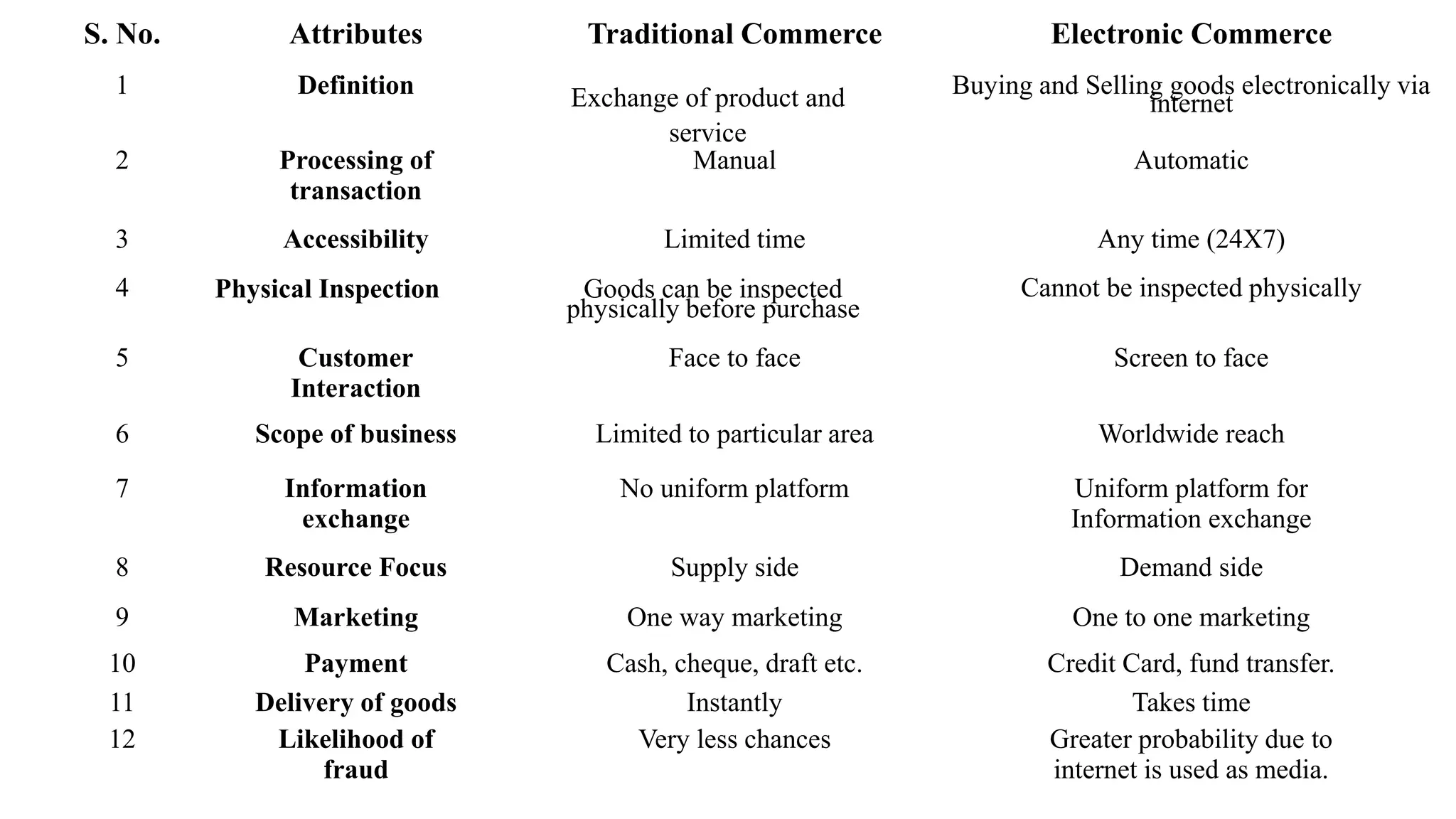
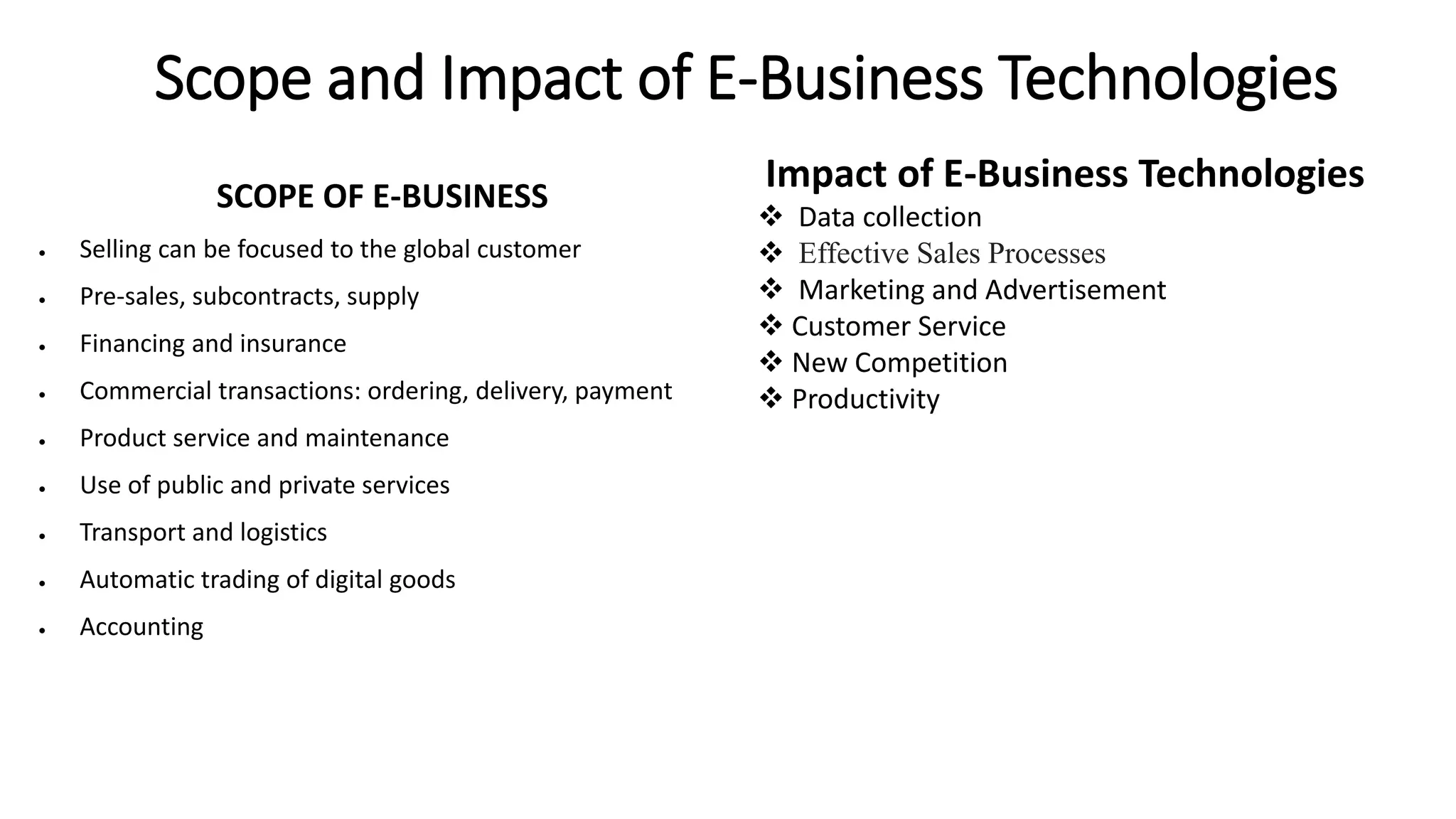
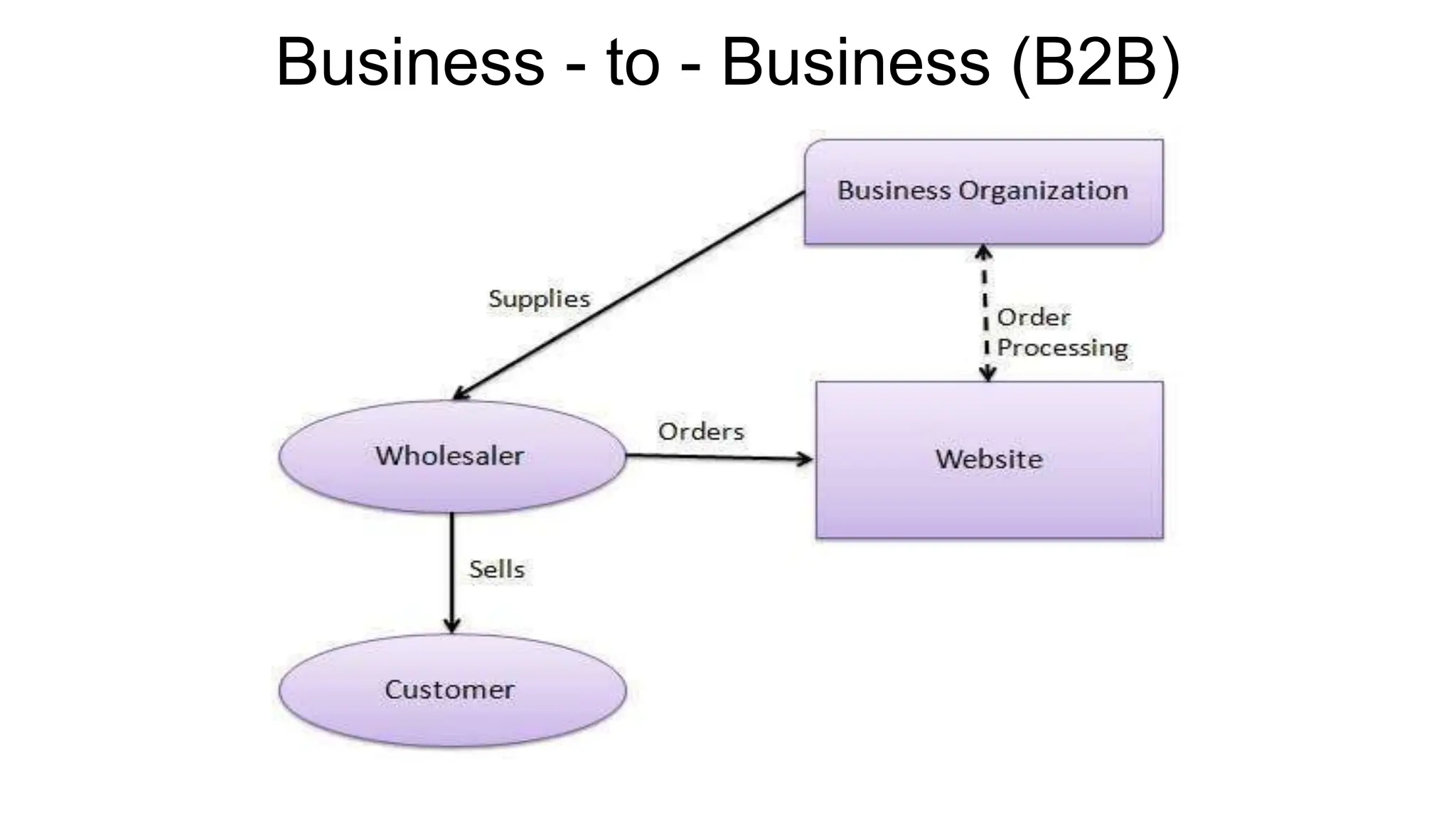
