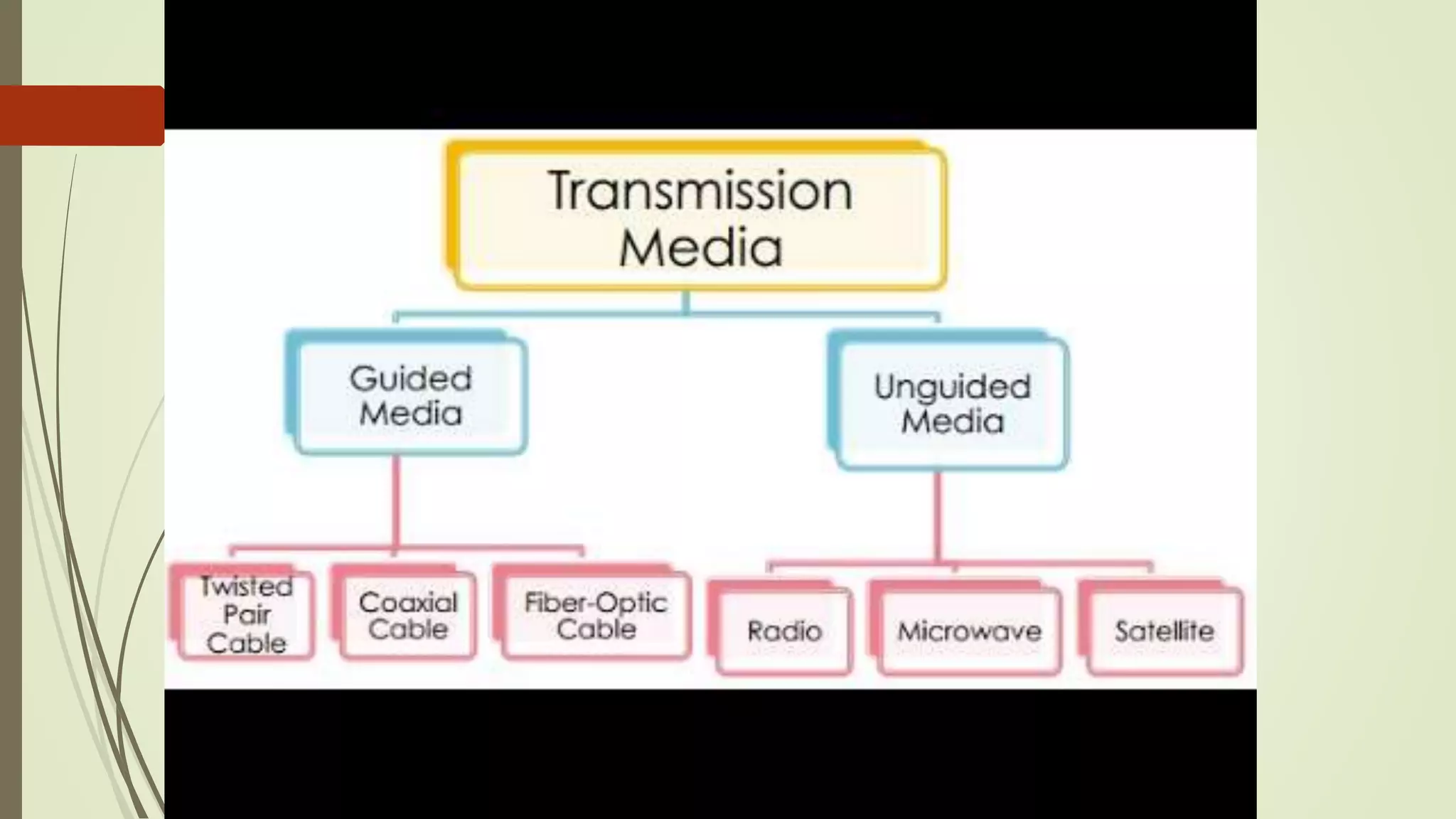
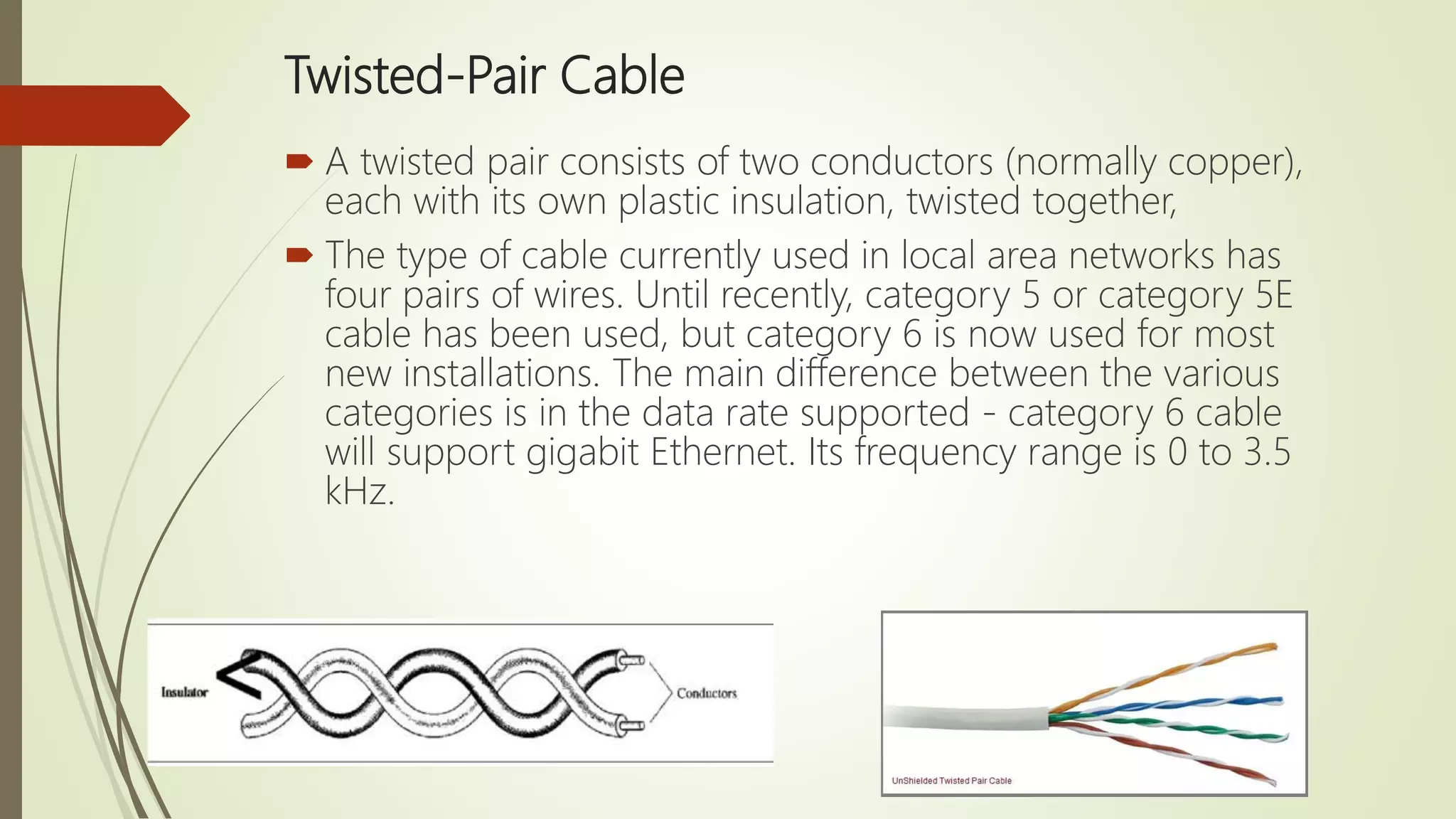
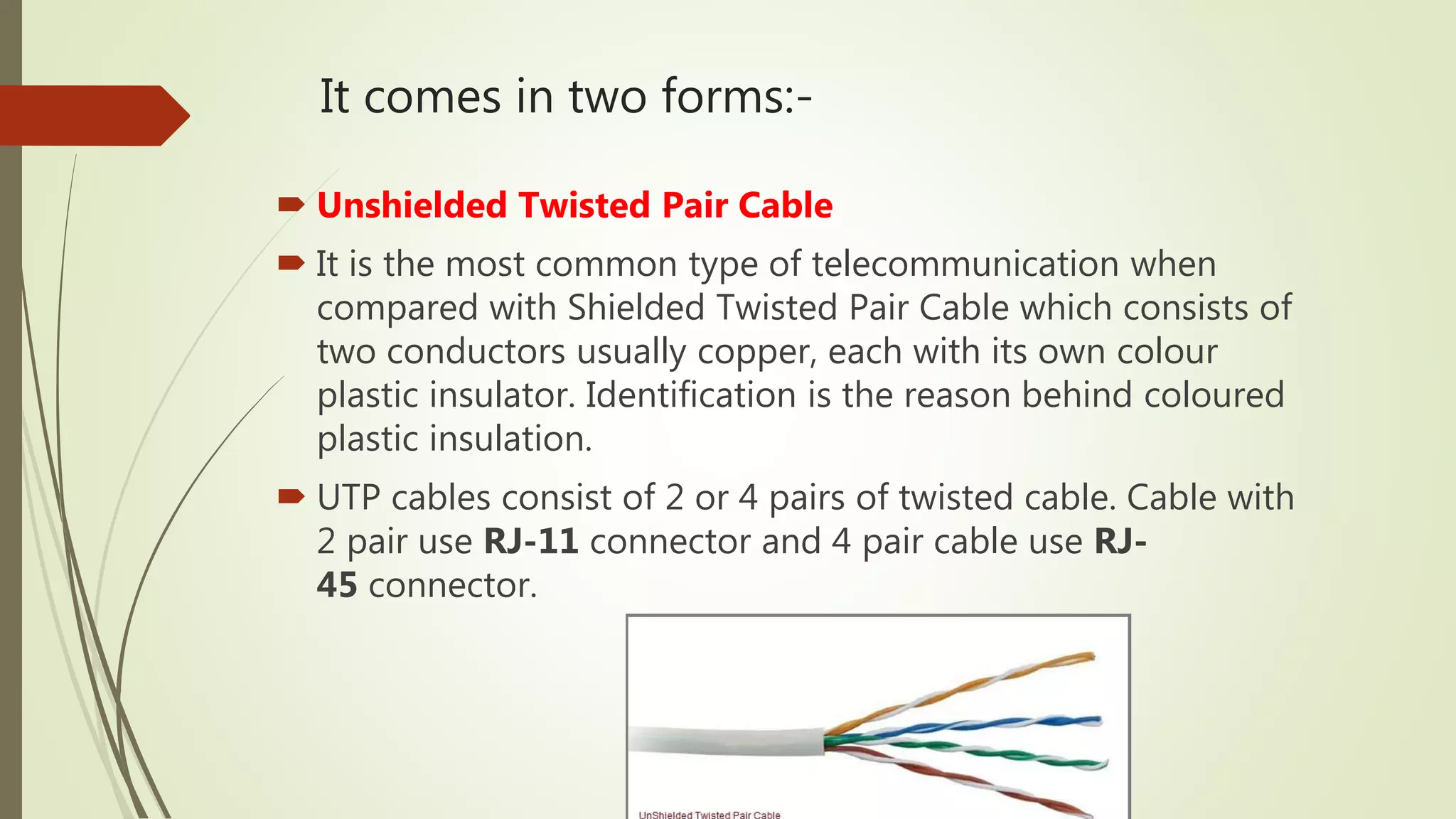
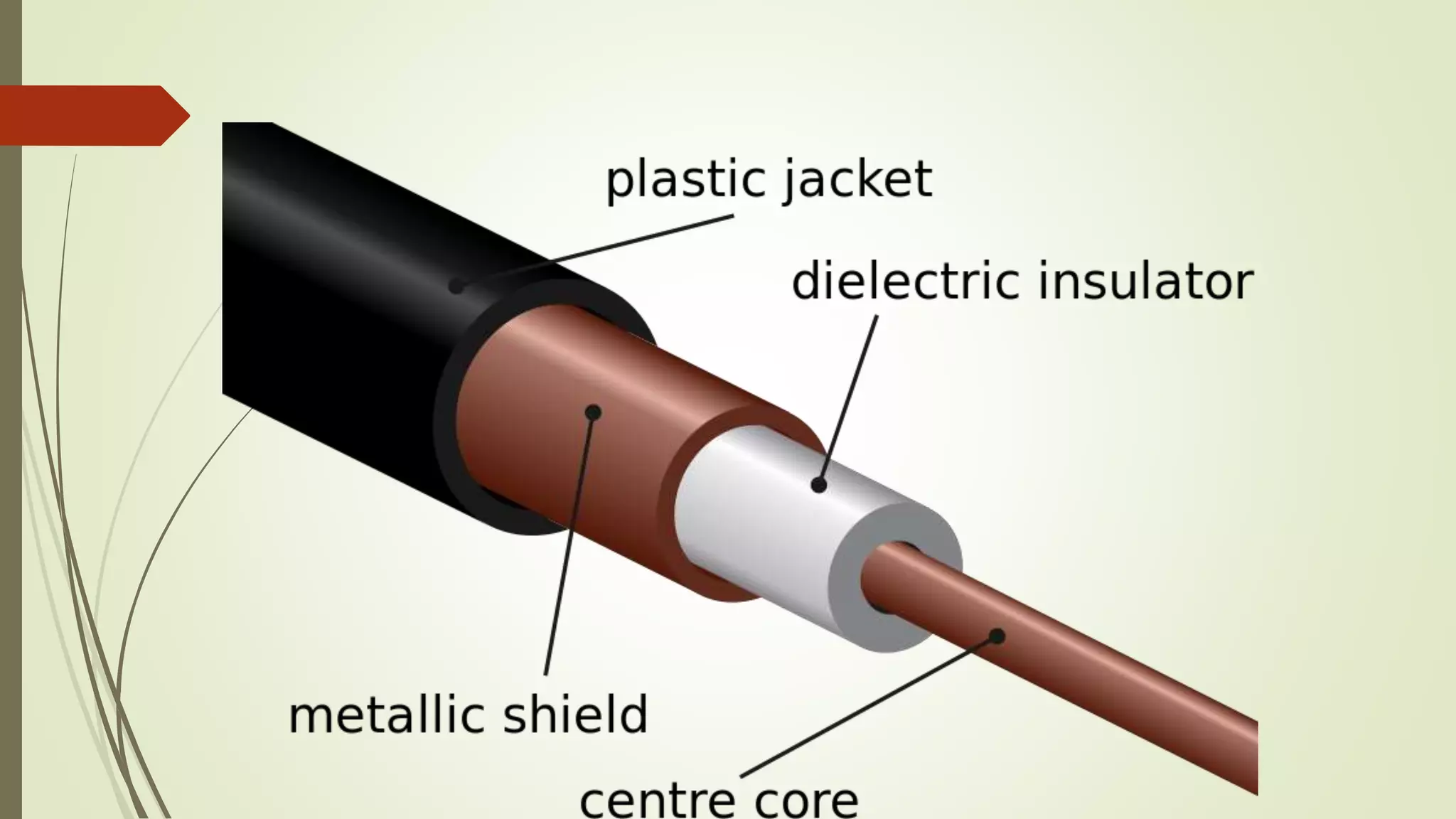
