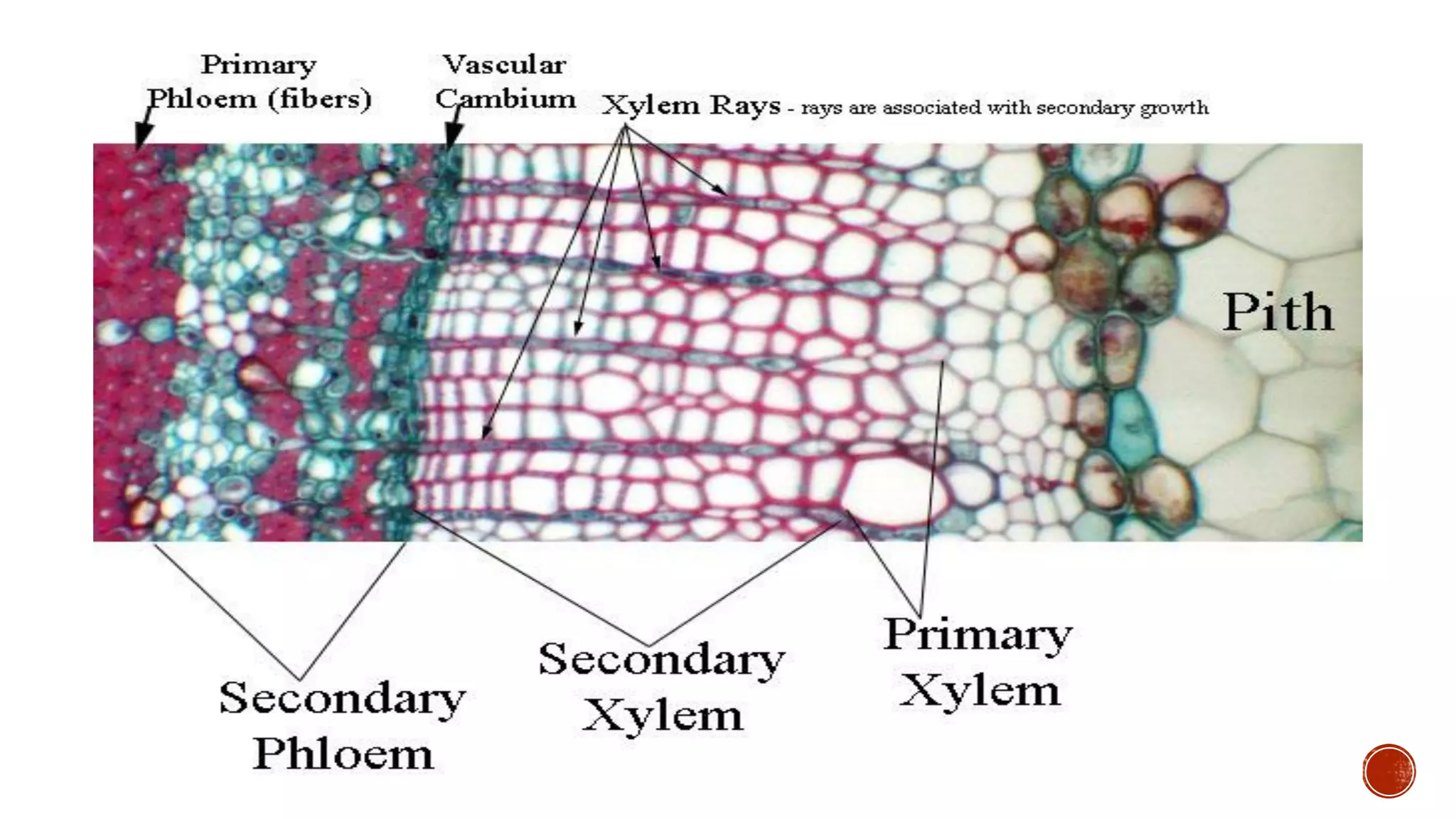
