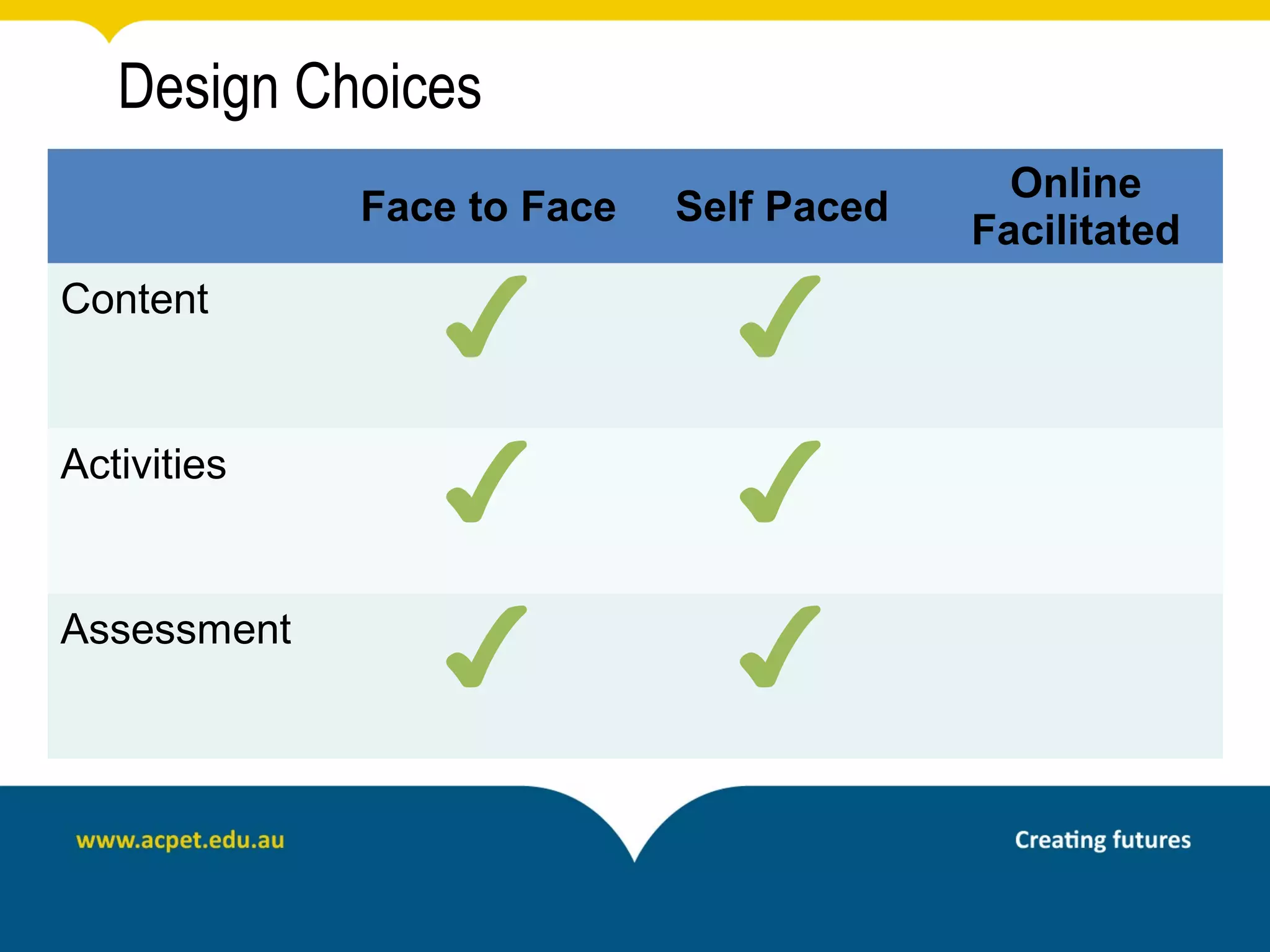
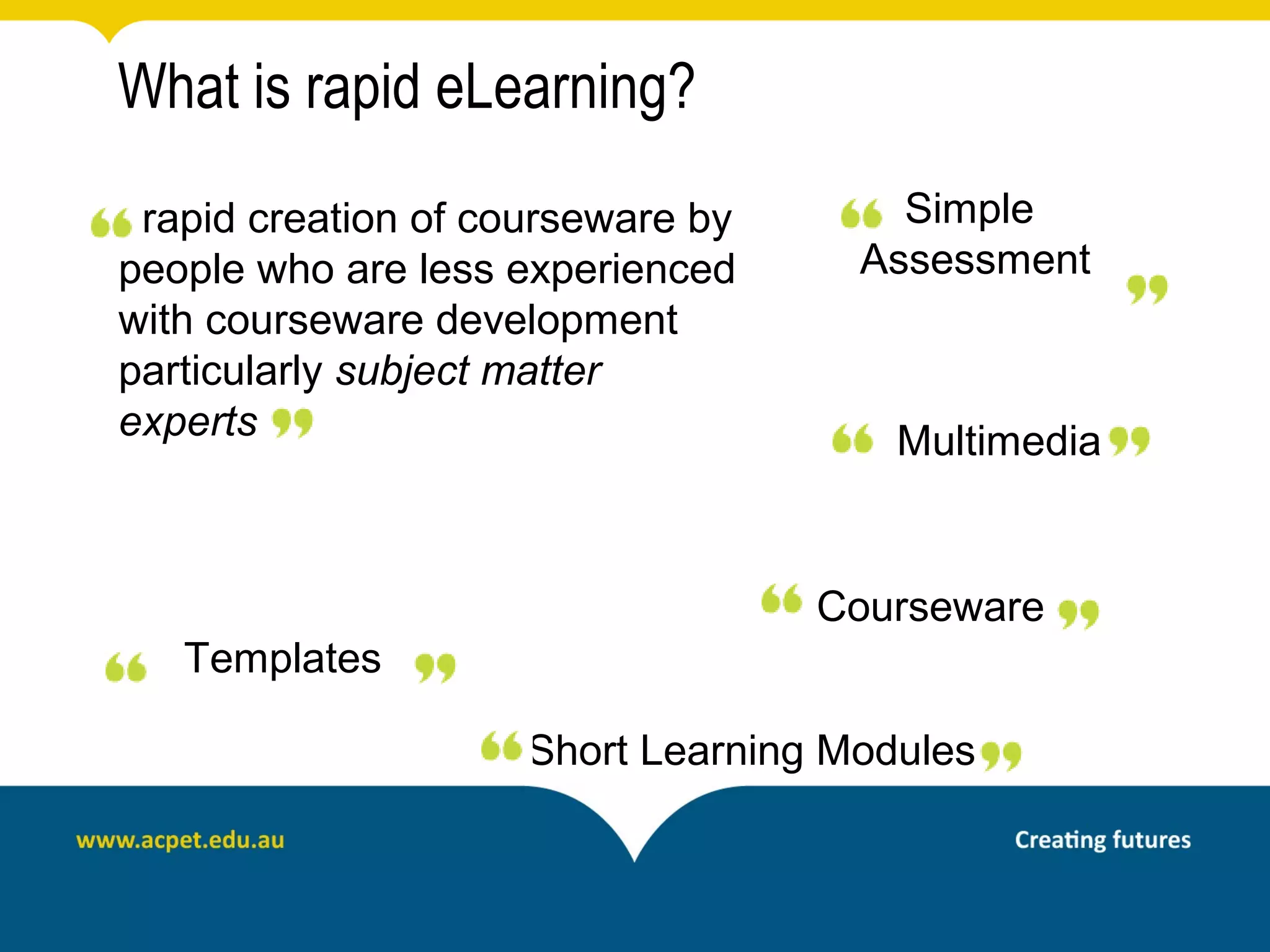
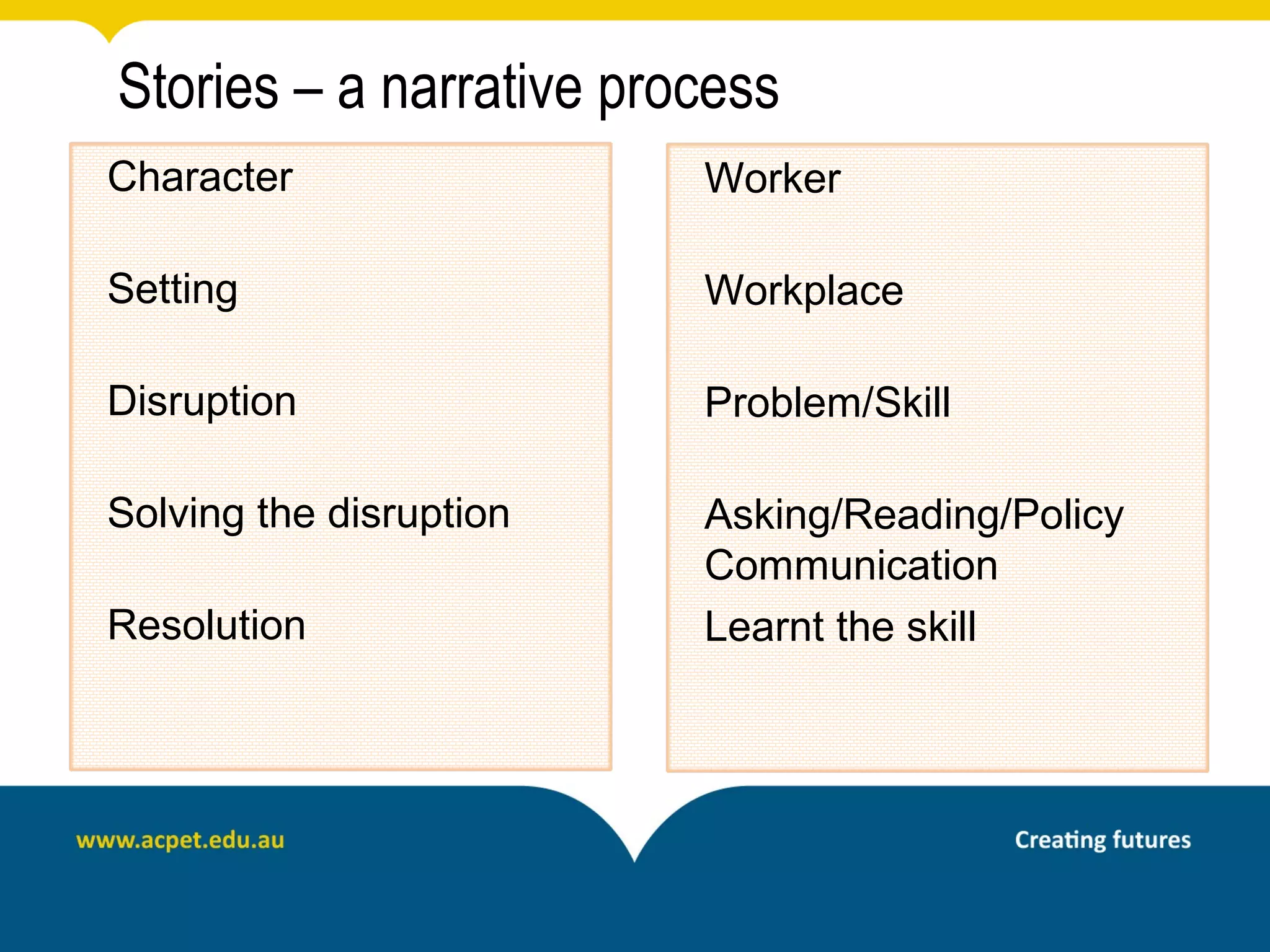
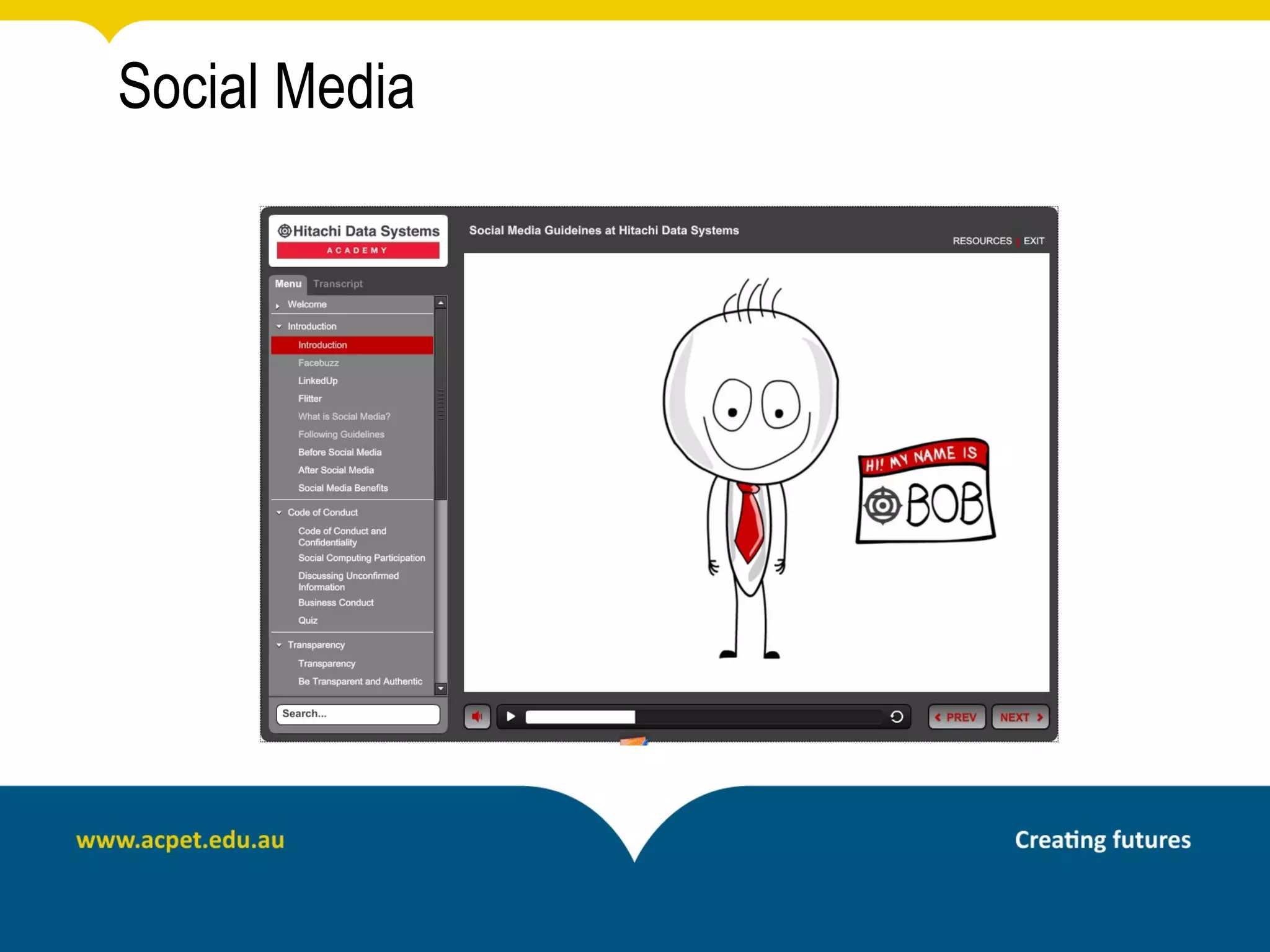