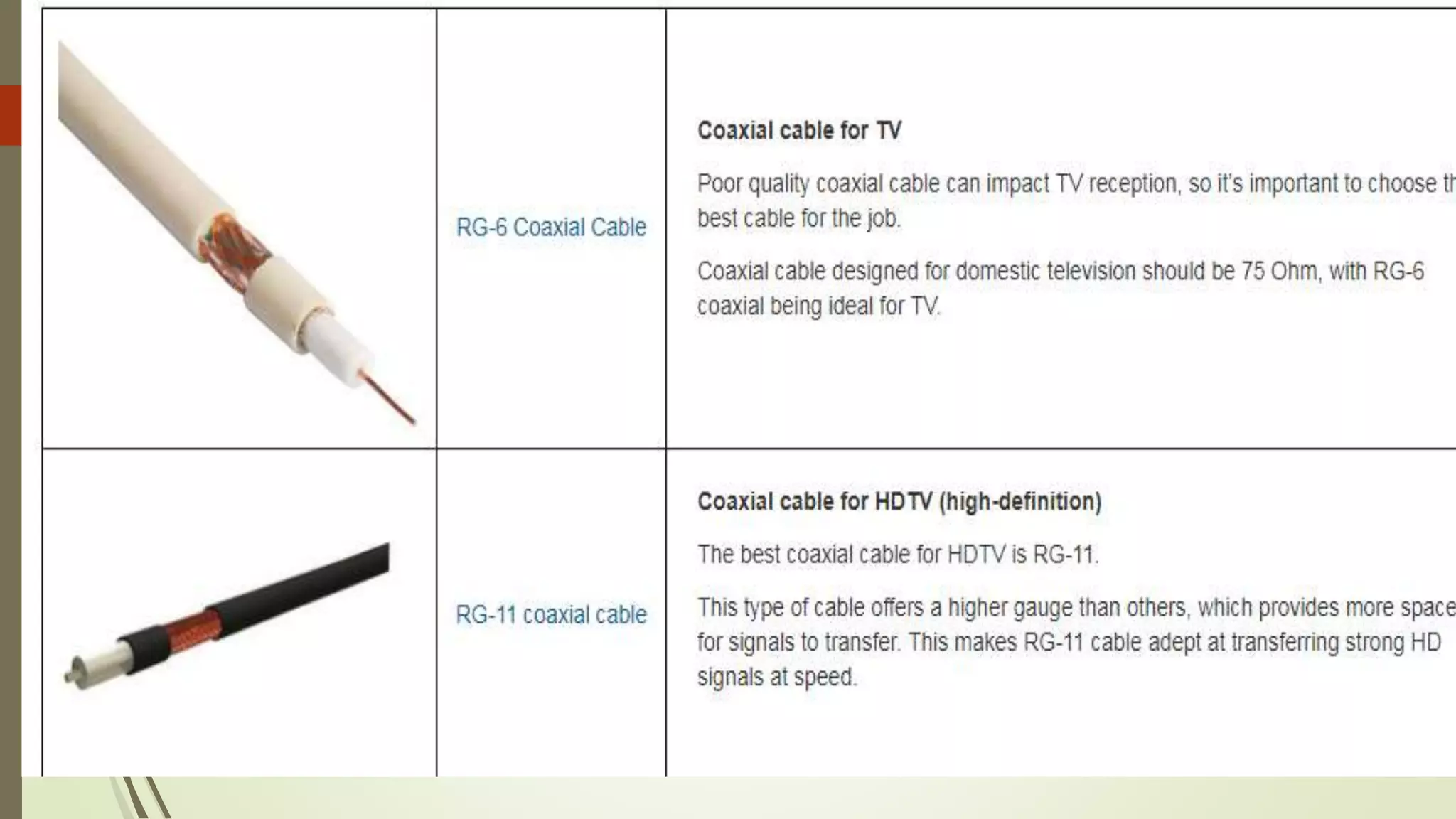
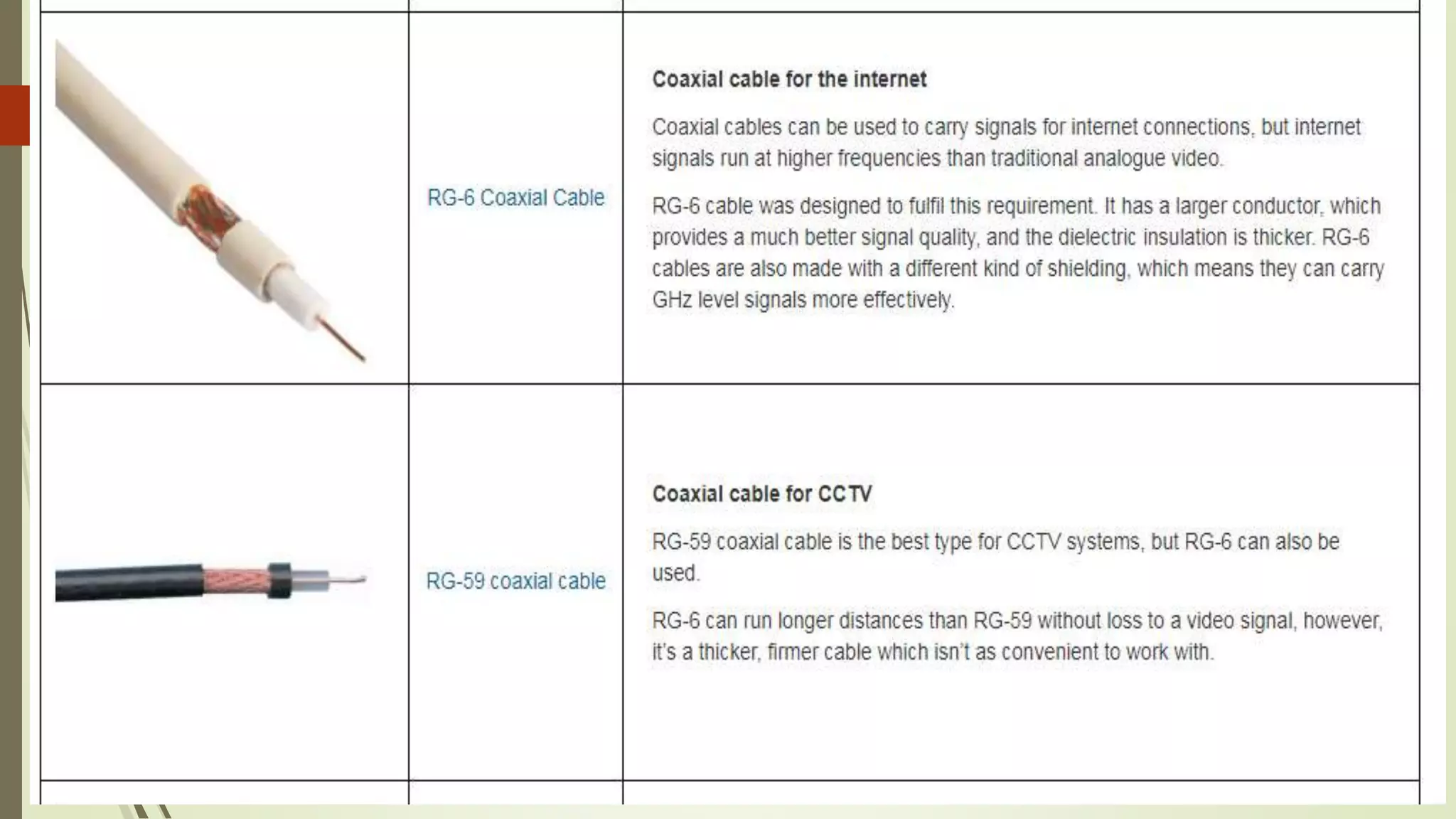
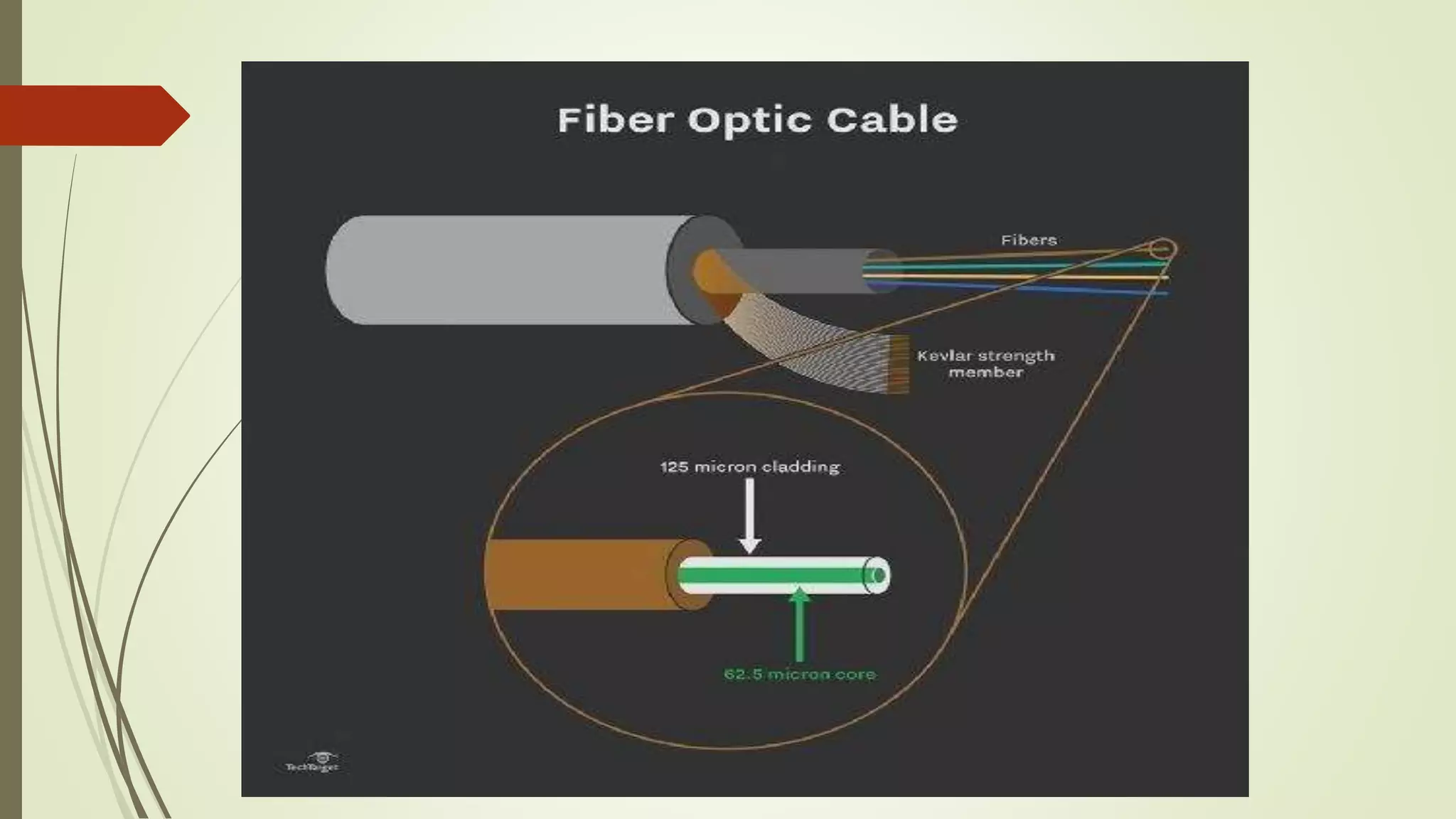