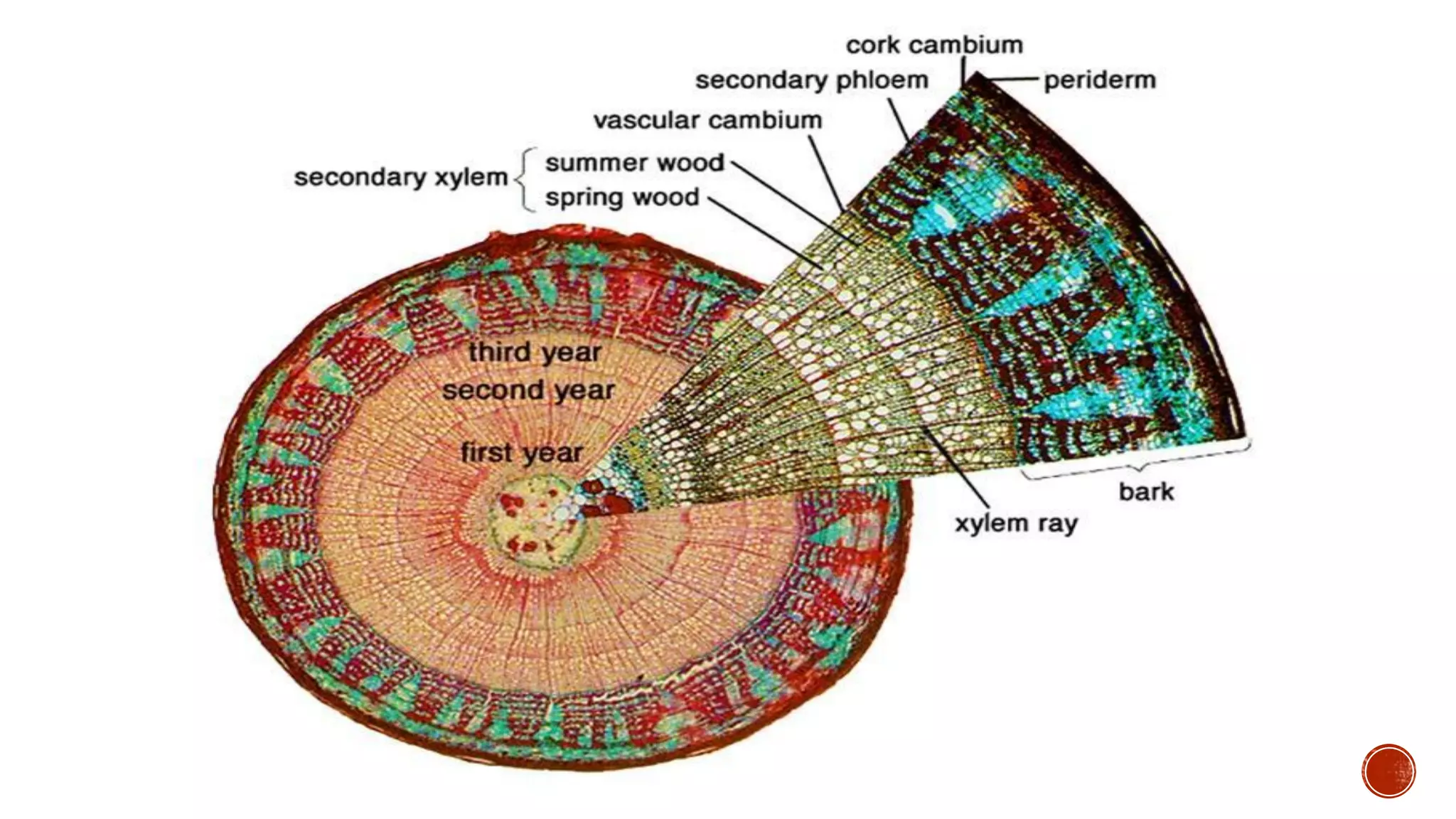
