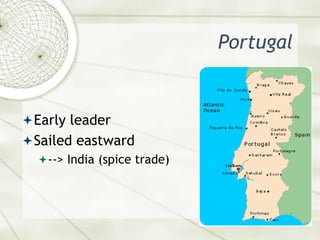
The document provides an overview of the motives and means of European exploration and expansion in the 15th-17th centuries. It discusses the 3 G's that drove exploration - God, Gold, and Glory. Portugal was an early leader in sailing eastward to India for the spice trade. Spain sailed westward seeking routes to Asia and settled in the Americas seeking gold, agriculture, and to convert natives to Catholicism. England's involvement grew due to strategic interests and the availability of colonists following the Protestant Reformation. Jamestown established England's first successful colony in North America in 1607. Puritans established the Plymouth colony in 1620 seeking religious tolerance. The economies of the colonies varied by region, with the Southern