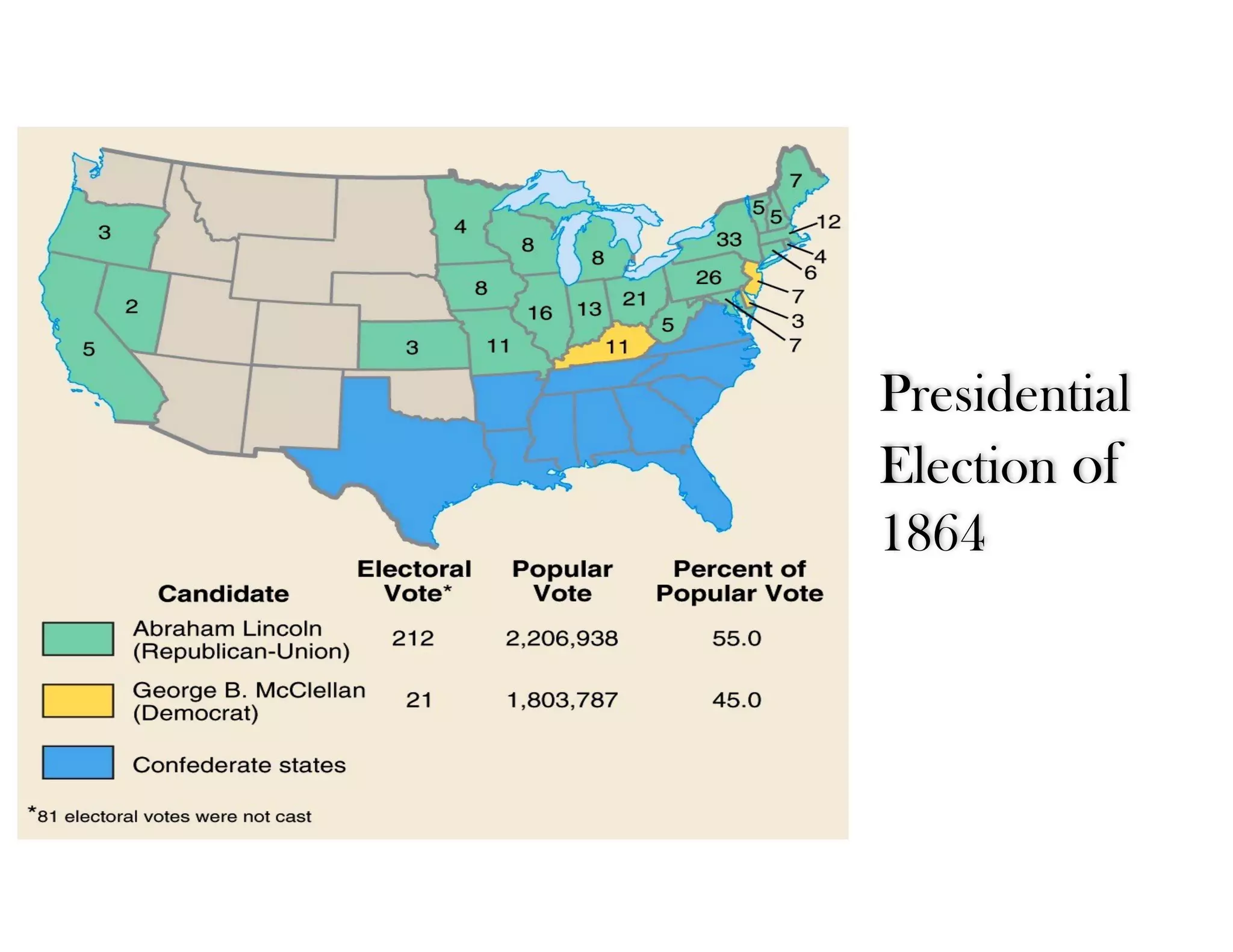
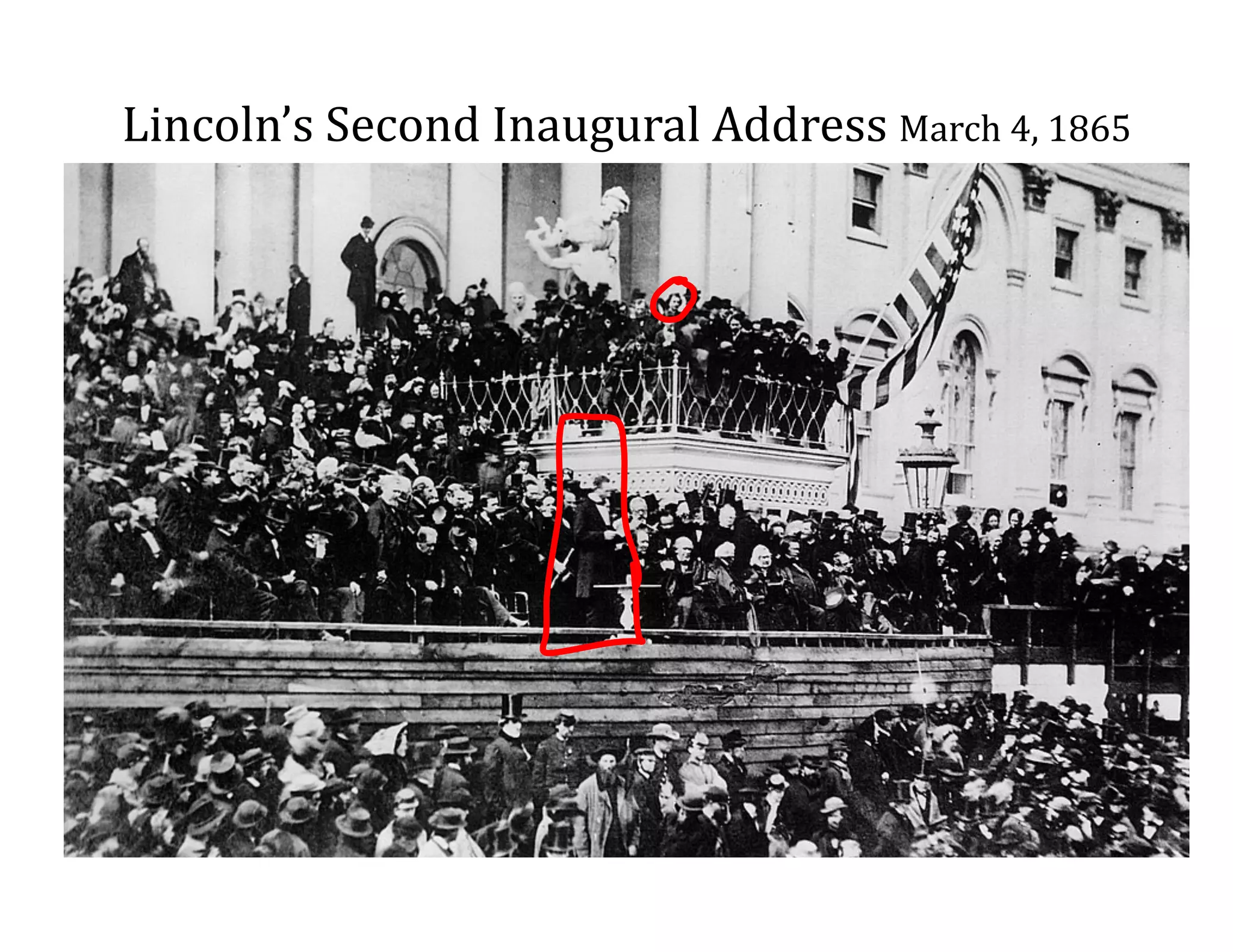
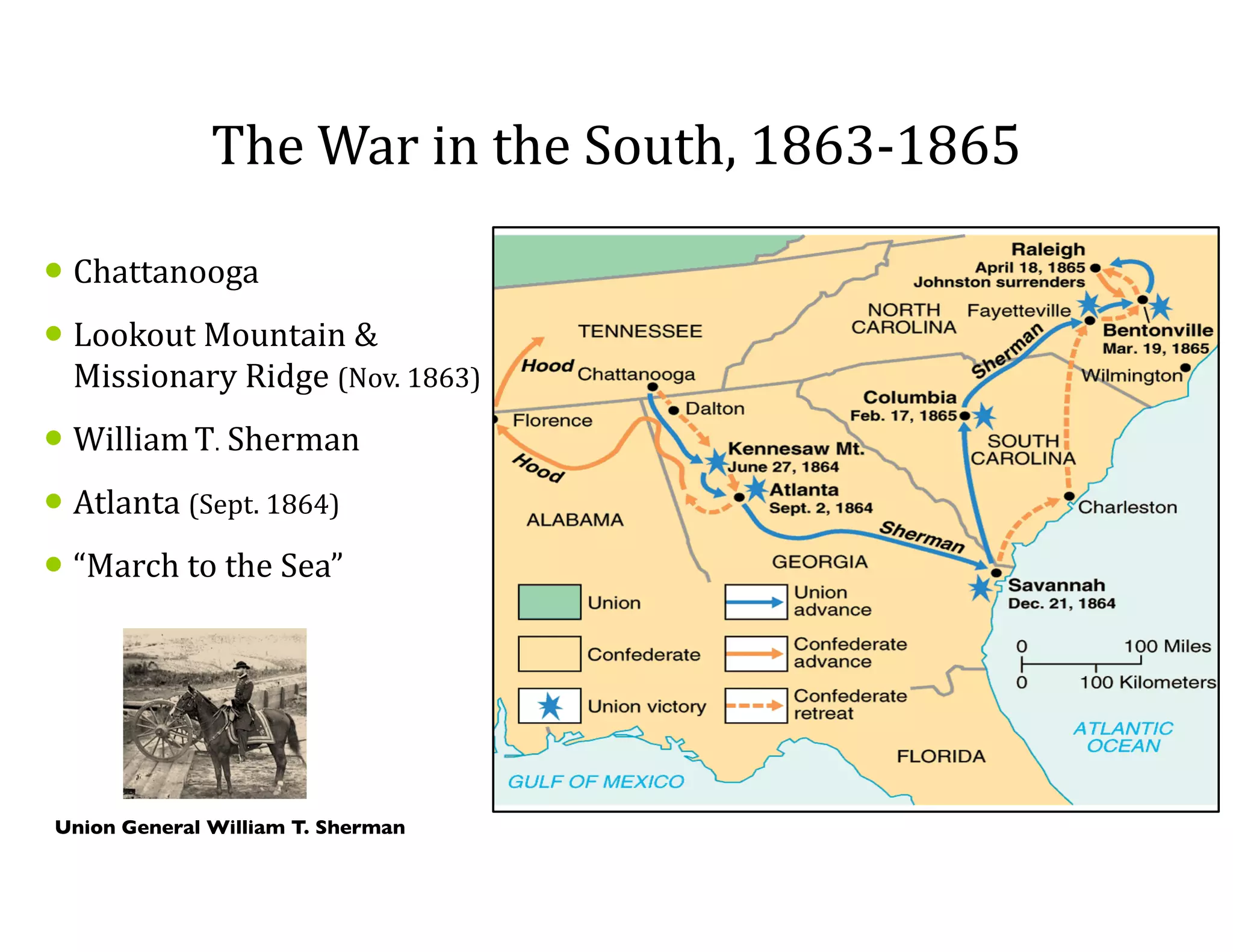