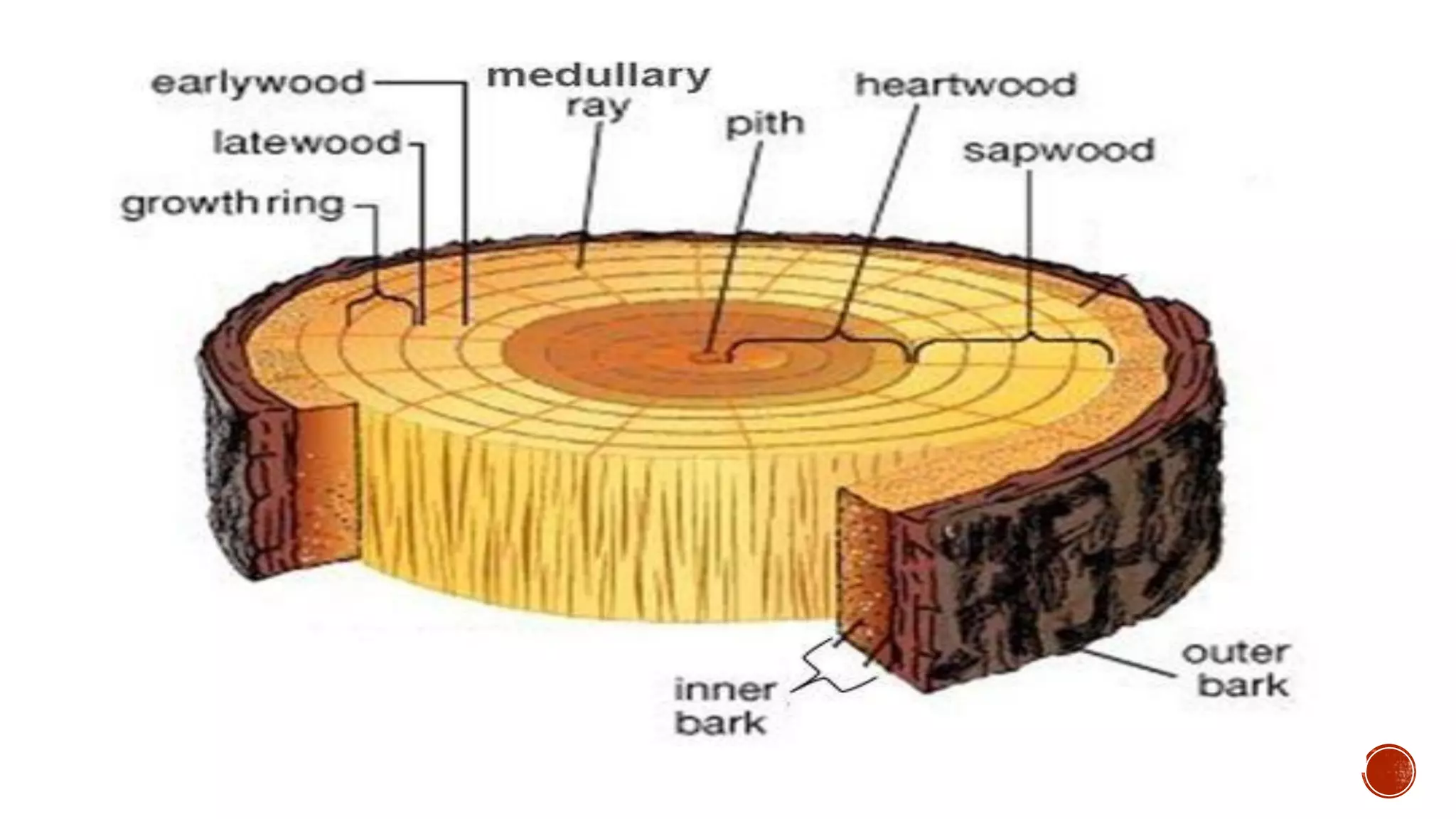