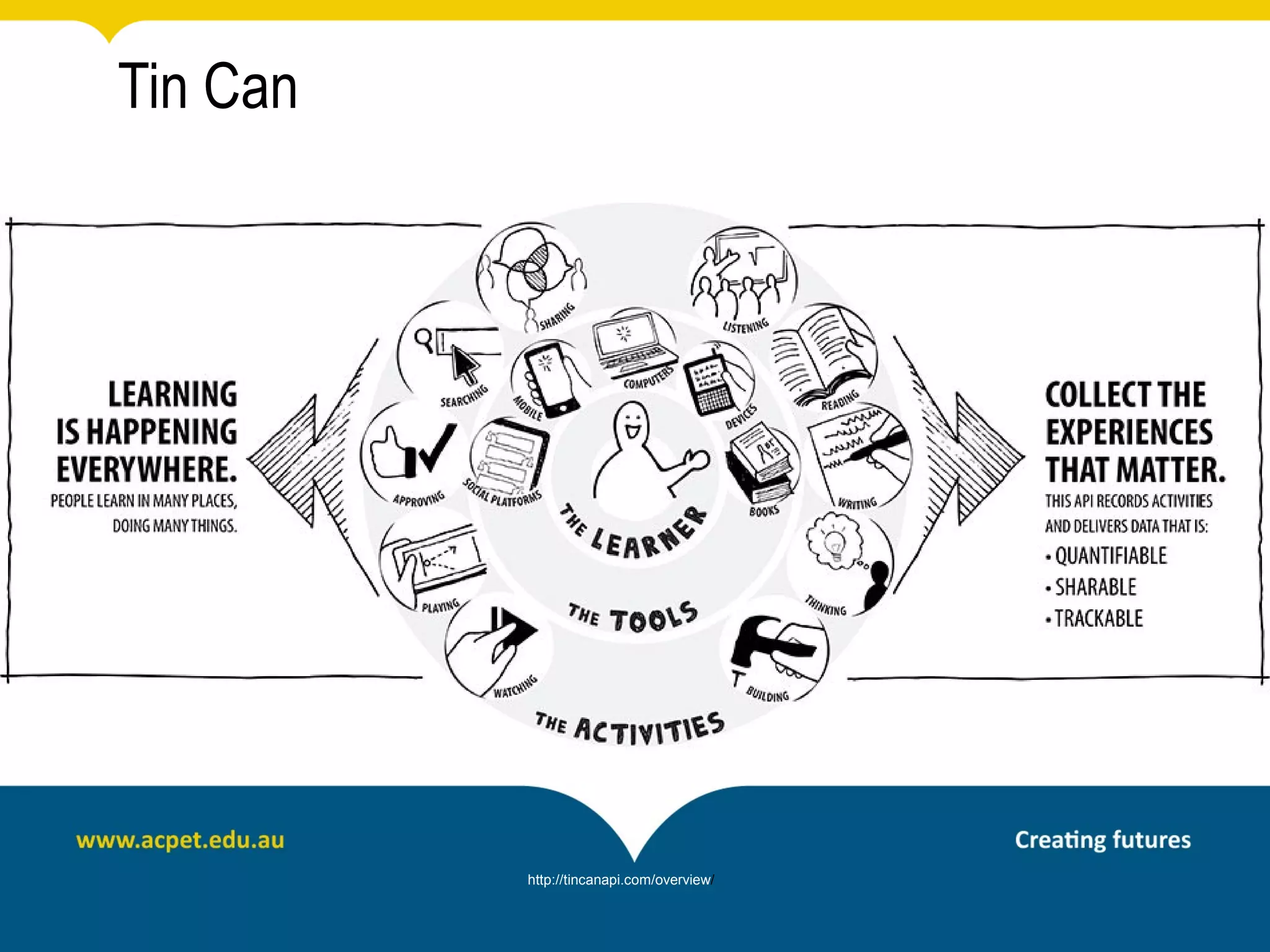
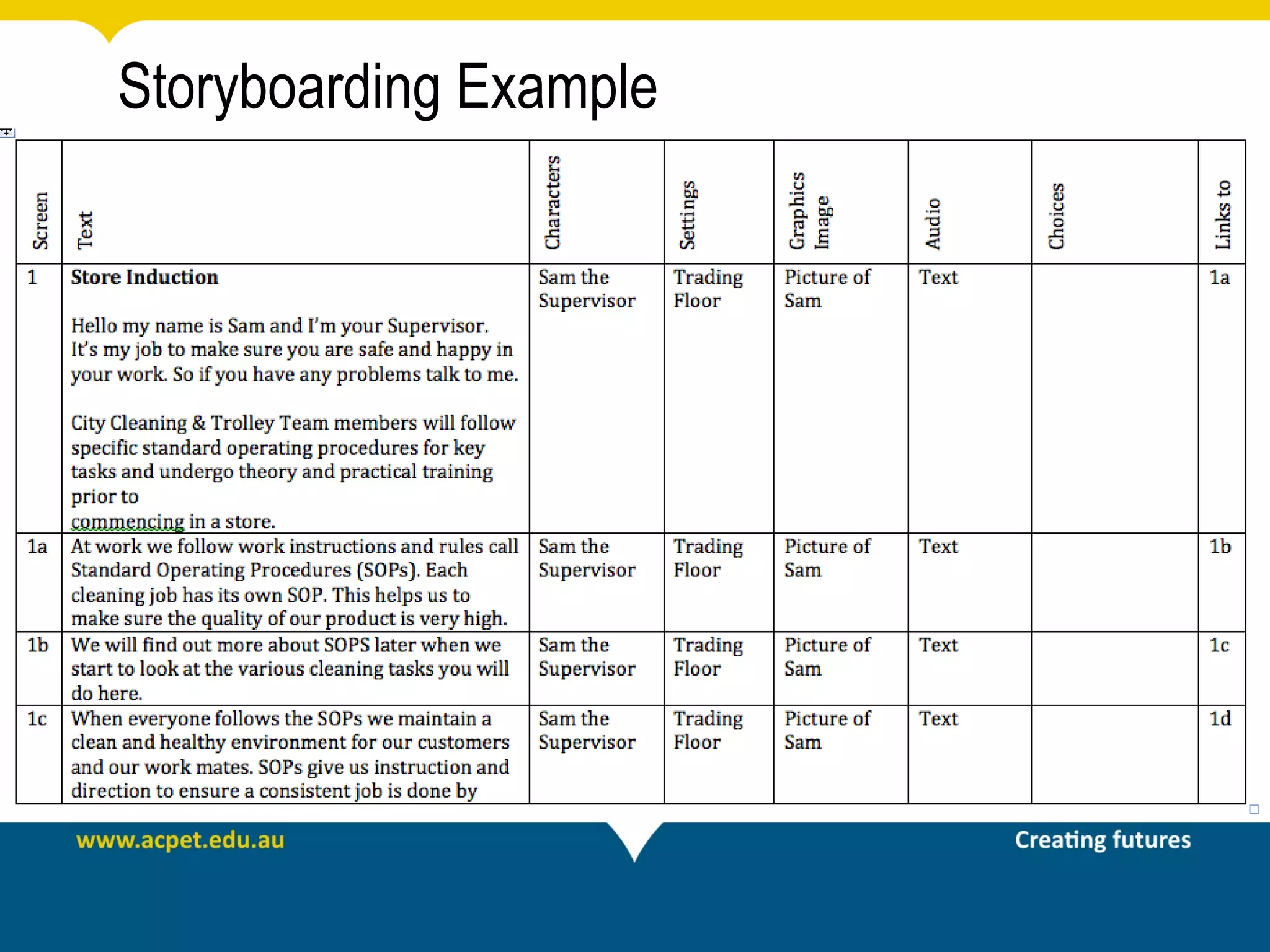
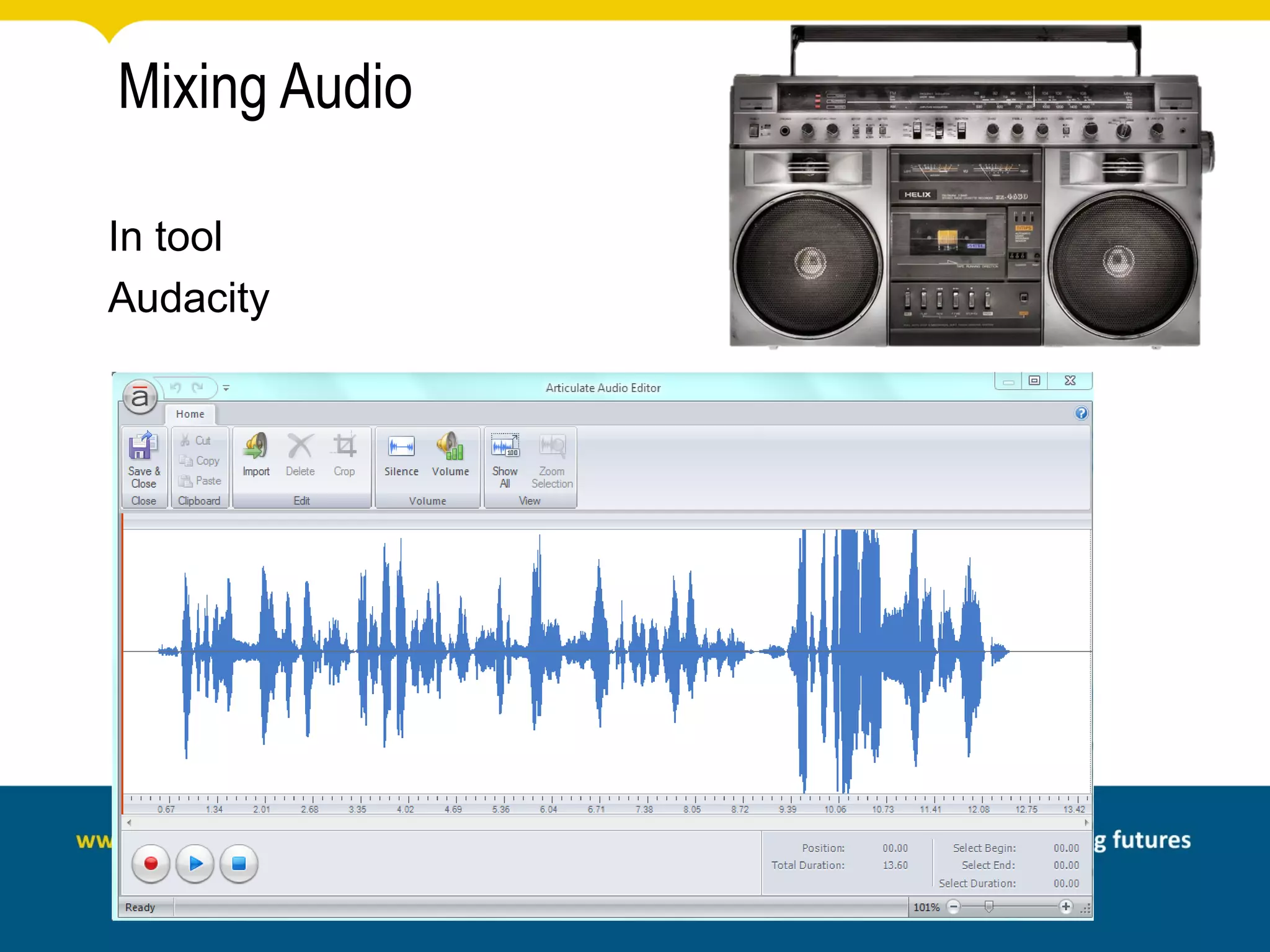
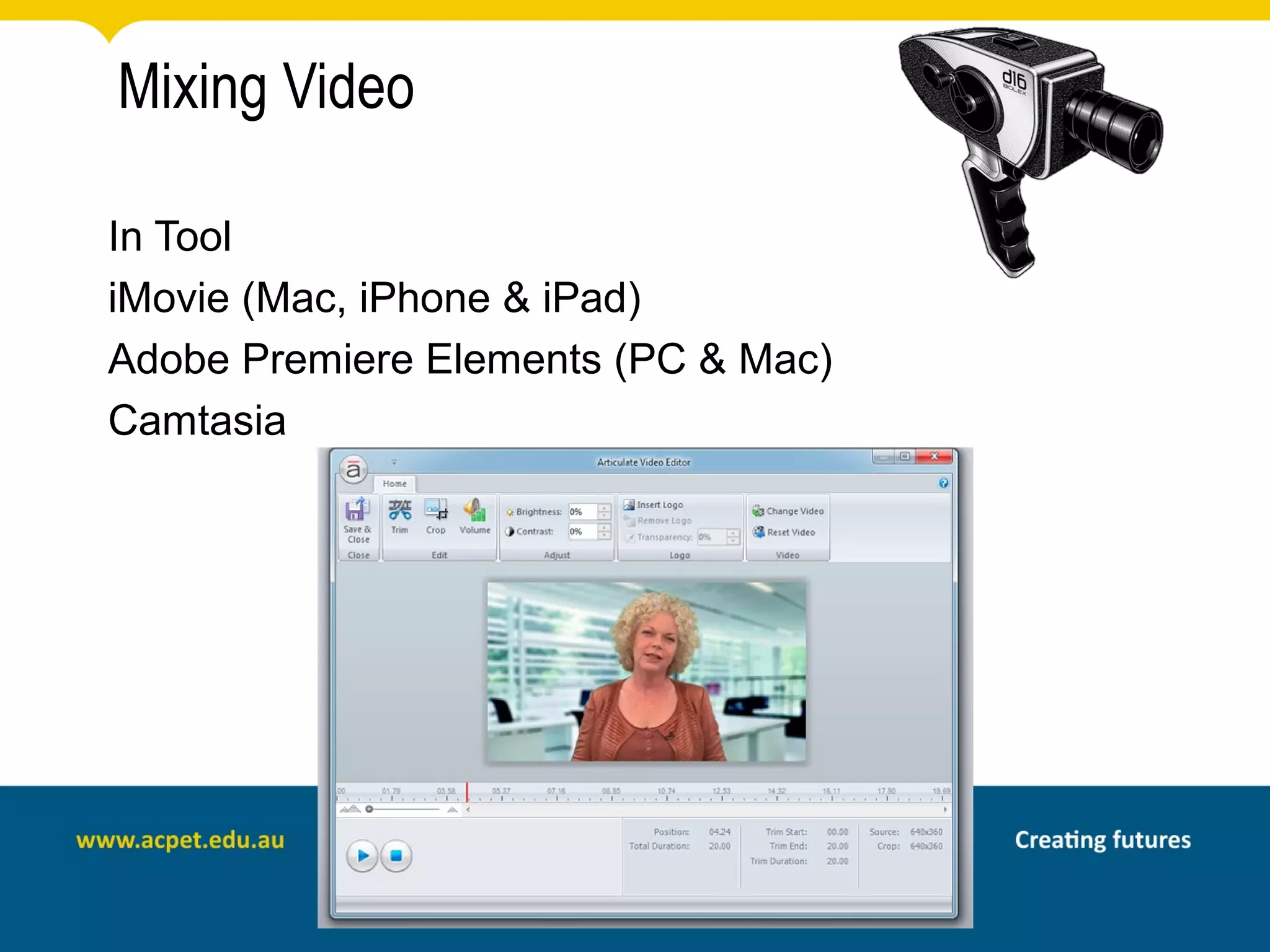
