The document discusses key concepts related to auditing, including:
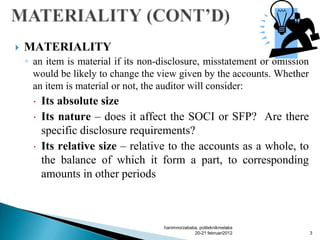
- Materiality refers to information that could influence users' economic decisions if omitted or misstated. Factors like qualitative considerations and expected users affect materiality judgements.
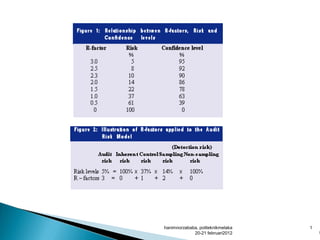
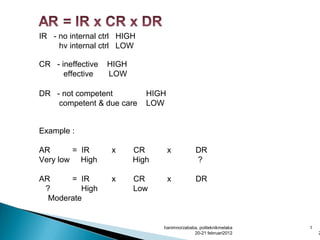
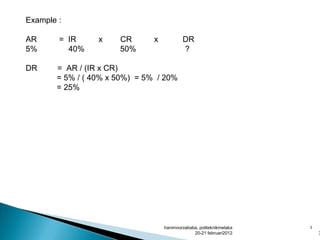
- Audit risk is the risk an auditor gives an inappropriate opinion if statements are materially misstated. It depends on inherent risk, control risk, and detection risk. Acceptable audit risk is how much misstatement an auditor will tolerate.
- Inherent risk relates to risks from a company's nature. Control risk considers risks internal controls fail to prevent or detect errors. Detection risk is the risk errors are not detected by audit procedures.