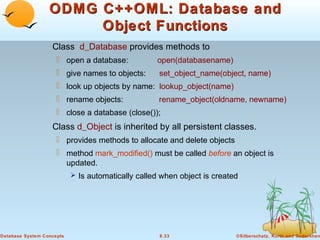
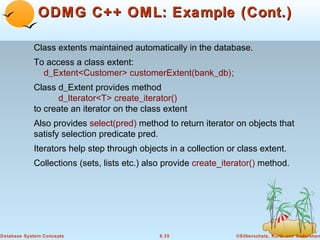
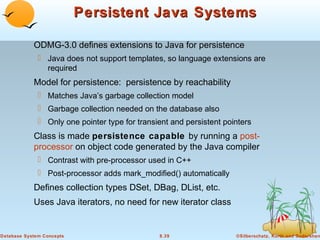
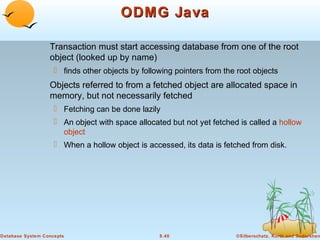
Object-oriented databases were developed to better support complex data types and object-oriented programming. The key aspects of the object-oriented data model include:
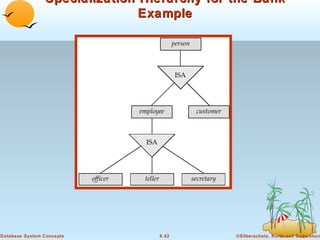
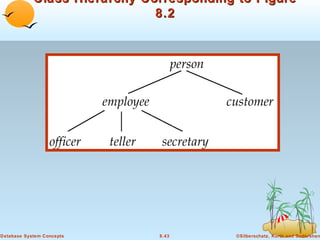
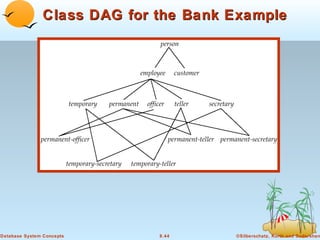
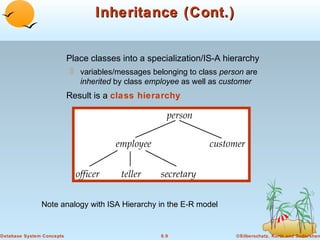
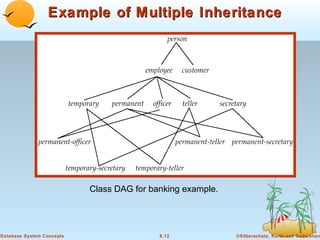
1) Objects that encapsulate both data and methods, and are grouped into classes with common properties. Classes can be organized into inheritance hierarchies.
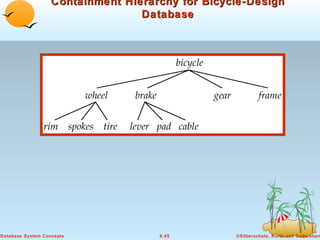
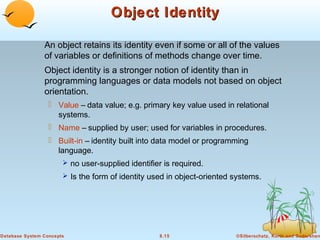
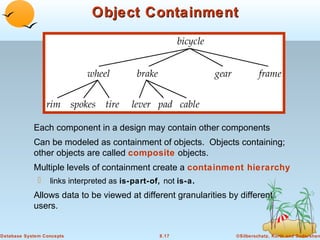
2) Objects are uniquely identified and can reference other objects. Complex data types like addresses can be modeled using object containment hierarchies.
3) Databases following this model support persistence of objects and queries using object-oriented languages that allow accessing and updating object properties through messages.
























![Implementing Relationships
E.g.
extern const char _owners[ ], _accounts[ ];
class Account : public d.Object {
….
d_Rel_Set <Customer, _accounts> owners;
}
// .. Since strings can’t be used in templates …
const char _owners= “owners”;
const char _accounts= “accounts”;
Database System Concepts
8.31
©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8-140116113413-phpapp02/85/Ch8-31-320.jpg)