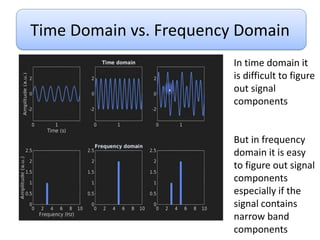
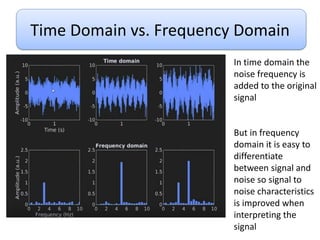
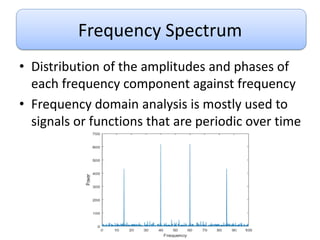
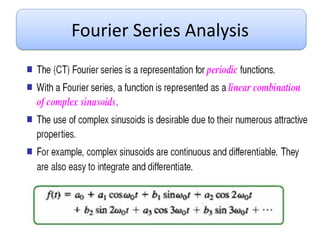
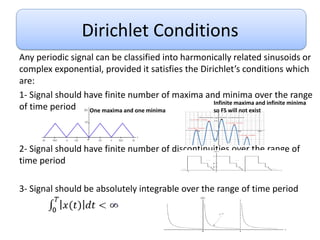
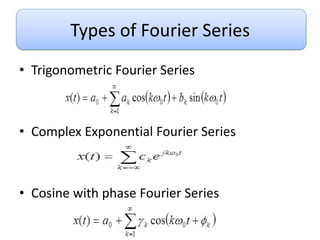
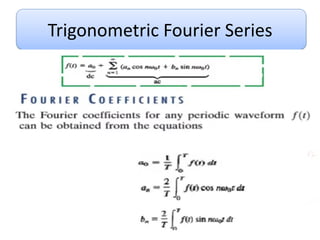
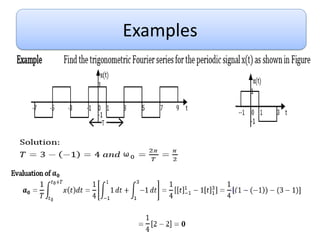
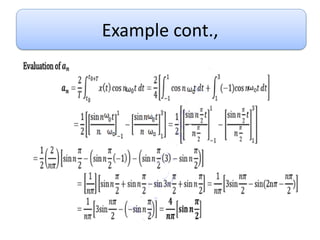
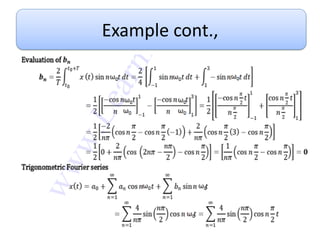
This document discusses Fourier series and the frequency domain. It begins by defining the frequency domain as analyzing signals based on frequency rather than time. The frequency spectrum shows the amplitudes and phases of frequency components. Fourier series can be used to analyze periodic signals by expressing them as sums of sinusoids. There are different types of Fourier series including trigonometric, complex exponential, and cosine with phase. Fourier series satisfy Dirichlet conditions of being periodic, having a finite number of discontinuities and maxima/minima to be absolutely integrable. Examples are provided of applying Fourier series to periodic signals.