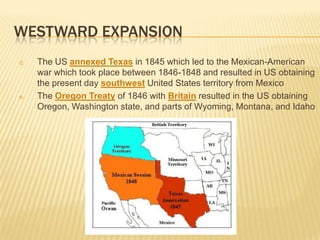
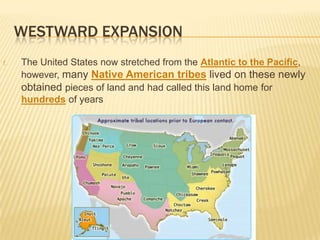
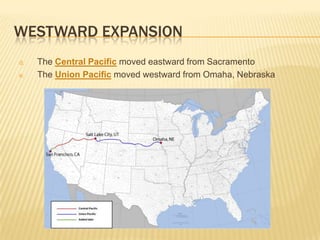
The document outlines the westward expansion of the United States, influenced by the belief in manifest destiny and significant events such as the Louisiana Purchase and the annexation of Texas. It highlights motivations for settlement, including the California Gold Rush and the Homestead Act, alongside the construction of the transcontinental railroad that facilitated migration. The expansion led to major changes in life for settlers, while also resulting in conflicts with Native American tribes over the newly acquired lands.