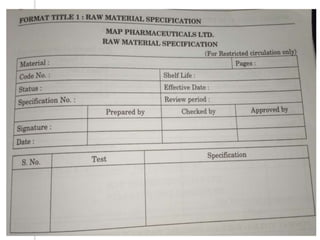
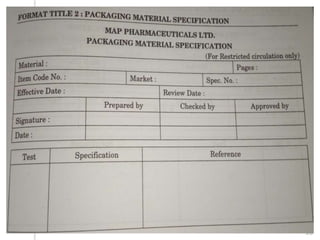
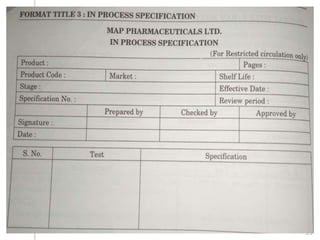
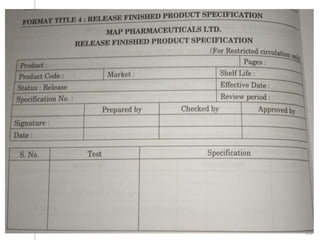
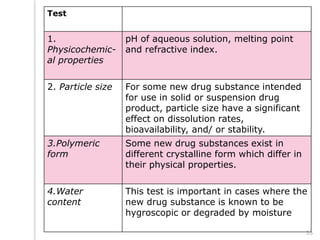
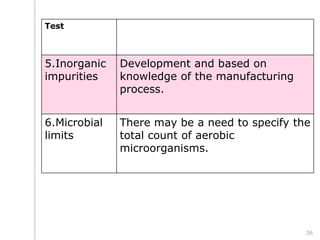
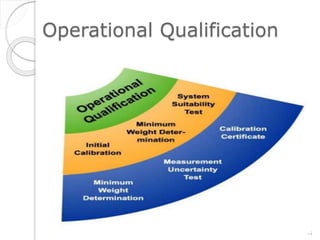
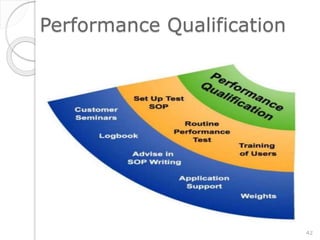
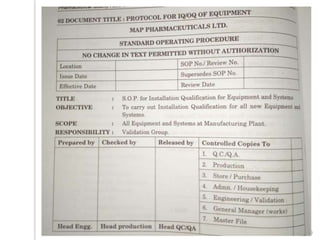
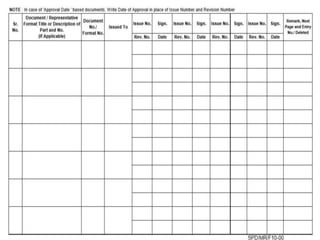
This document outlines the significance of documentation in the pharmaceutical industry, detailing its definition, importance, and the standards for creating specifications for various materials and products. It emphasizes the role of documentation in ensuring quality control, regulatory compliance, and traceability throughout the manufacturing and distribution processes. The document also lists various components necessary for effective documentation, including test procedures, protocols, and record-keeping practices.