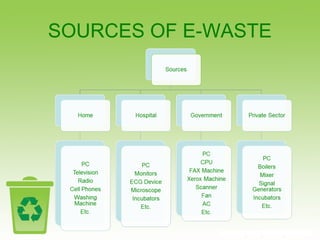
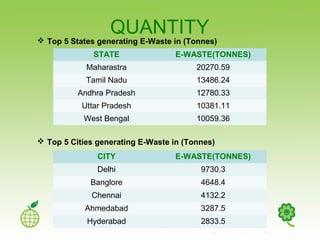
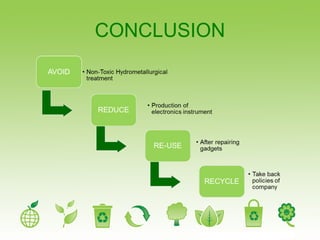
E-waste refers to discarded electronic devices and is a growing problem in India. Large amounts of e-waste are generated in major cities and states each year, totaling hundreds of thousands of tons. Improperly handled e-waste recycling can release toxic chemicals like lead and cadmium into the environment, posing hazards to human health. There is lack of public awareness about e-waste and its risks. Manufacturers also do little to promote take-back programs for obsolete electronics. Non-toxic recycling methods need to be implemented to handle India's increasing volumes of e-waste in an environmentally responsible way.