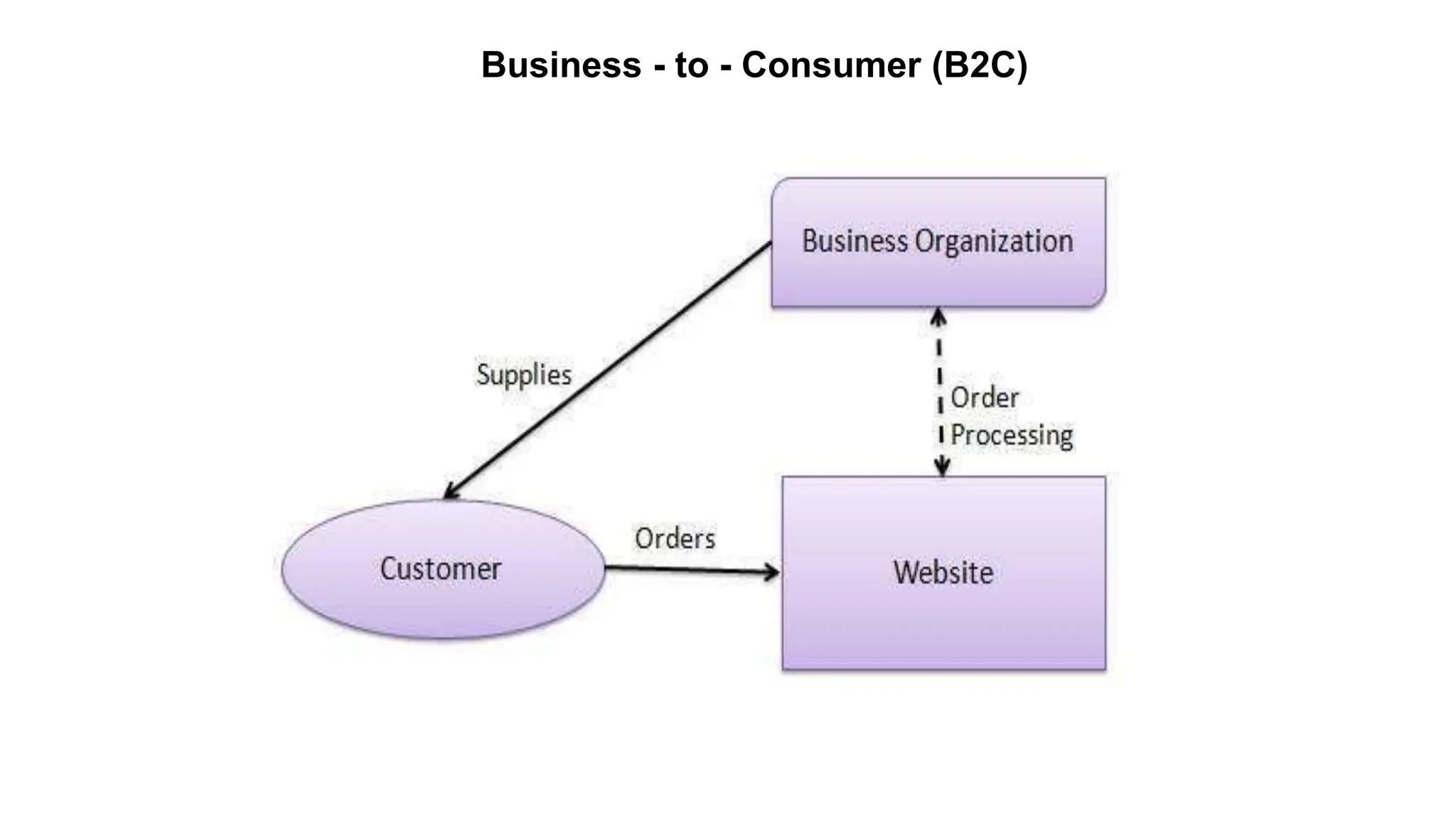
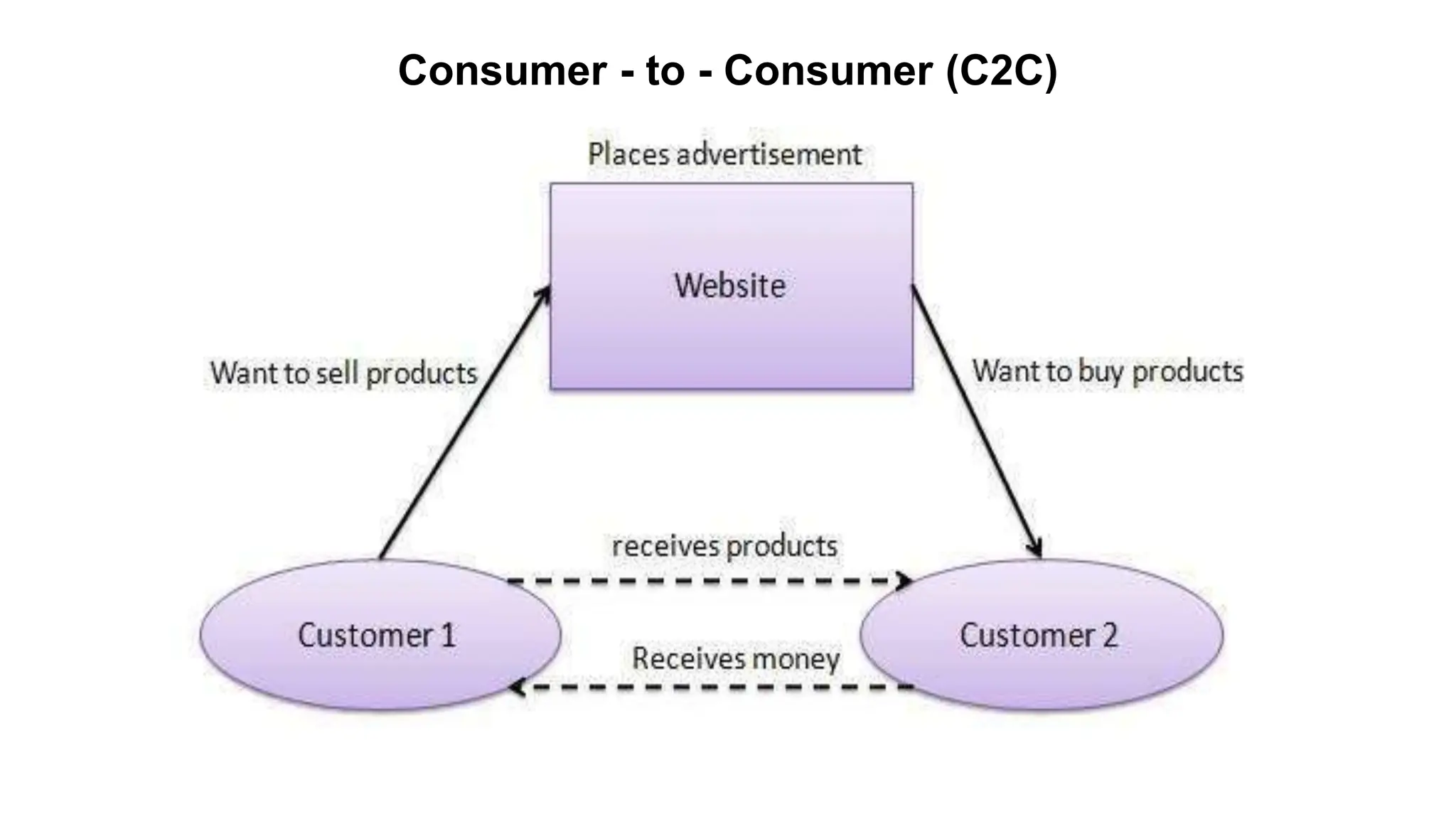
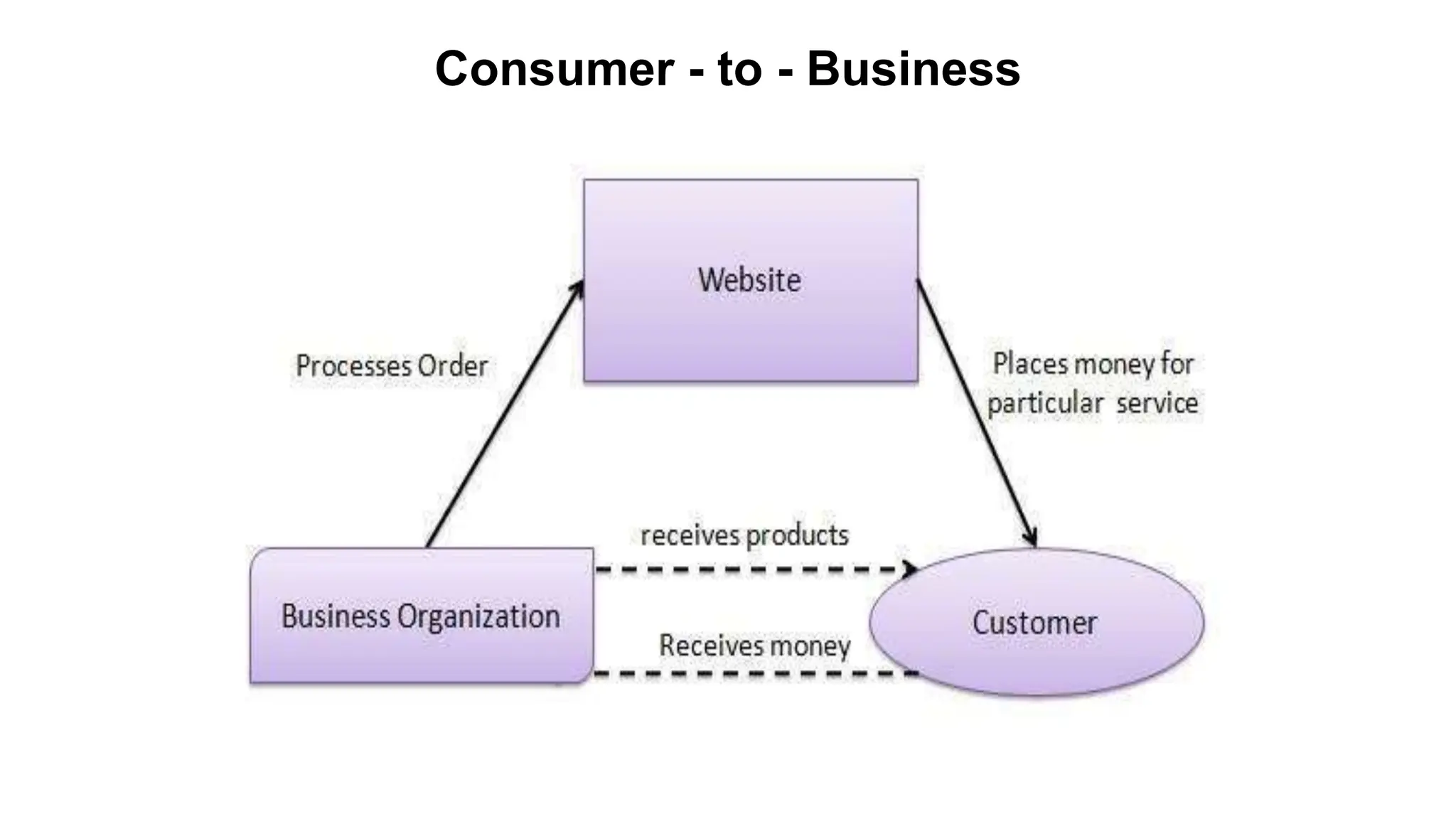
