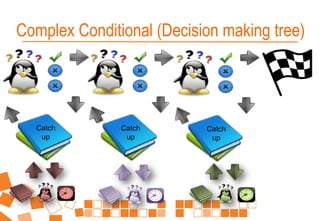
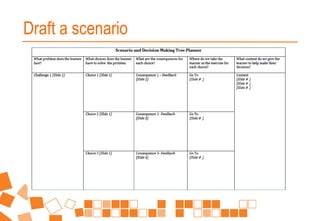
This document provides an overview of a workshop on building eAssessment. The workshop agenda includes defining e-assessment, facilitating webinar and discussion forum-based assessments, group work projects, tools for mobile evidence capture and student productivity. It discusses principles for developing self-paced assessment tasks. The document outlines various e-assessment methods like quizzes, webinars, mobile evidence, discussion forums, and trends in areas like simulation, questioning and placement reporting. It provides examples of using these methods and addresses issues around identity, cheating and skills assessment in an online environment.