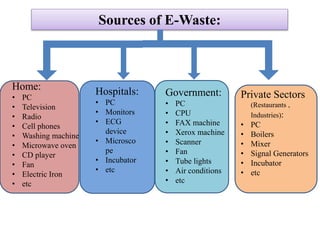
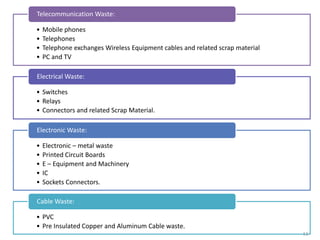
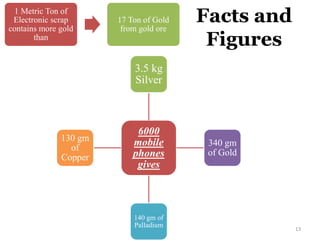
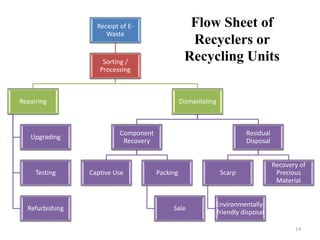
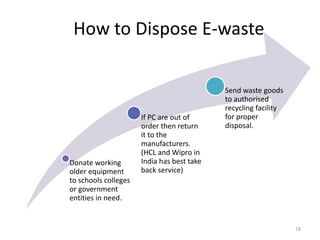
This document discusses electronics waste (e-waste) and its management. It defines e-waste and lists major sources like computers, phones, TVs. India generates 0.8 million tons of e-waste annually, which is growing 10% each year. E-waste contains valuable and toxic materials. The document outlines recycling and disposal methods like reuse, dismantling, and material recovery which can have environmental and economic benefits but are currently not well regulated in India. It calls for more awareness, legislation, and safer recycling practices to better manage the large and growing quantities of e-waste.