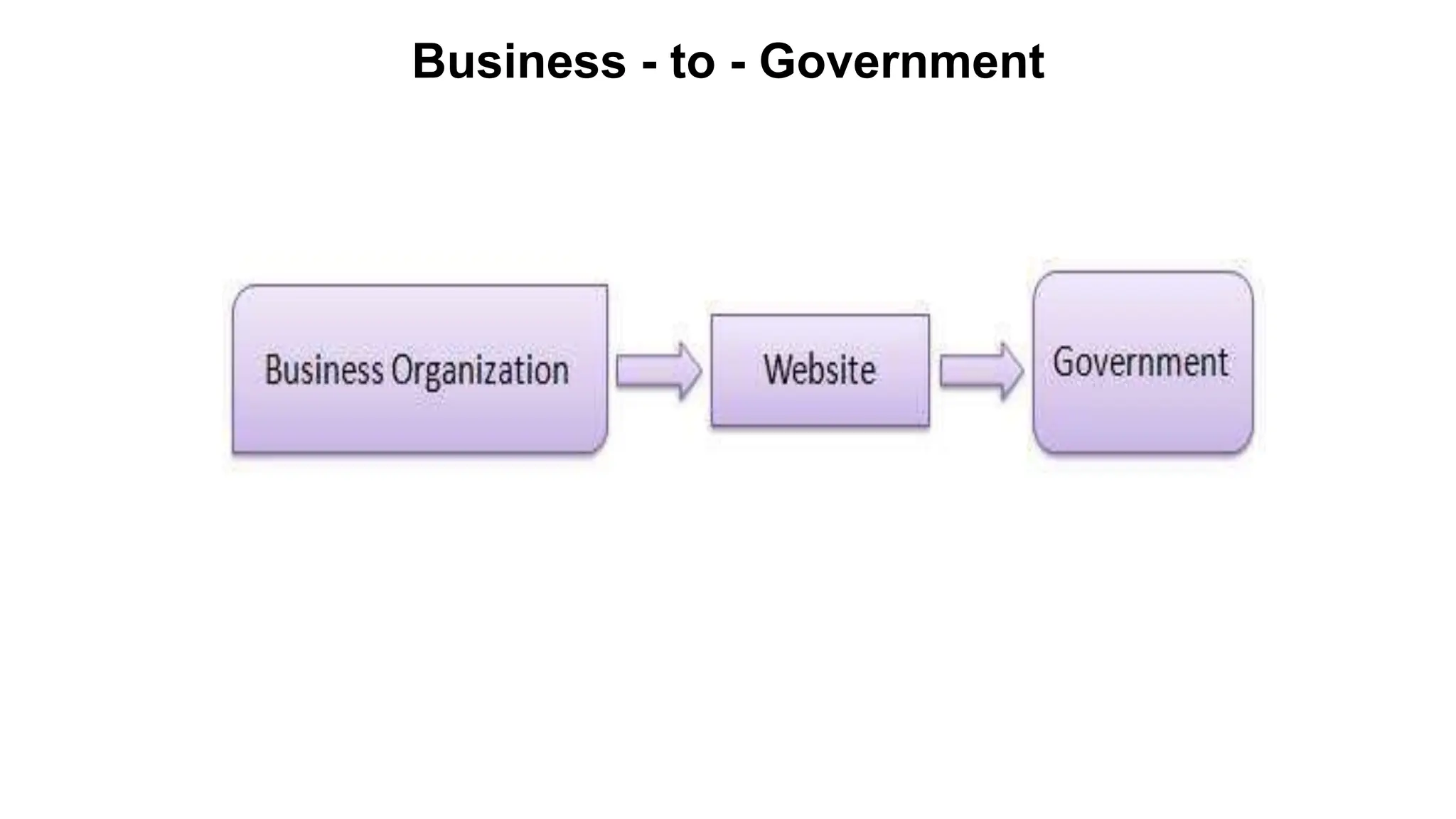
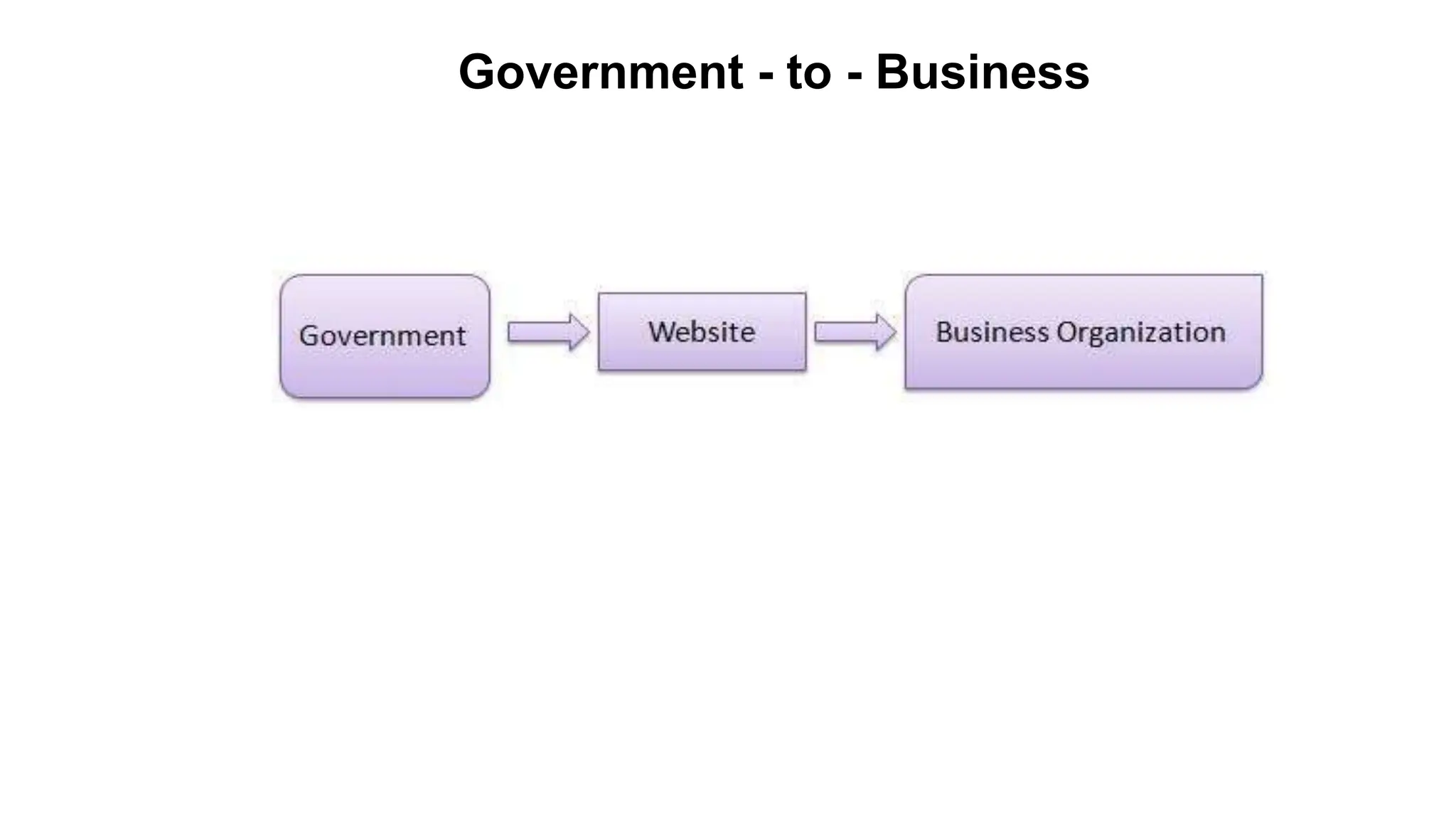
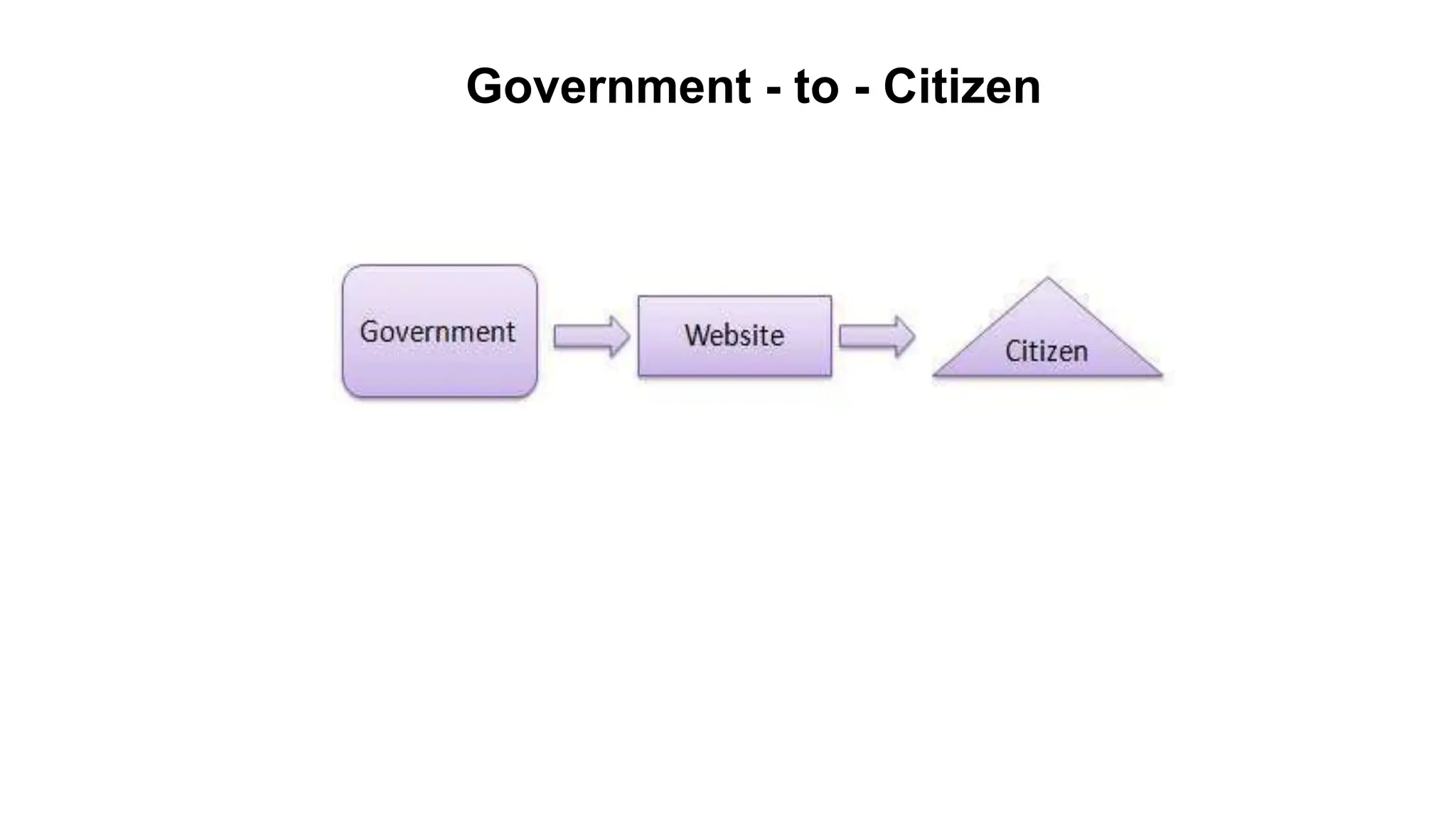
