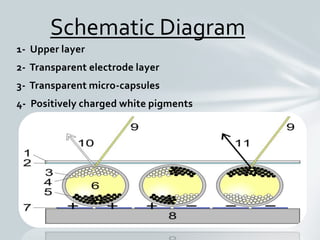
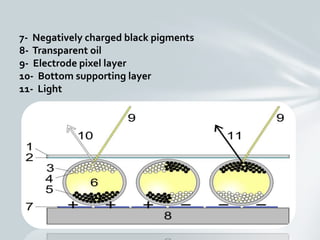
E ink is an electronic paper display invented in 1996 at MIT. It uses microcapsules containing charged black and white pigment particles that are moved to the top or bottom of the capsule by electric fields to display text and images. E ink displays are used in e-readers and other devices because they are bi-stable, require no power to maintain a display, and can be read in direct sunlight. The document discusses the history, working mechanism, applications, advantages like low power consumption, and future uses of e ink technology.