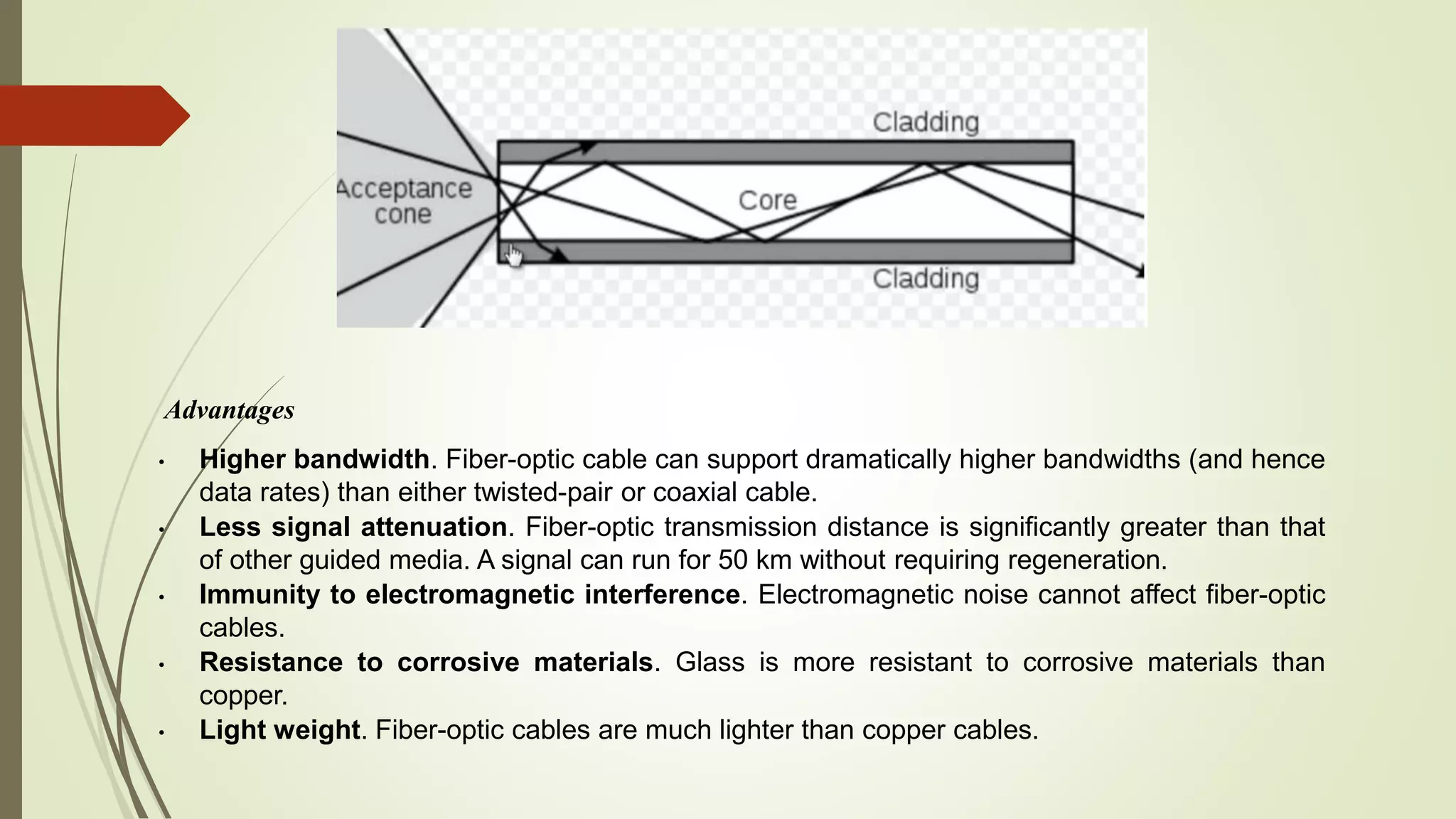
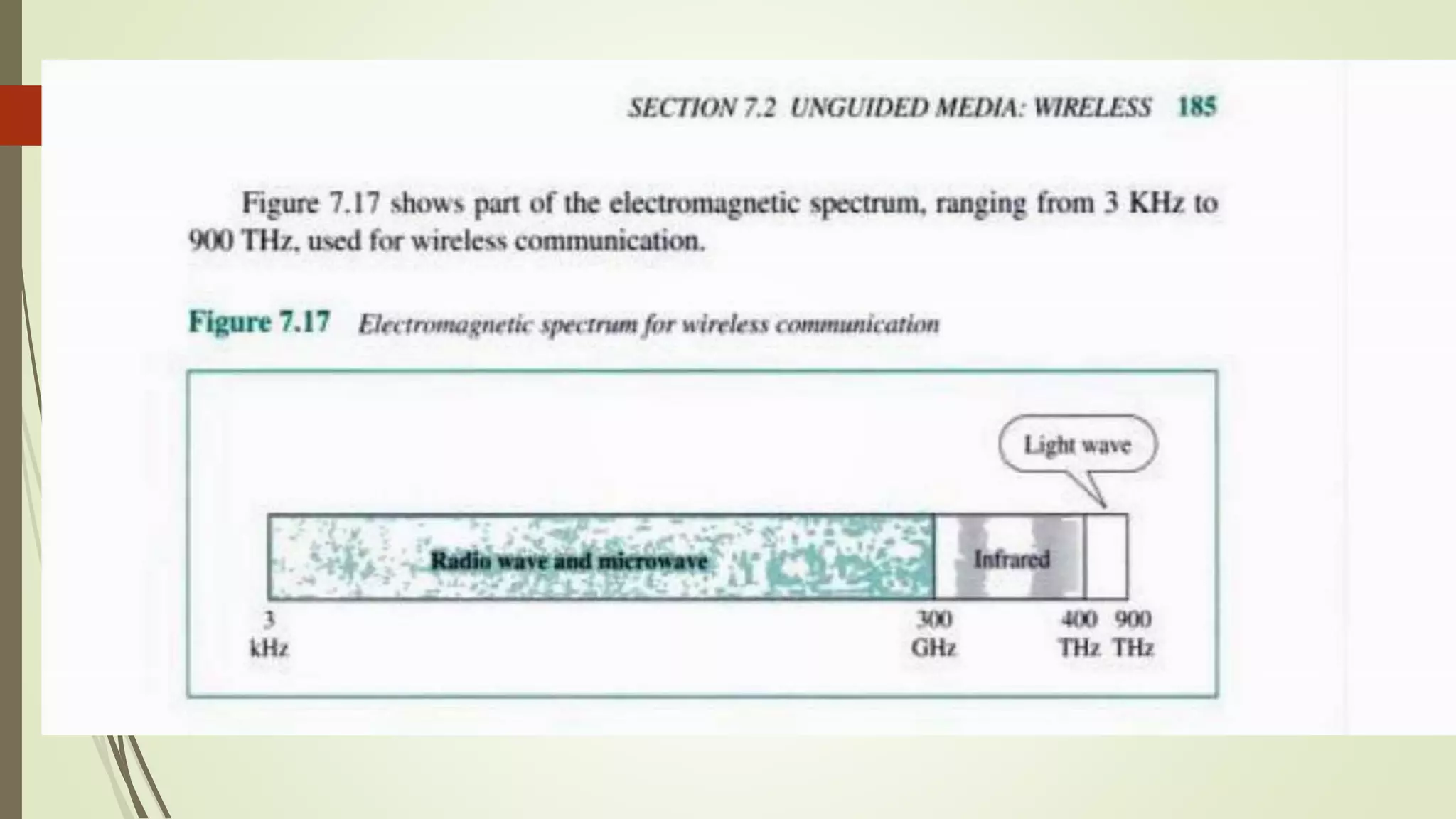
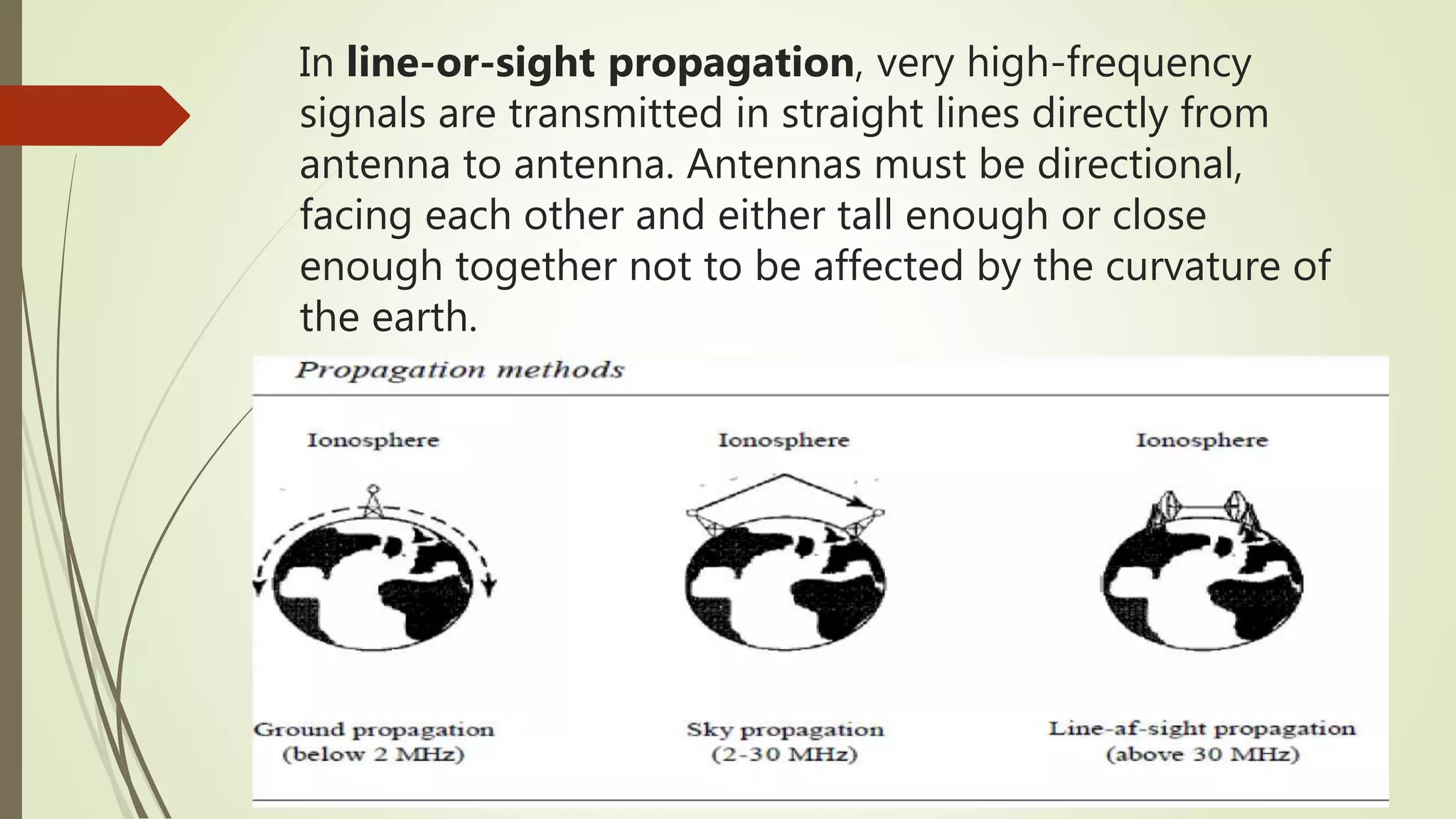
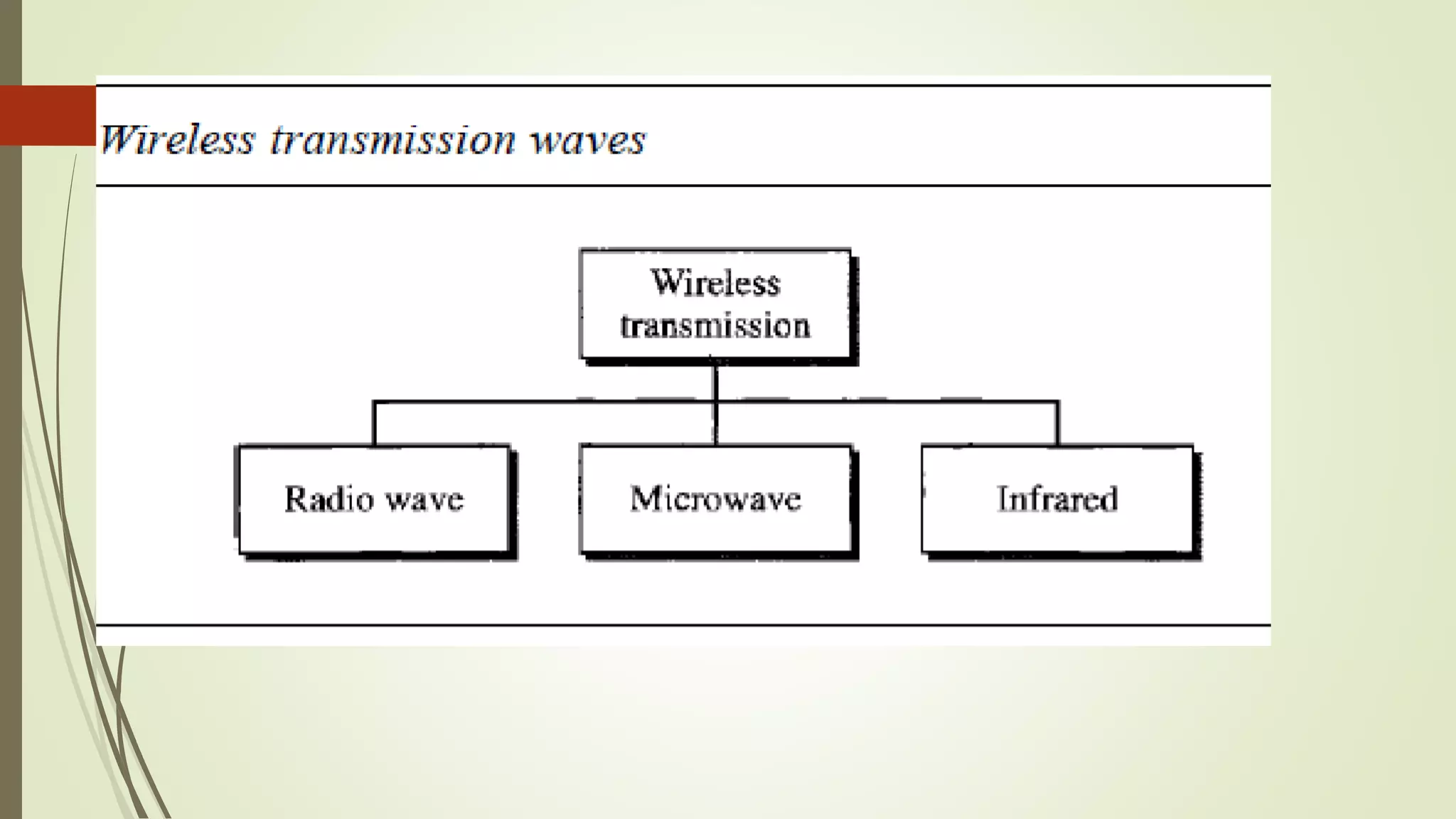