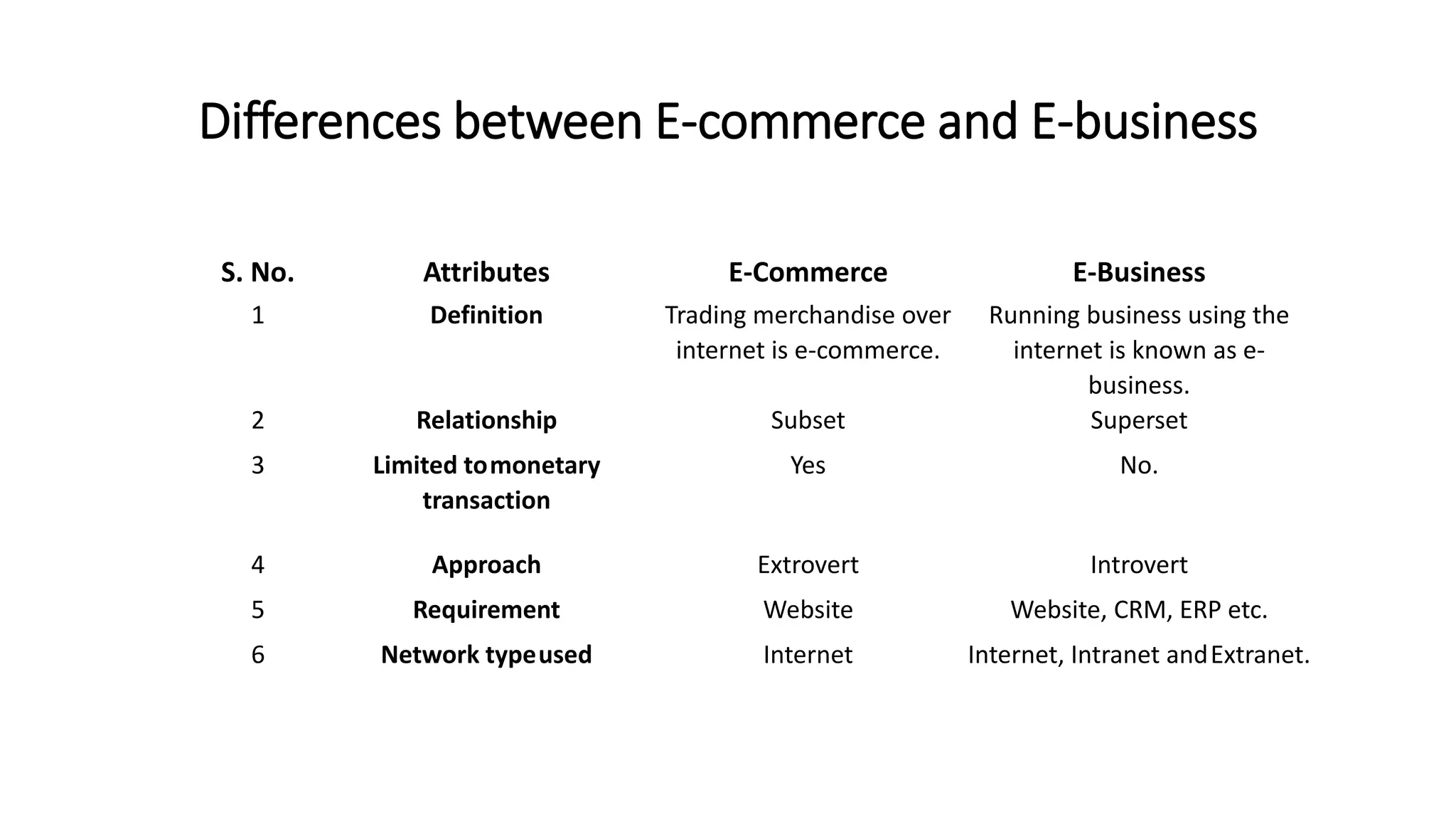
The document introduces e-business, highlighting its definition, differences with e-commerce, and the history of its development. It outlines features, advantages, and disadvantages of e-business, emphasizing its global reach, improved customer service, and efficiency, while also noting challenges like security and compatibility. Additionally, it discusses various business models, applications, and the significant contributions of e-business technologies to economic growth and productivity.
