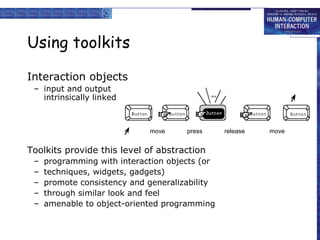
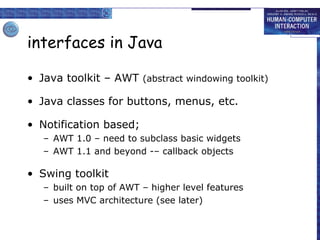
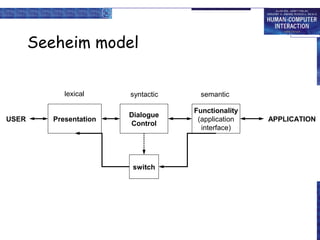
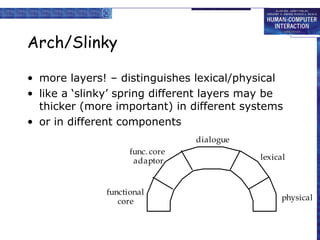
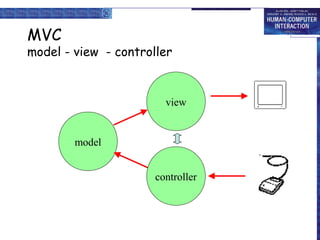
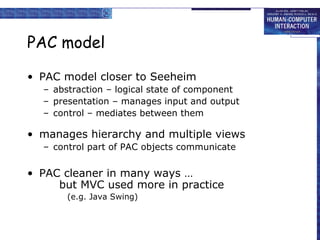
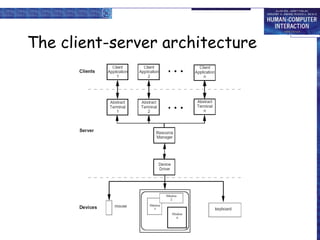
Windowing systems provide core support for separate user-system activities through device independence and allowing multiple simultaneous tasks. Programming tools have evolved from low-level read-evaluation loops to higher-level notification-based and interaction toolkit approaches. User interface management systems introduce conceptual architectures like Seeheim that separate the presentation, dialogue control and application layers, and provide techniques for graphically specifying dialogues.









![Programming the application - 1
notification-based
void main(String[] args) {
Menu menu = new Menu();
menu.setOption(“Save”);
menu.setOption(“Quit”);
menu.setAction(“Save”,mySave)
menu.setAction(“Quit”,myQuit)
...
}
int mySave(Event e) {
// save the current file
}
int myQuit(Event e) {
// close down
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e3-chap-08-140116112945-phpapp02/85/E3-chap-08-11-320.jpg)