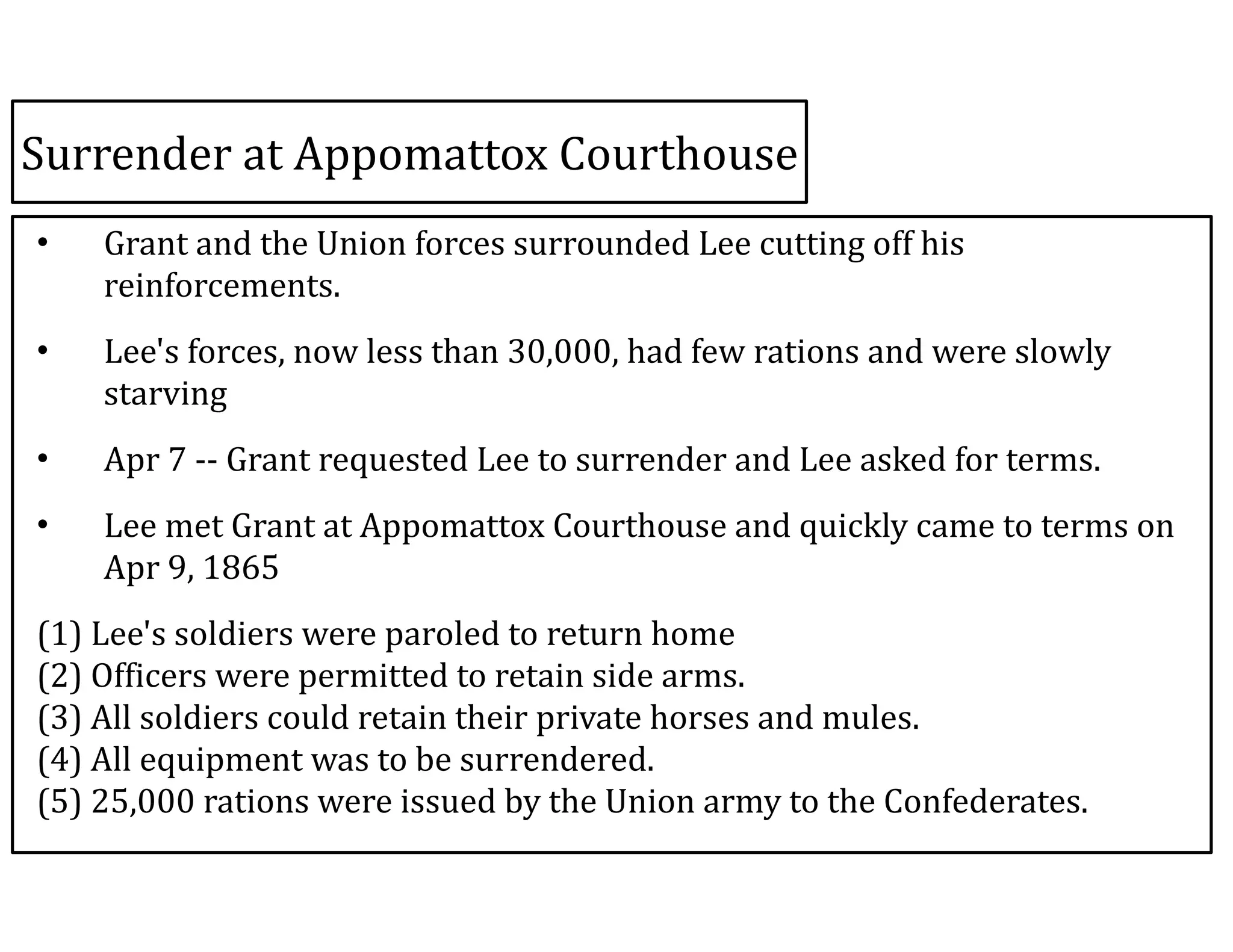
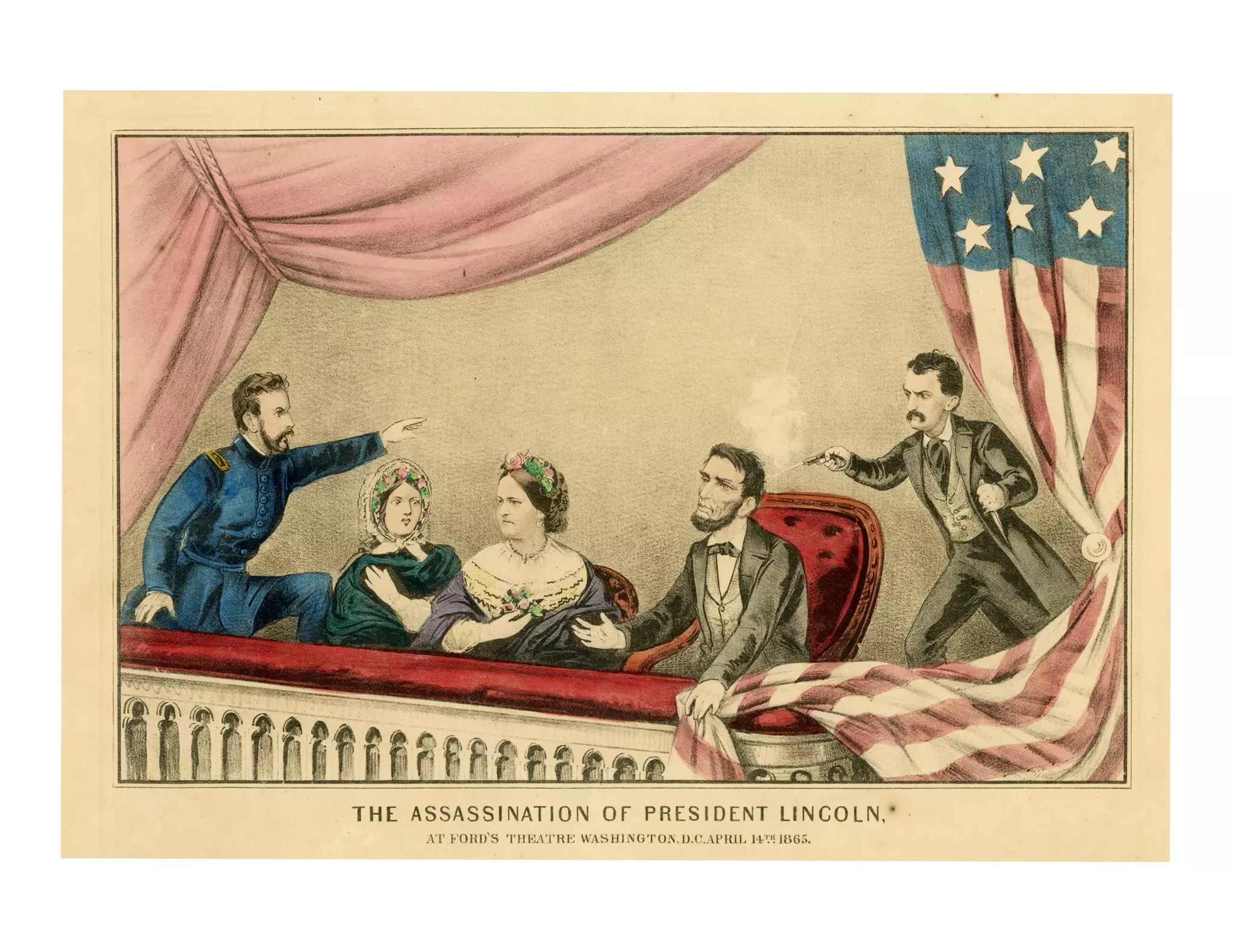
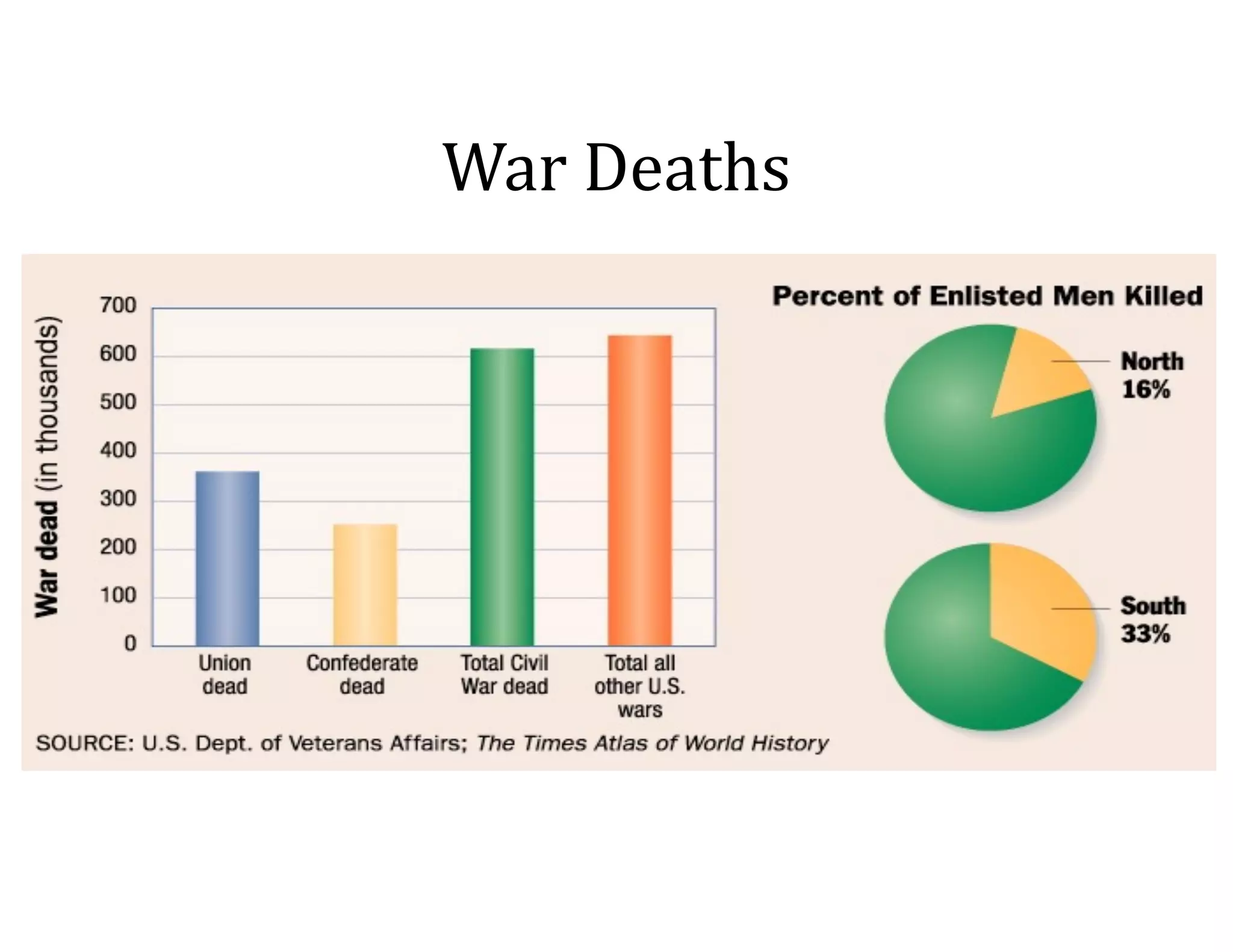
This document provides an overview of the American Civil War from 1861-1865. It includes summaries of key battles in both the Eastern and Western theaters, as well as statistics and facts about the war. Some notable events covered include the First Battle of Bull Run, Shiloh, the battles of Antietam and Fredericksburg, and naval developments such as the battle between the USS Monitor and CSS Virginia. The document examines how the Union and Confederacy differed in resources and manpower, and how the Union was able to eventually wear down and defeat the South.