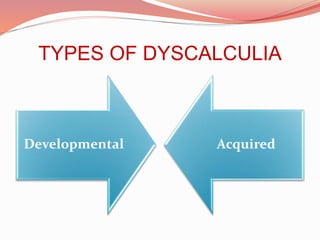
This document discusses dyscalculia, a learning disability related to difficulties with mathematics. It defines dyscalculia as a condition affecting the ability to acquire arithmetic skills. The document notes that approximately 3-6% of the population has dyscalculia. Common symptoms include difficulties with calculations, telling time, understanding numbers and mathematical concepts. The causes may include genes, brain development, environment or brain injury. Teachers can help students with dyscalculia by using concrete examples, repeated practice, encouragement, multisensory teaching methods, and memory tricks.