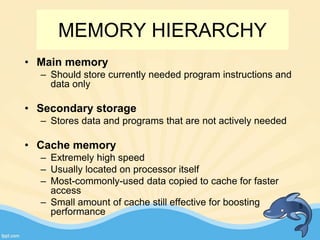
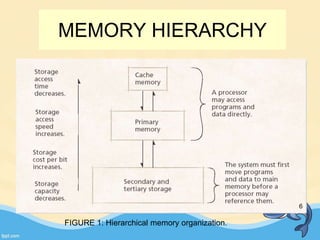
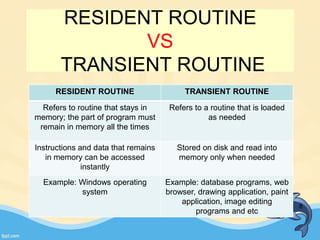
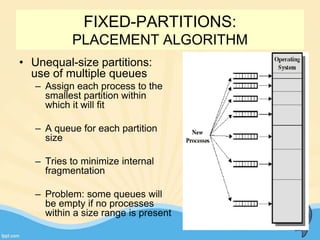
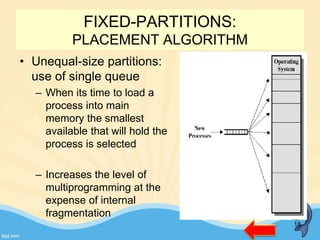
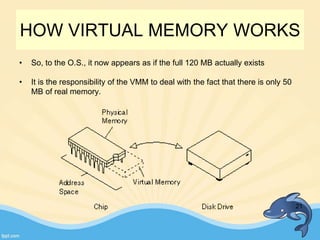
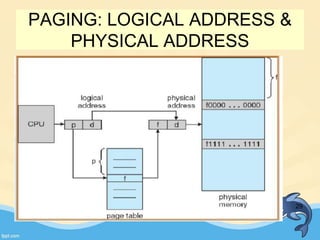
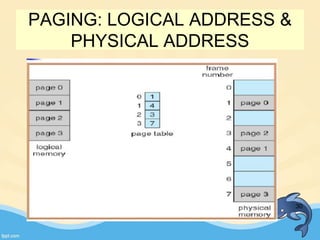
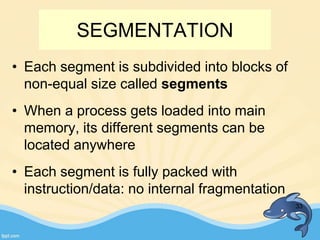
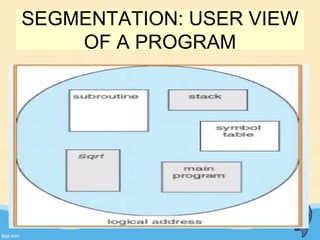
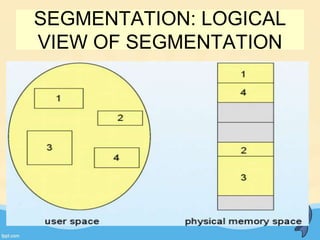
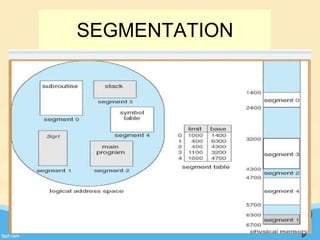
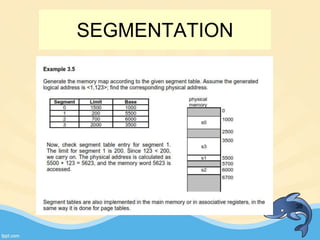
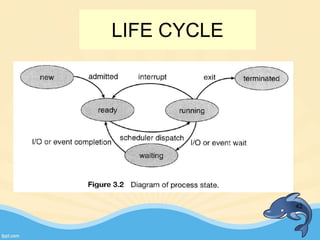
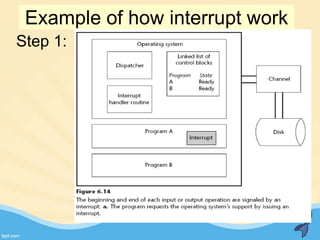
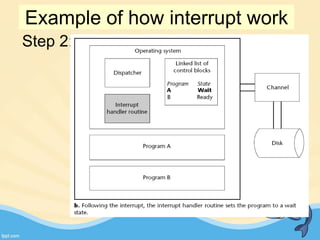
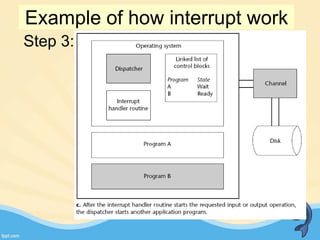
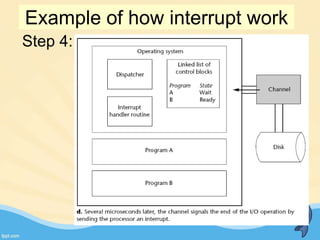
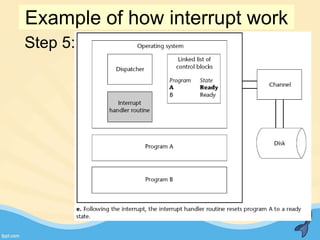
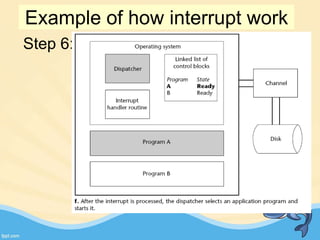
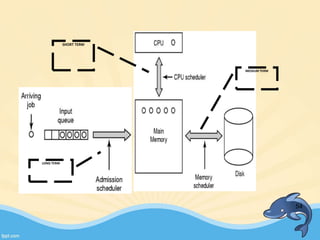
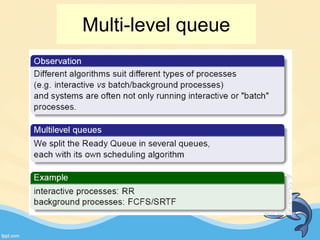
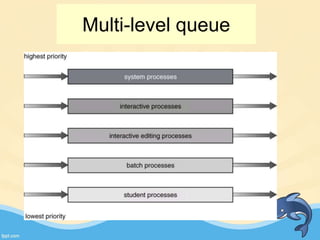
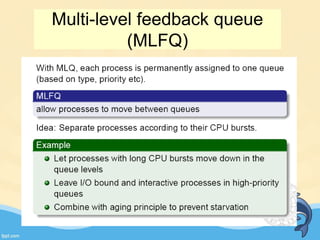
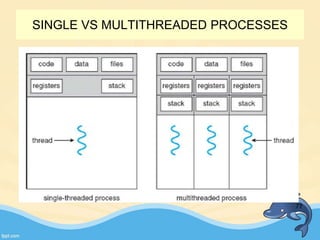
This document discusses memory management and paging in operating systems. It explains that memory management allocates space for application routines and prevents interference between programs. The memory hierarchy includes main memory, cache memory, and secondary storage. Paging is a memory management technique that divides processes and main memory into equal pages. It allows processes to be non-contiguous in memory. The operating system uses page tables to map logical addresses to physical addresses stored across different pages and frames. Paging reduces external fragmentation but can cause internal fragmentation.