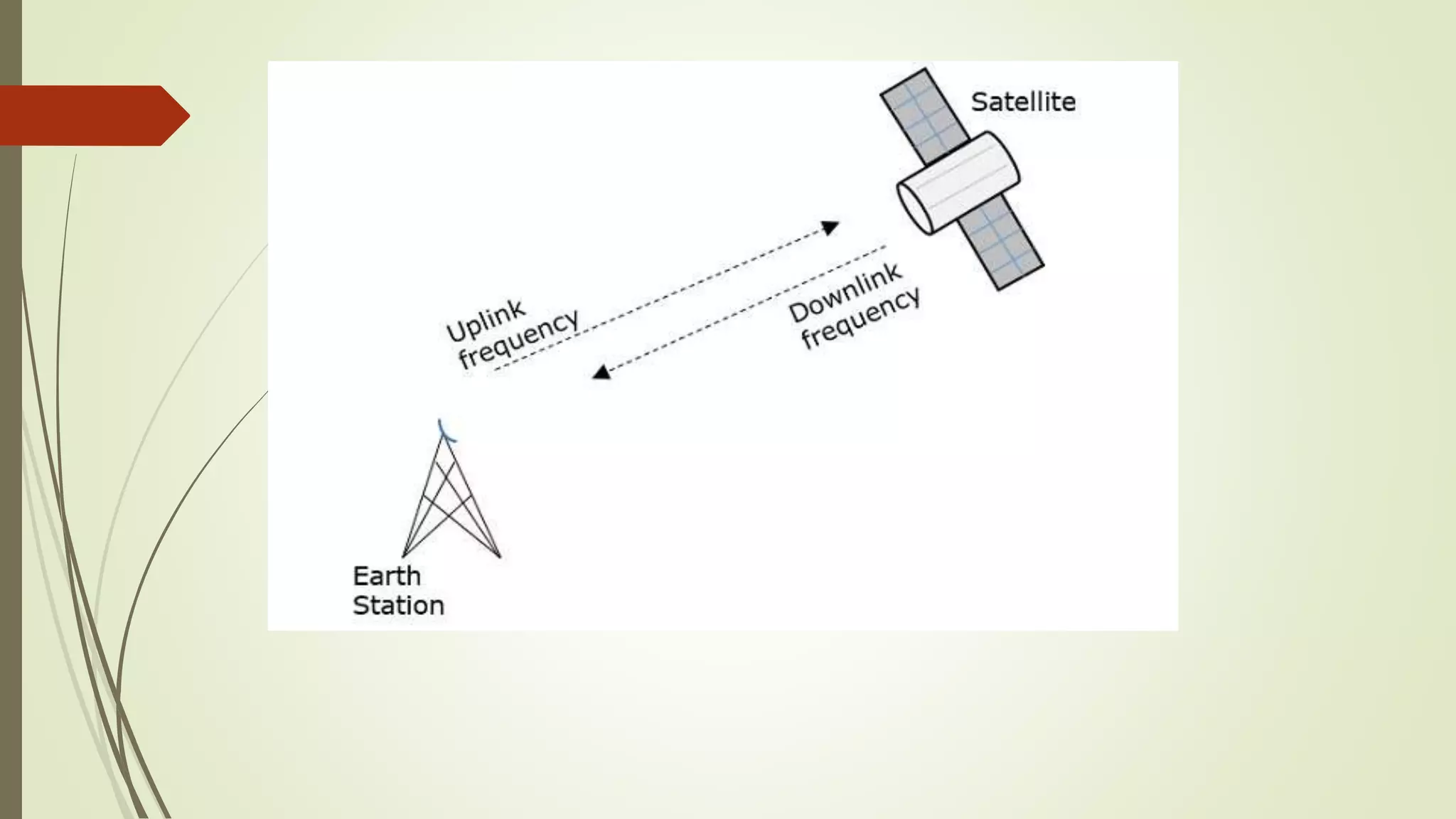
The document discusses various transmission media and connecting devices. It describes twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, fiber optic cable and wireless transmission media such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, and satellite communication. For each medium, it covers characteristics, applications, advantages and disadvantages. Twisted pair cable is commonly used for telephone lines and local area networks. Coaxial cable provides high bandwidth and is used in cable TV networks. Fiber optic cable has the highest bandwidth and longest transmission distances. Wireless media transmit signals through free space using electromagnetic waves.