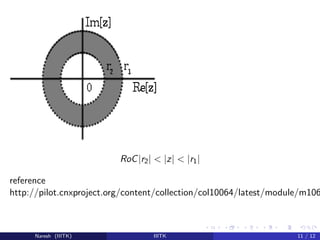
The document compares and contrasts the z-transform, Fourier series, and Fourier transform.
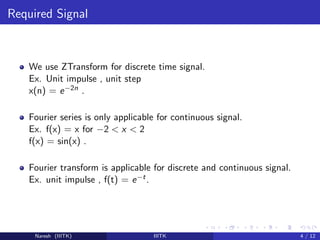
1) The z-transform is used for discrete-time signals, Fourier series is used for continuous periodic signals, and Fourier transform can be used for both discrete and continuous signals.
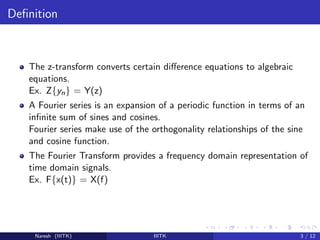
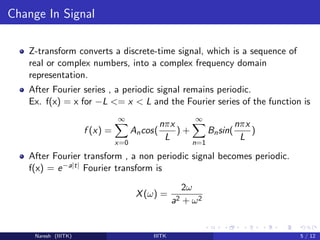
2) The z-transform converts difference equations to algebraic equations. Fourier series expands periodic functions as an infinite sum of sines and cosines. The Fourier transform provides a frequency representation of signals.
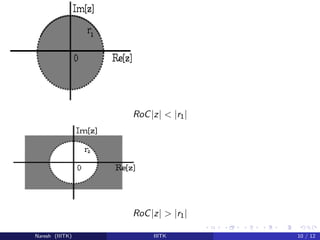
3) The inverse of the z-transform and Fourier transform are defined mathematically, while there is no inverse of a Fourier series since it does not change the domain of the original signal.