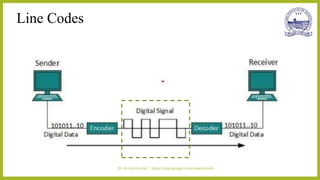
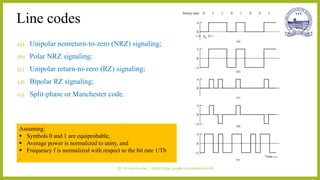
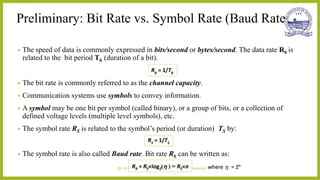
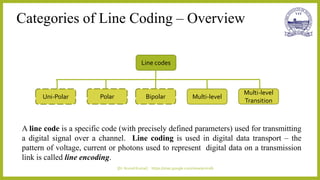
This document discusses different types of line codes used for digital communication systems. It begins by introducing line codes as electrical representations of encoded binary data streams produced by transmitters. It then describes several common line coding techniques like unipolar NRZ, polar NRZ, unipolar RZ, bipolar RZ, and Manchester coding. For each technique, it discusses properties like bandwidth requirements, error detection capabilities, and power spectral density. It also provides examples of polar NRZ signals and Manchester encoding. The document aims to analyze and characterize various line coding techniques in both the time and frequency domains.