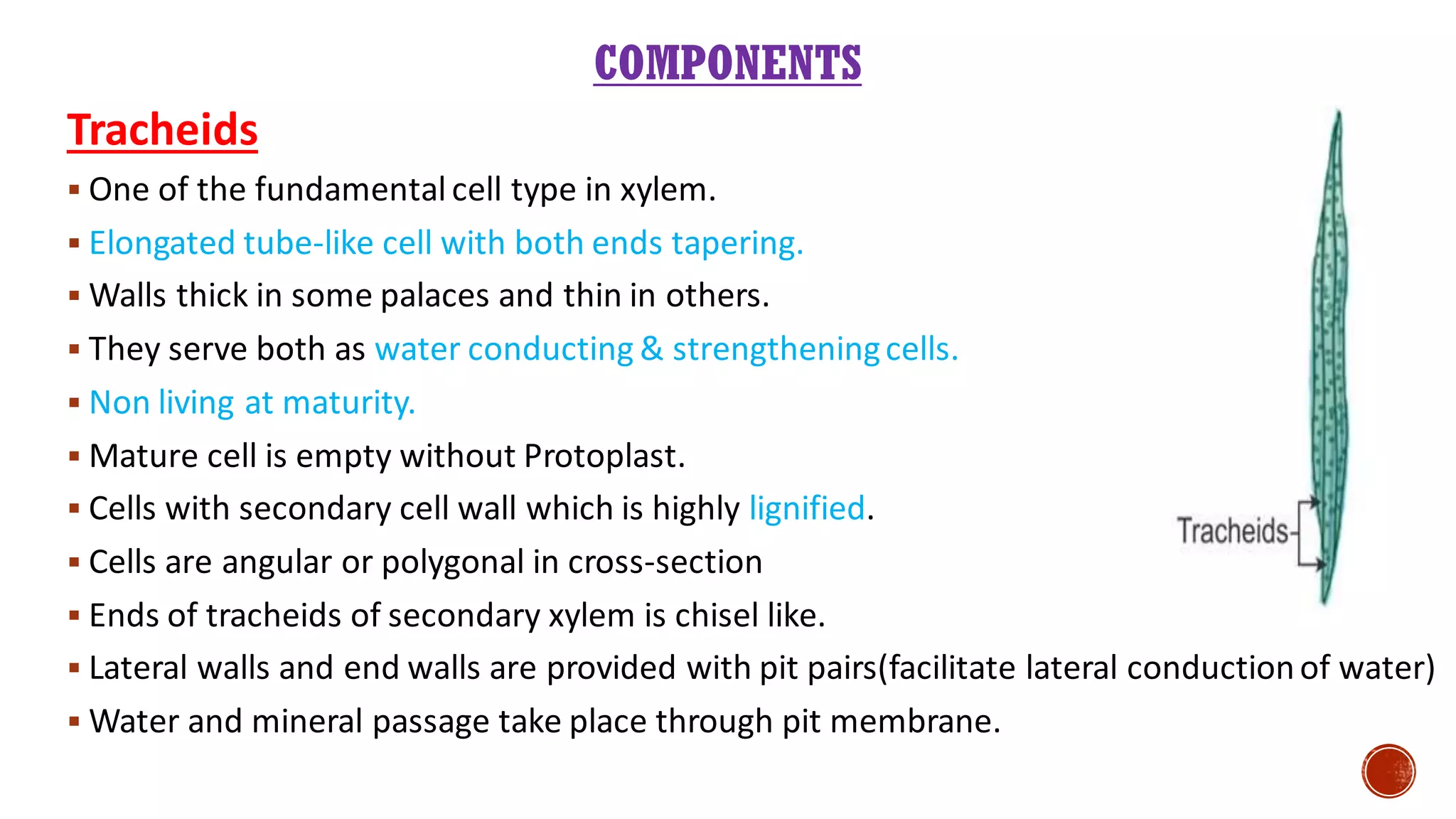
