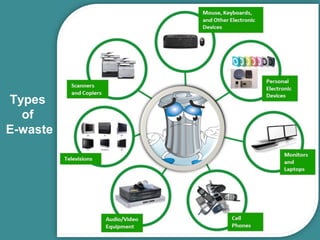
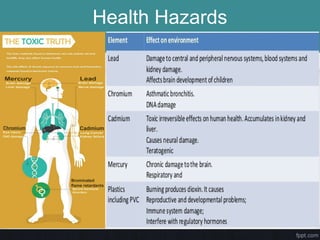
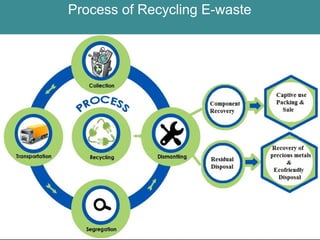
This document discusses electronic waste (e-waste) and its impact. It defines e-waste as electronic and electrical waste that contains toxic chemicals and metals. The document outlines the different types of e-waste including components containing lead, cadmium, mercury, and other toxins. It discusses the health hazards of e-waste and reasons for its generation. The document provides an overview of e-waste recycling processes and notes India's large e-waste production and lack of proper infrastructure for recycling. It concludes with a call for responsible e-waste disposal and donation of refurbished electronics.