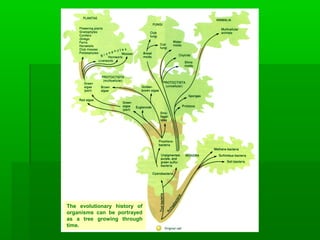
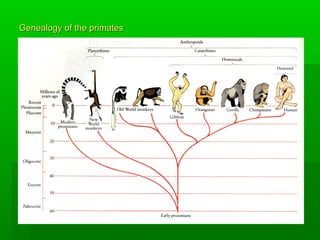
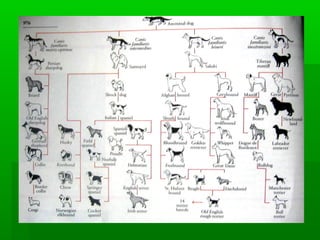
Darwin's theory of evolution proposed that all species evolved over time from common ancestors through a process of natural selection acting on hereditary variation in populations. His main ideas included common descent, whereby all organisms are related through descent from some unknown ancient ancestor; gradualism, where new species slowly accumulate adaptations to different environments over time; and natural selection, as the mechanism driving evolution by preferentially reproducing individuals with advantageous traits.