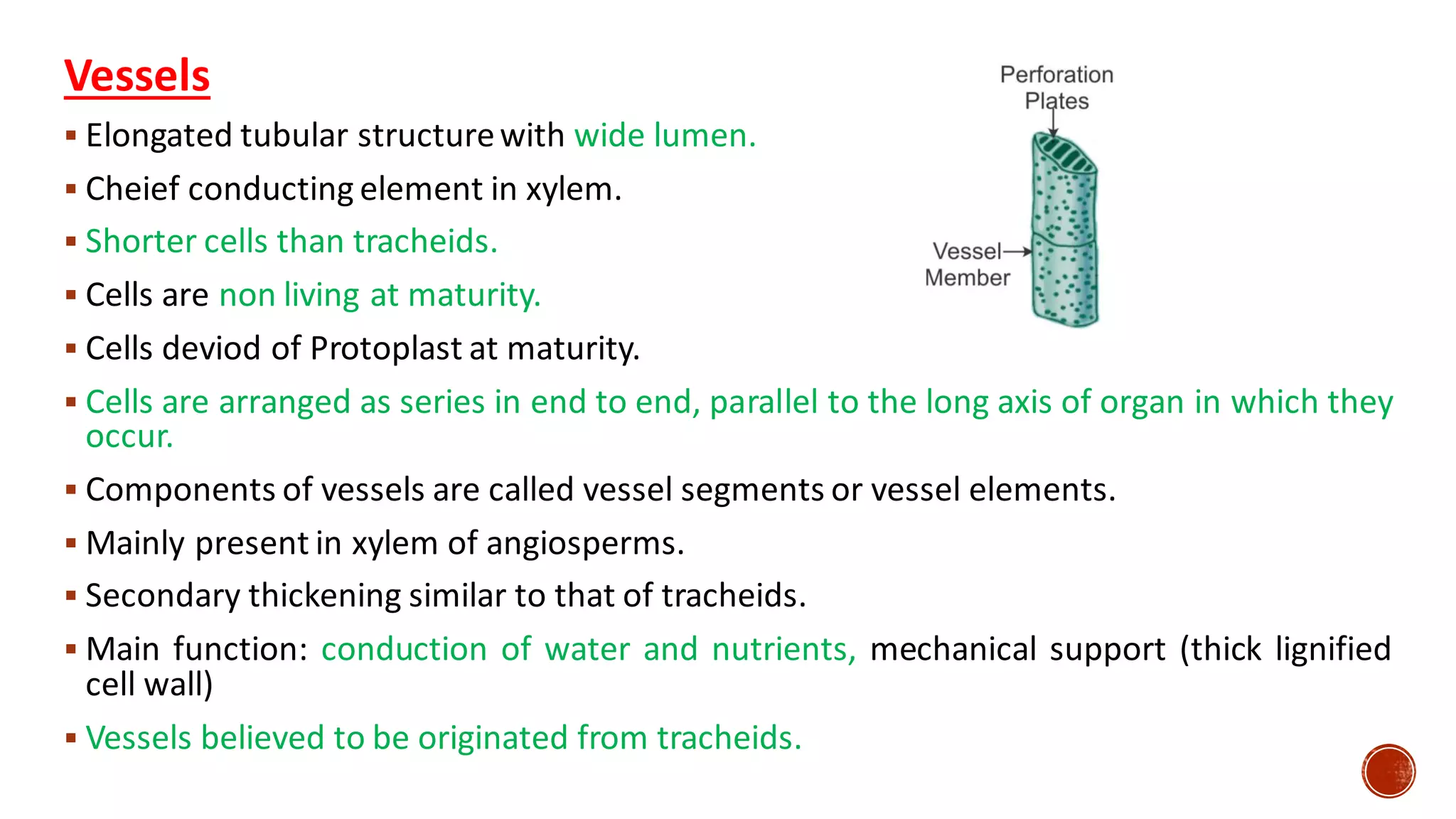
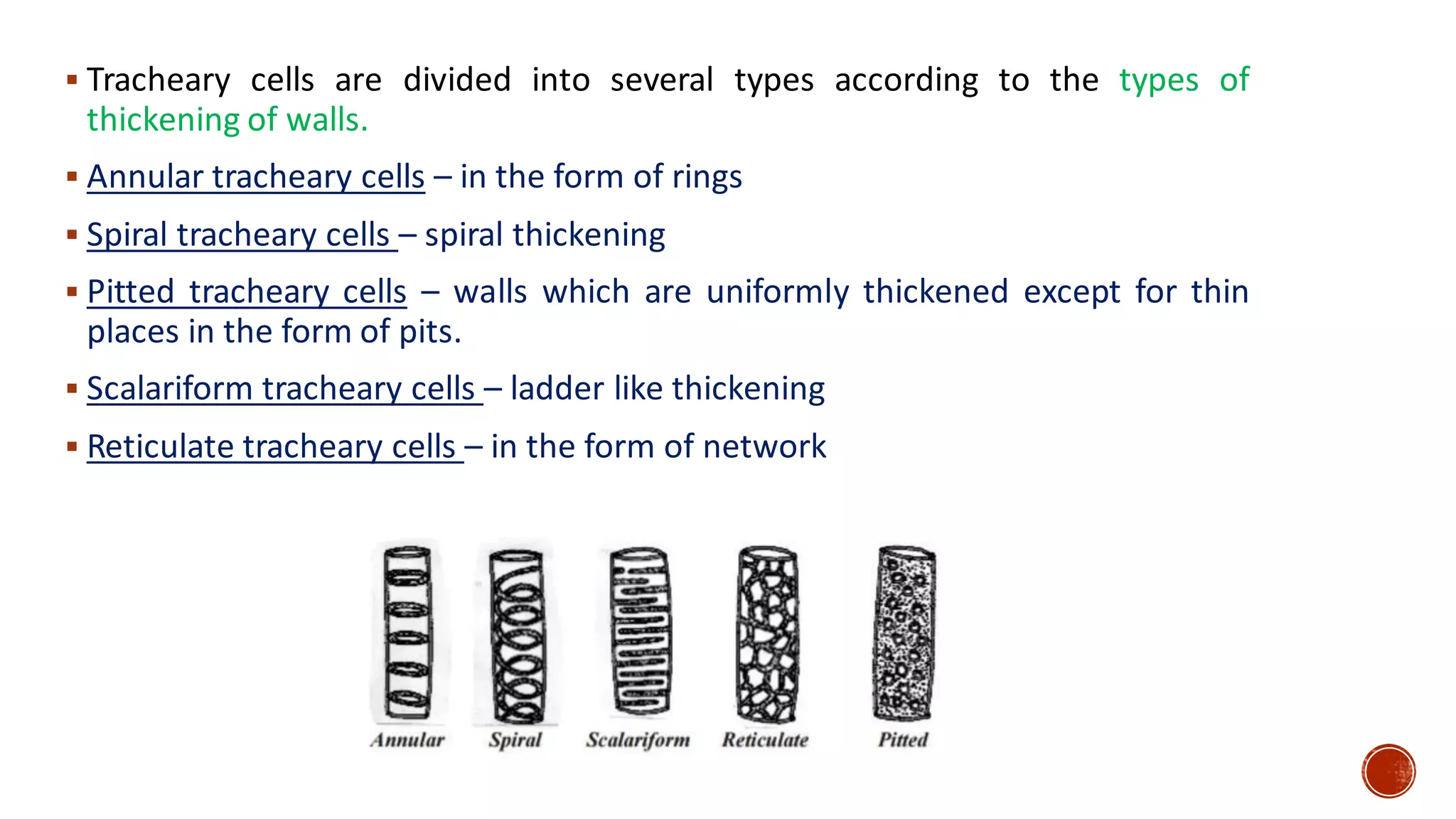
