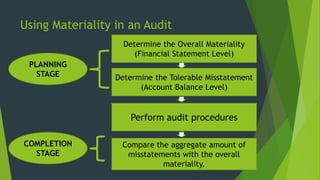
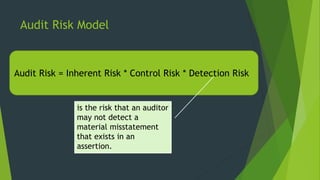
The document discusses audit planning which involves developing an audit strategy and approach. Adequate planning ensures important areas are addressed, potential problems identified, and work is completed efficiently. It involves understanding the client's business, internal controls, and risks. Analytical procedures are used in planning to identify audit areas and risks. The auditor estimates materiality and assesses inherent, control and detection risks to determine the audit approach using the audit risk model. Documentation includes the audit plan, program and time budget.