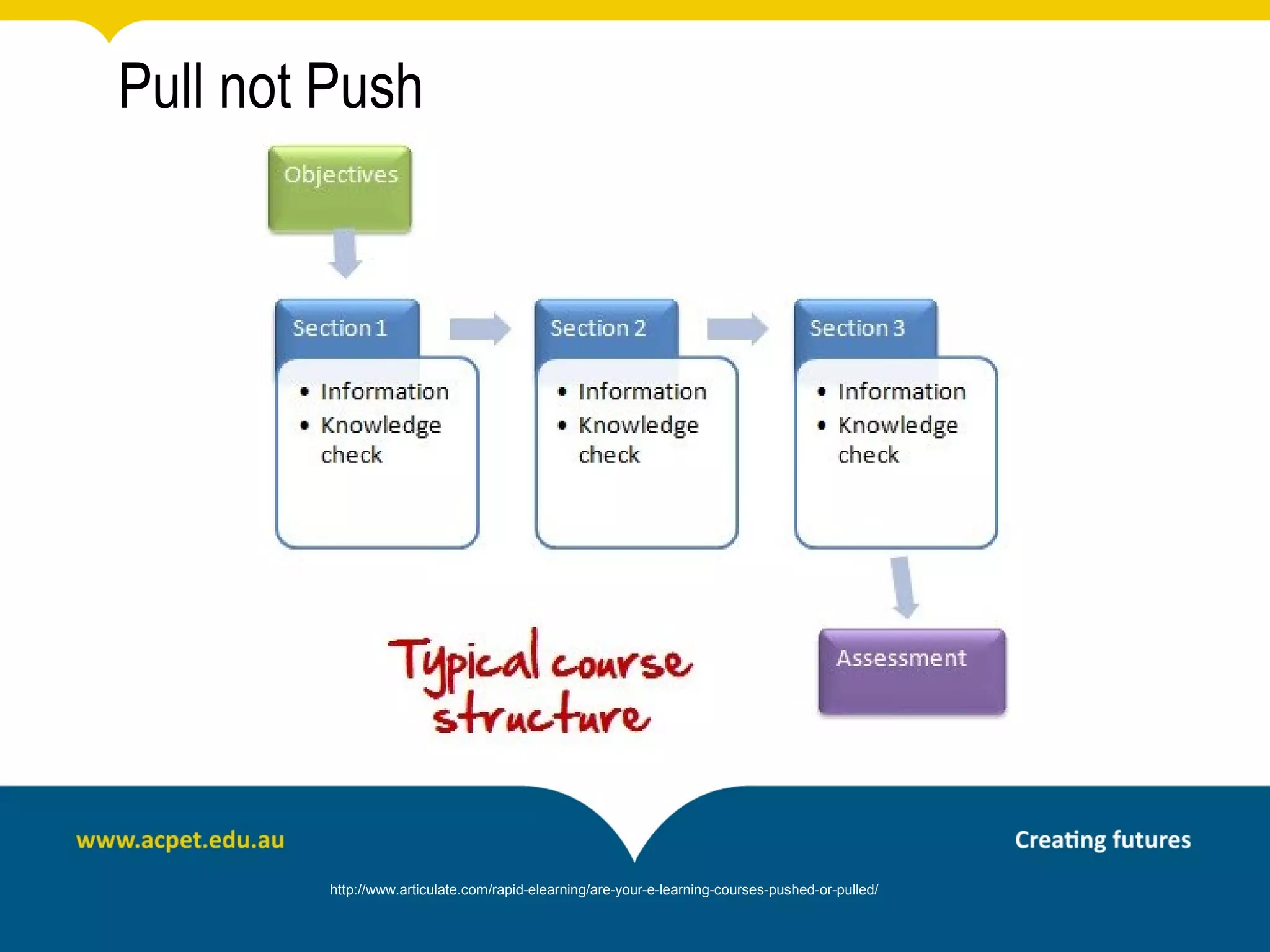
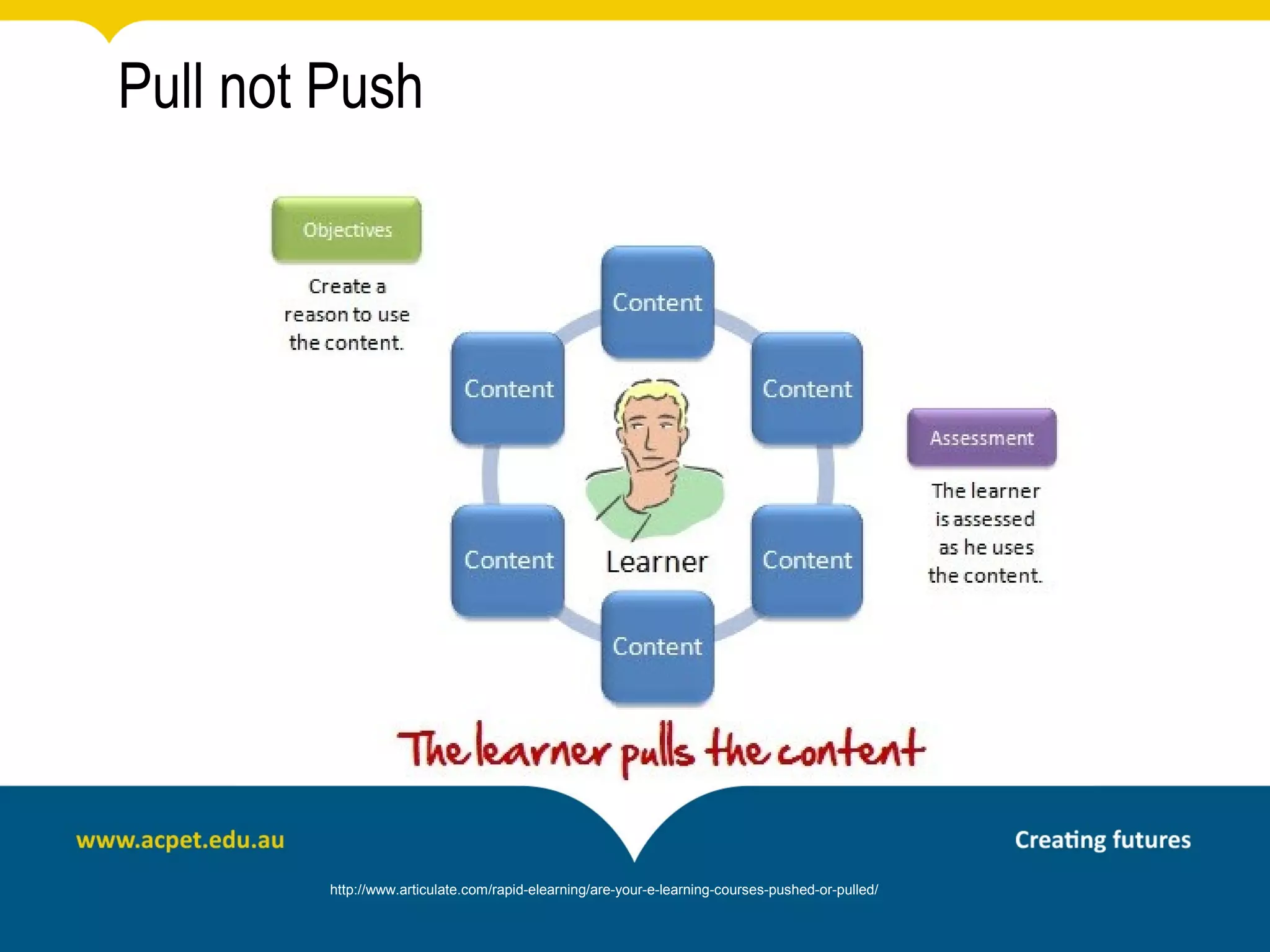
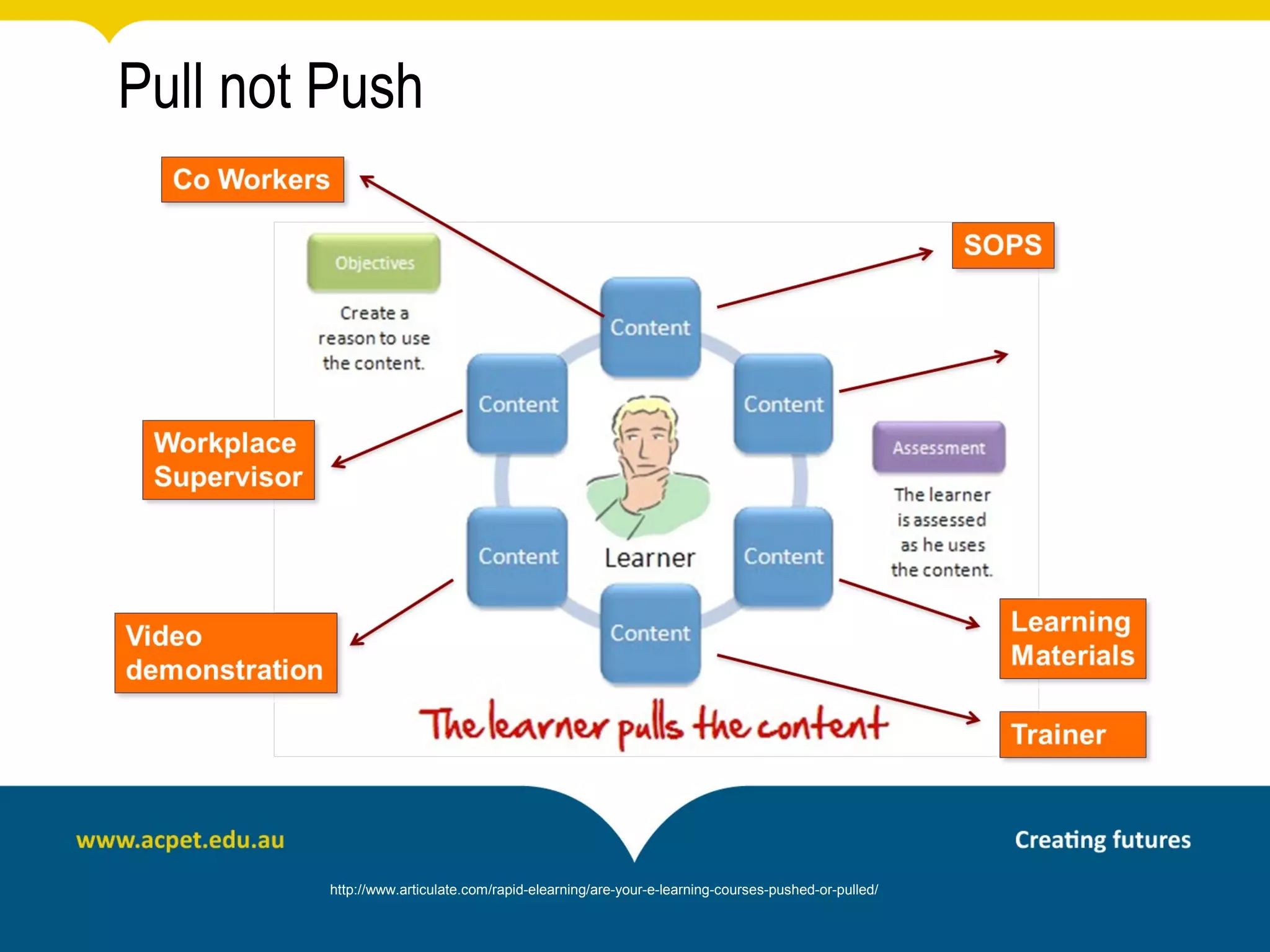
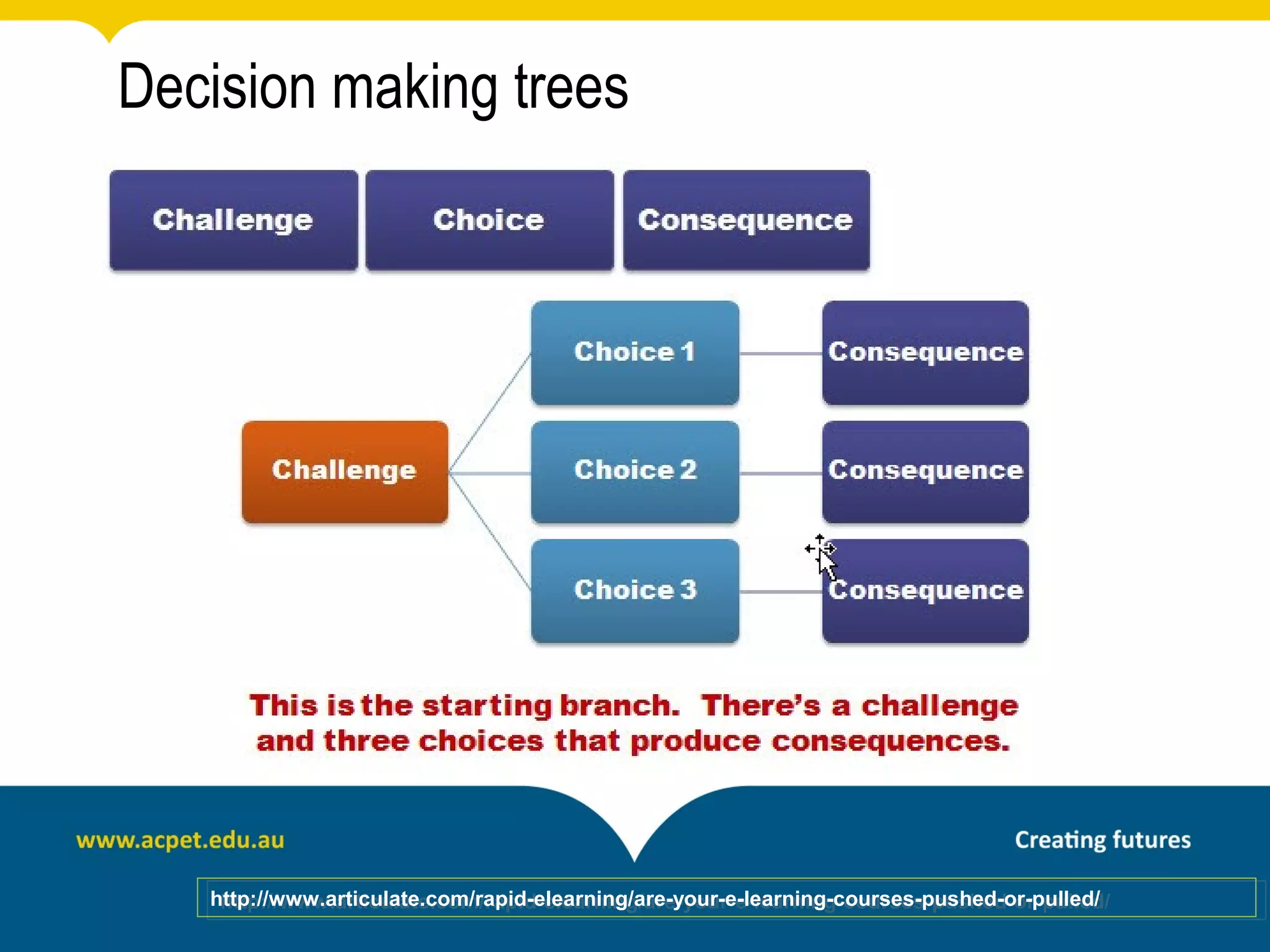