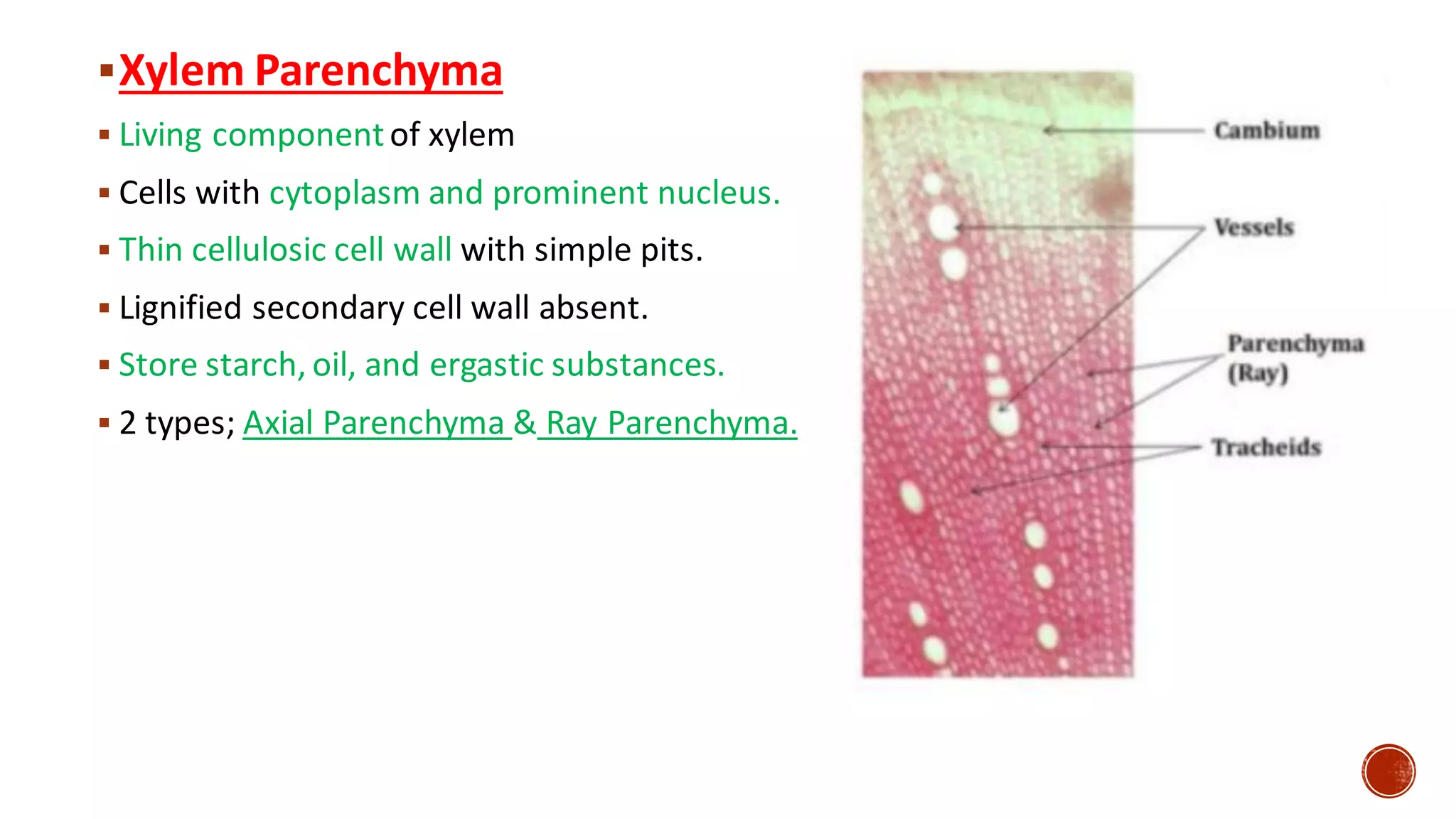
