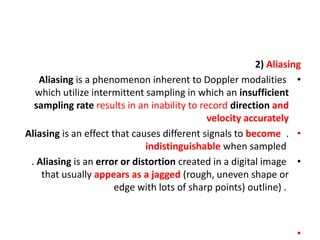
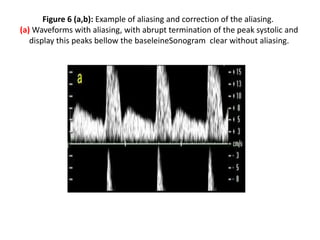
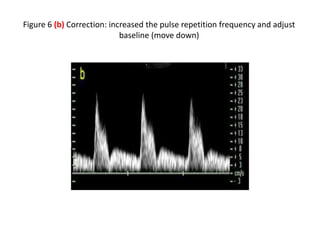
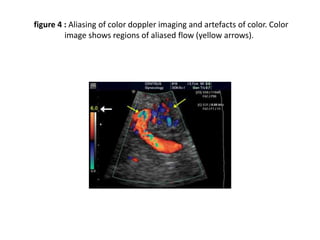
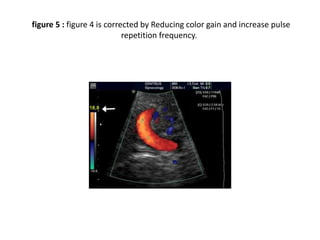
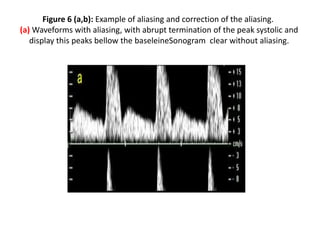
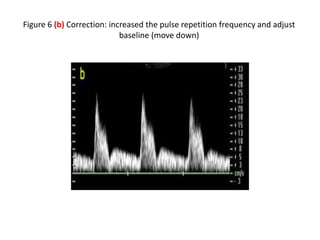
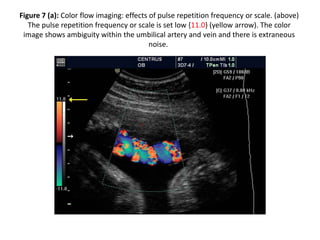
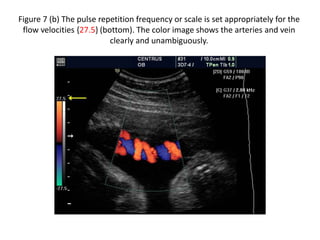
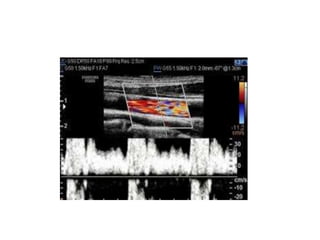
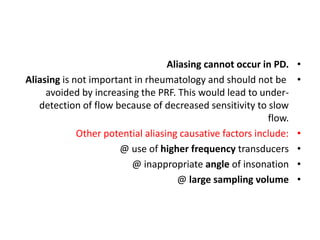
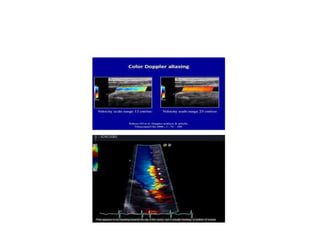
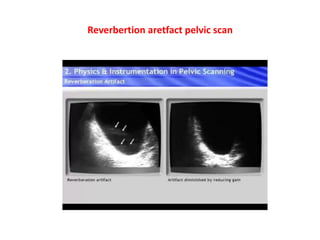
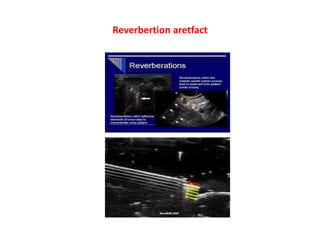
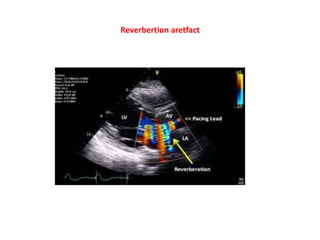
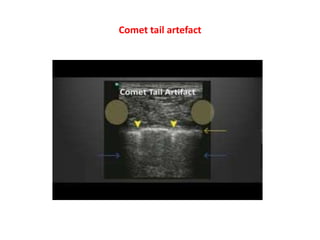
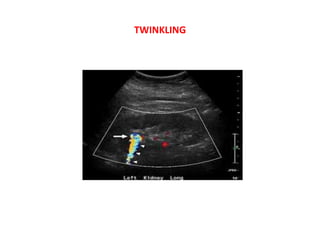
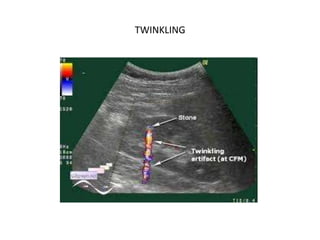
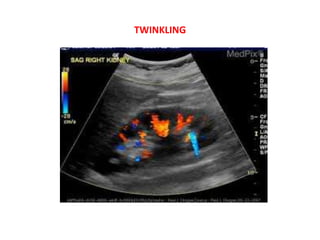
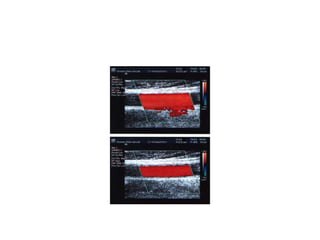
1. Aliasing occurs when the Doppler shift is higher than half the pulse repetition frequency, causing signals to become indistinguishable and display with the wrong color or velocity. It can be corrected by increasing the pulse repetition frequency or adjusting the baseline.
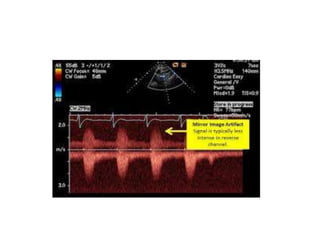
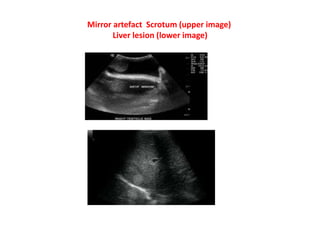
2. Mirror artifacts occur when the ultrasound beam reflects off a structure like bone or diaphragm before returning to the transducer, creating a duplicate image. Changing the angle of insonation can help avoid it.
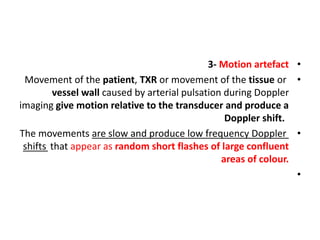
3. Motion artifacts appear as random color flashes caused by movement of the patient, transducer, or tissue during imaging. They can be minimized by comfortable patient positioning and a stable scanning arm.