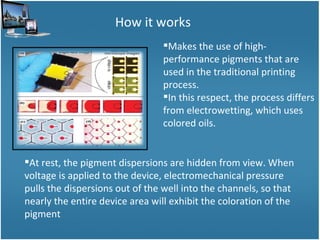
This document discusses emerging display technologies, including electrophoretic pixels, multimode photonic ink, and electrofluidic pixels. Electrophoretic pixels use electrically charged pigment particles that are attracted or repelled by an electric field to display black or white pixels. Multimode photonic ink can be switched between e-paper, LCD, and transflective modes, allowing it to be visible indoors and outdoors with minimal power usage. Electrofluidic pixels use electrically controlled fluid movement to spread pigment across a pixel area, similar to printed ink, enabling high brightness and fast switching speeds for video. These technologies promise improvements over conventional displays but are still in development.