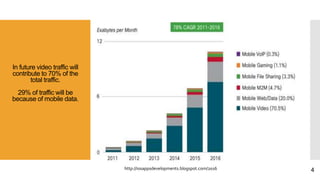
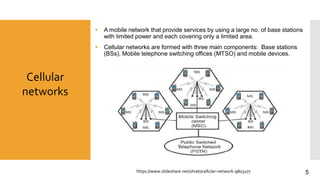
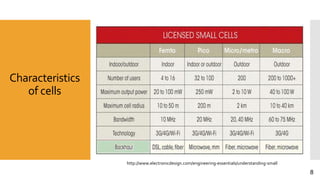
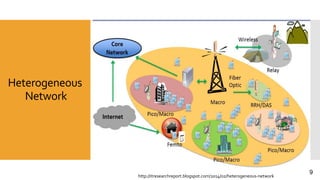
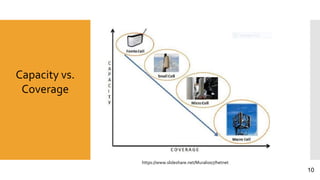
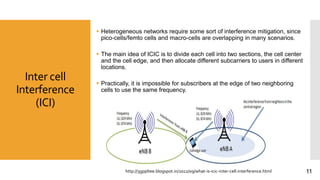
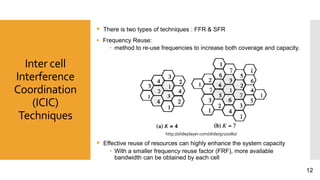
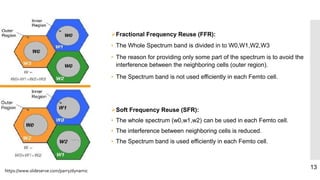
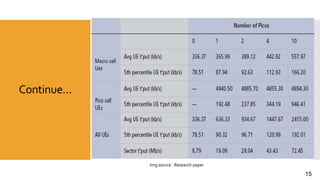
This document discusses heterogeneous networks (hetnet) as a solution to the rising demand for mobile data and emphasizes the importance of increasing network capacity while managing coverage and interference issues. It outlines the components of hetnets, including macro, pico, and femto cells, and describes techniques for mitigating intercell interference. The conclusion highlights the need for a multi-tier cellular network approach to enhance data capacity and overall network performance.