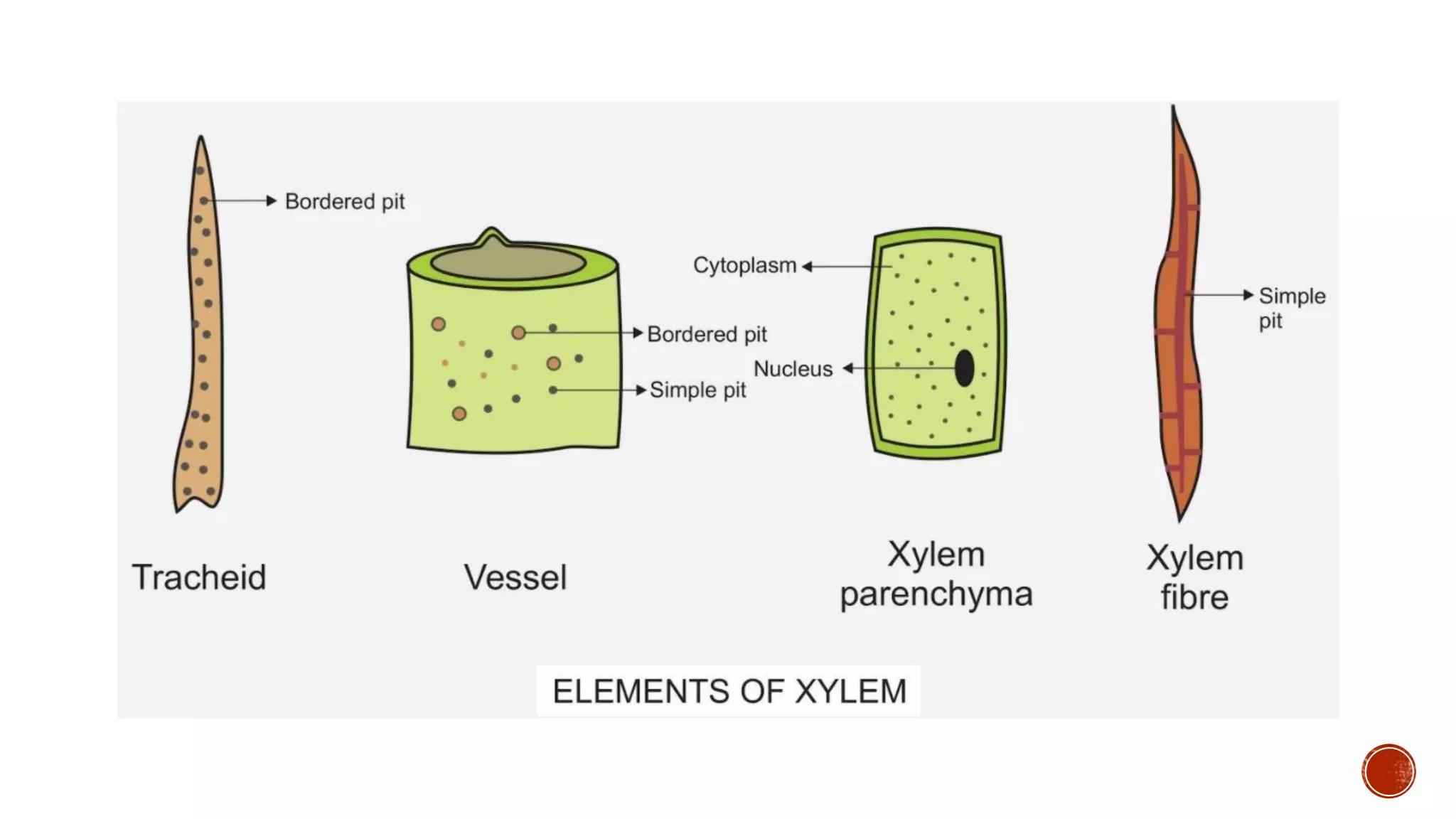
