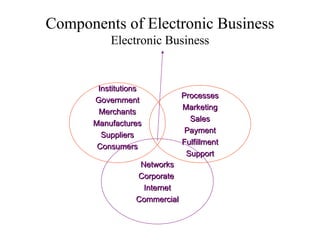
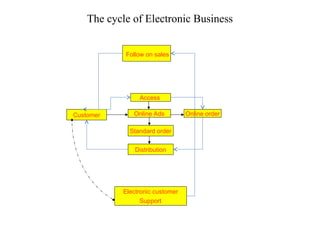
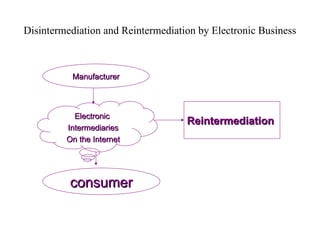
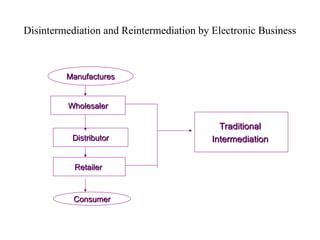
The document outlines the course on electronic business, covering its definitions, types, and benefits, as well as the impact of e-commerce on the market. It emphasizes the growing importance of efficient communication and transaction processing in business-to-consumer, business-to-business, and consumer-to-consumer interactions. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of e-business, highlighting its potential to reduce costs and improve customer experiences.