![UNIT:1
INTRODUCTION [7hrs]
Presented by
Er.Harendra Bikram Shah
[Lecturer]
Department of BBA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1introduction-240726093319-c91ee87c/75/UNIT-1-Introduction-EBUSINESS-study-about-e-business-1-2048.jpg)


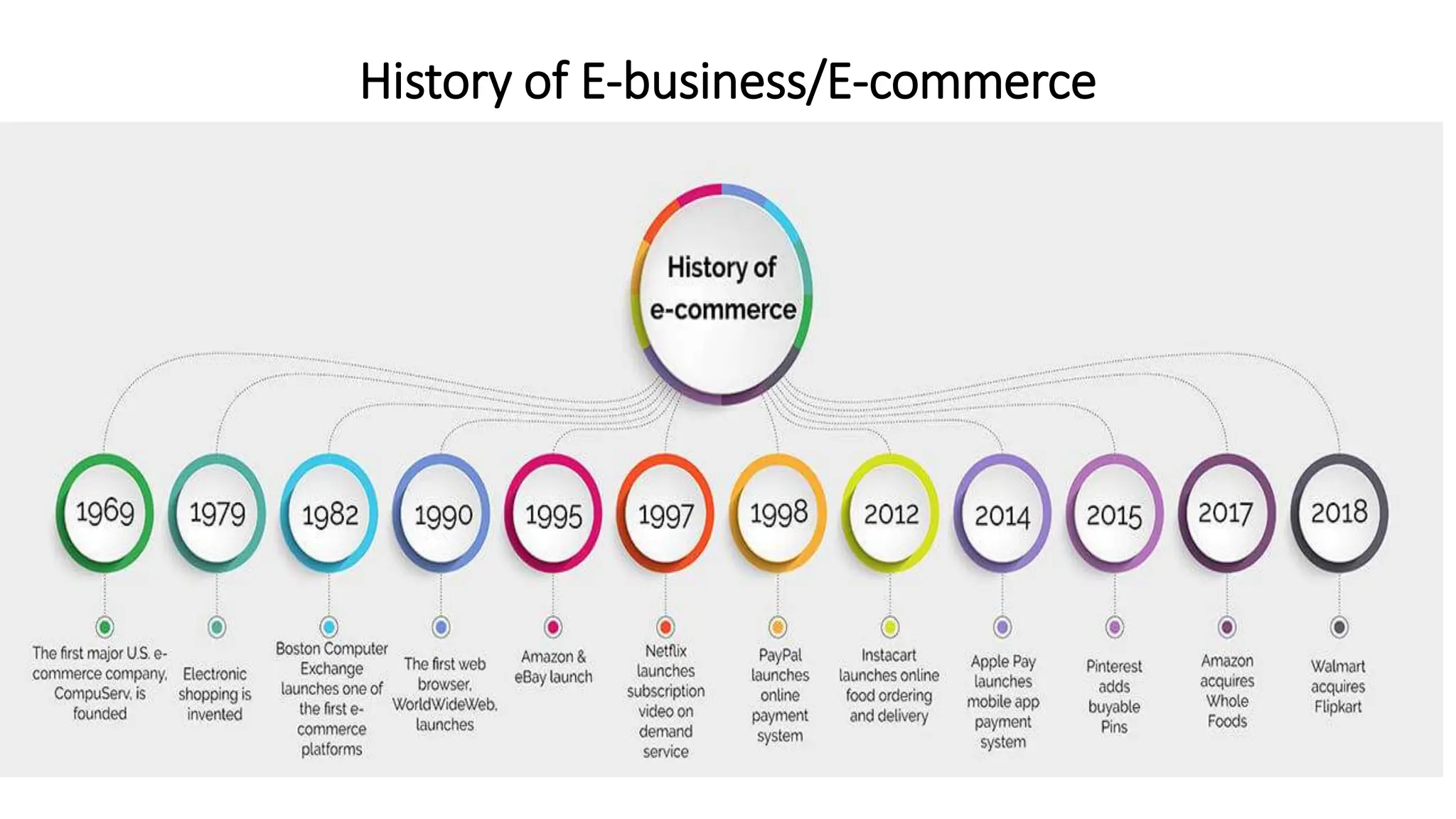
![History of E-business/E-commerce
1960’s: CompuServe Founded/EDI is used
1972: Computers Facilitate the First Online Sale
1976: Online Transaction Processing Introduced
1979: Electronic Shopping Invented[Michael Aldrich ]
1983: Electronic Commerce Acknowledged[California's Electronic Commerce Act passed ]
1984: CompuServe Opens the Electronic Mall
1990: World Wide Web Launches
1994: The First Secure Online Transaction is Made
1995: Amazon, eBay, and the Online Marketplace Boom
1998: PayPal Launches
1999: Global eCommerce reaches $150 Billion
2000: The Dotcom Burst and Online Advertising
2005: eCommerce Makes a Comeback
2006: Online Shopping Platforms Increase
2010’s: E-commerce becomes Unstoppable
2020: COVID-19 boost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1introduction-240726093319-c91ee87c/75/UNIT-1-Introduction-EBUSINESS-study-about-e-business-5-2048.jpg)