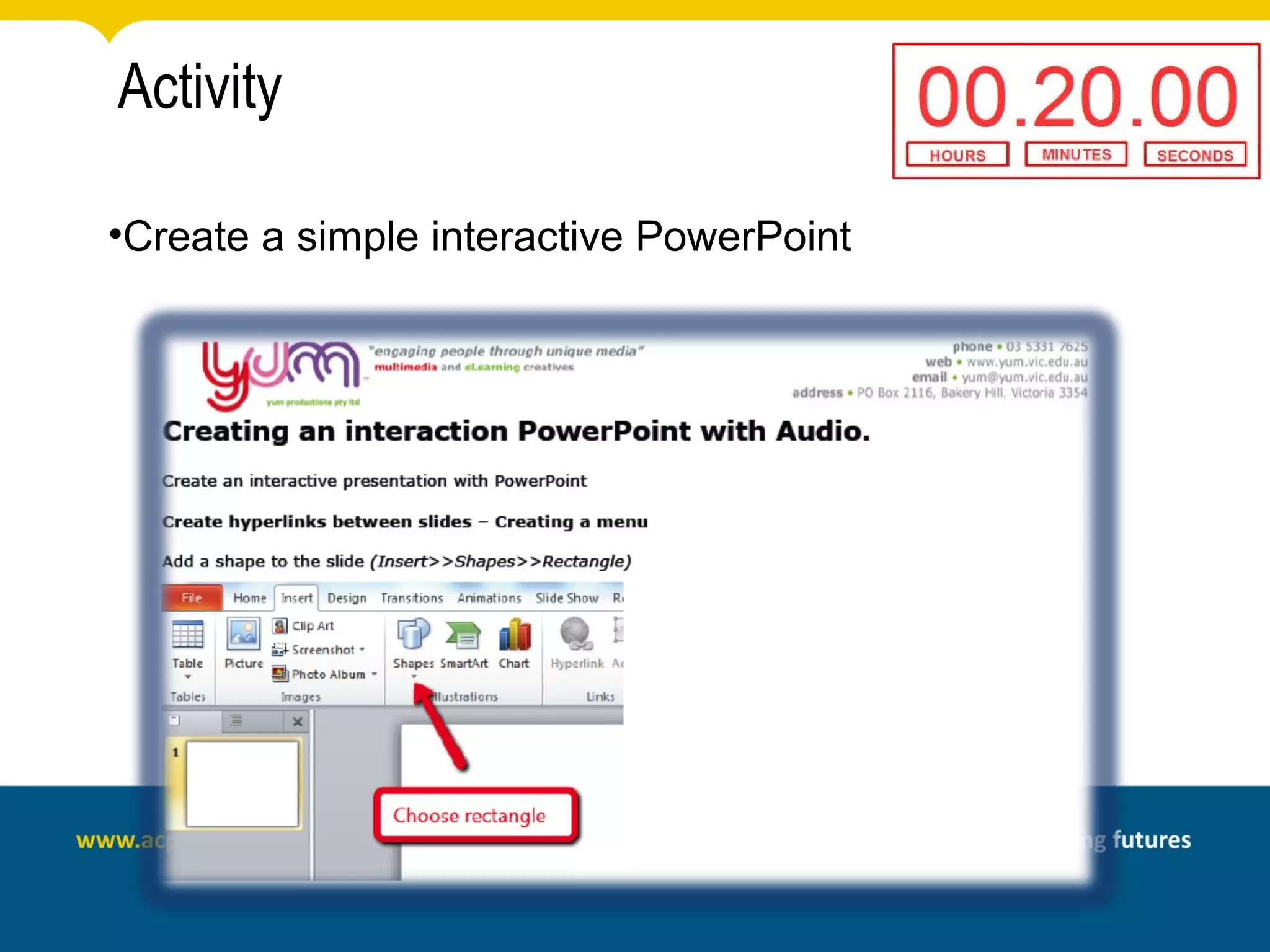
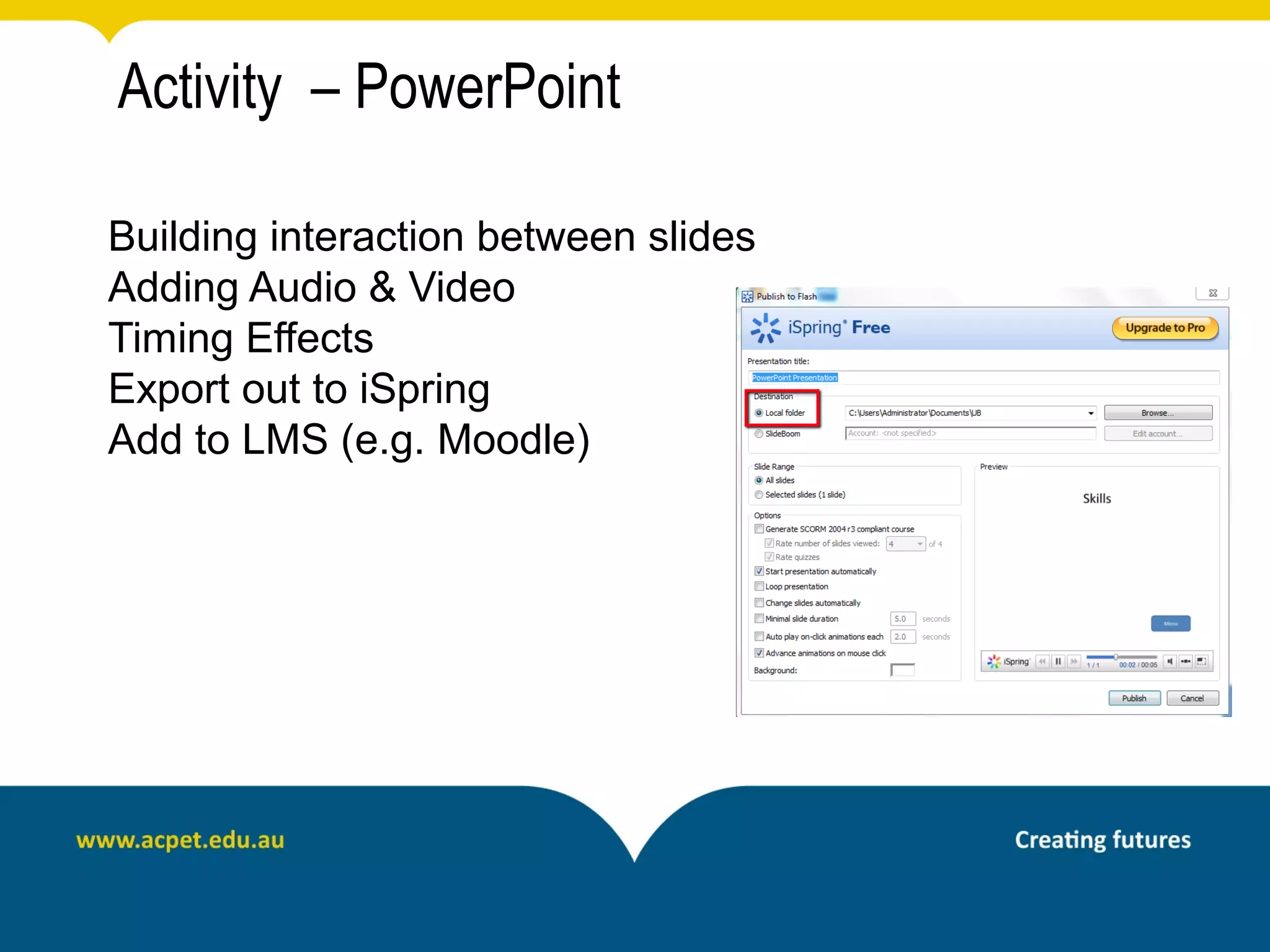
This document discusses rapid eLearning and provides guidance on creating self-paced eLearning content. It defines rapid eLearning as the rapid creation of courseware by subject matter experts with less experience in course development. It emphasizes using templates, short learning modules, and multimedia like images and video. The biggest challenge of rapid eLearning is engagement. The document provides best practices for self-paced content like incorporating activities that apply learning to real work contexts. It also provides examples of interactive content types like decision trees, scenarios, and assessments. Overall, the document aims to equip readers to efficiently create engaging, interactive self-paced eLearning content.