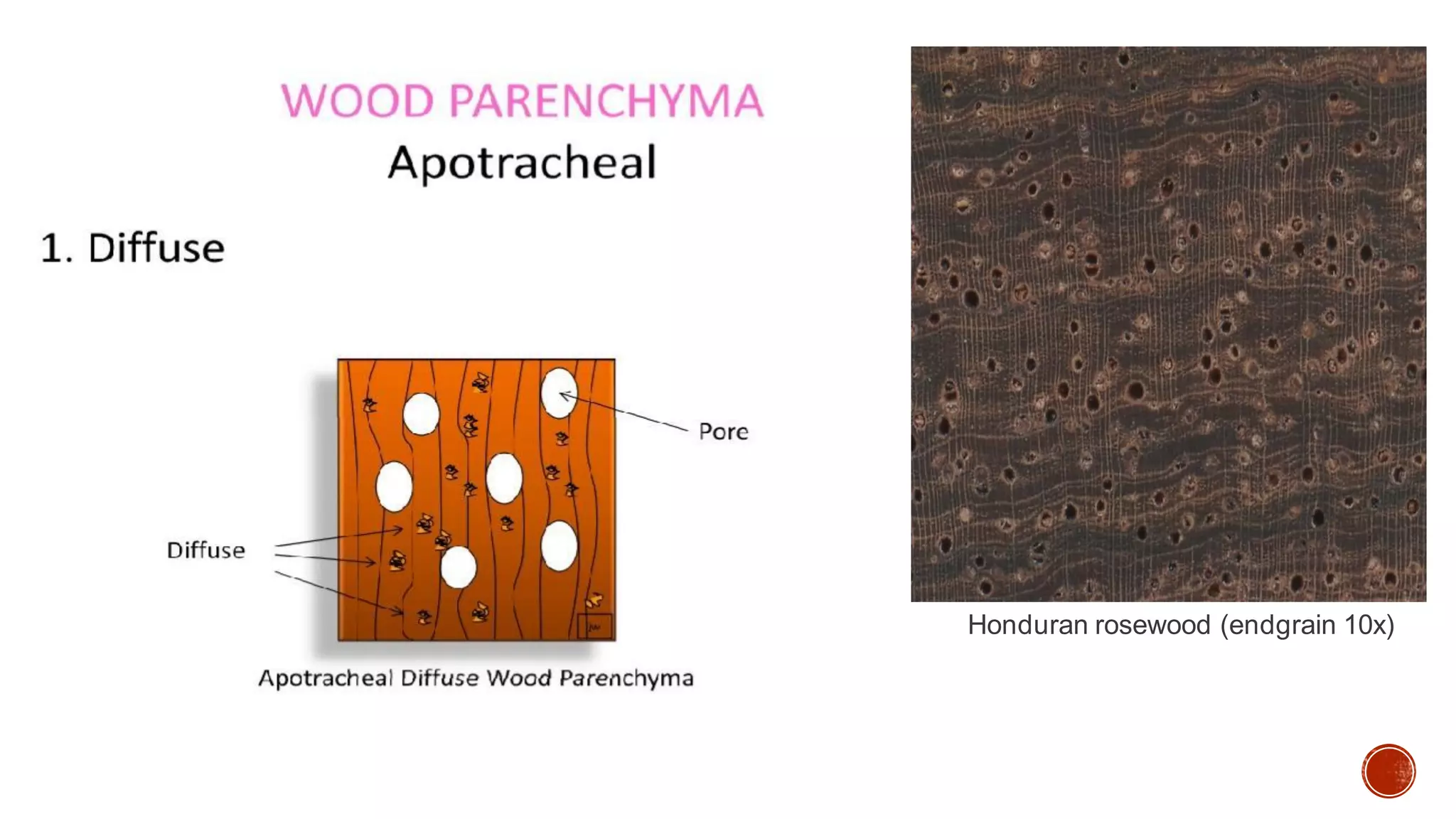
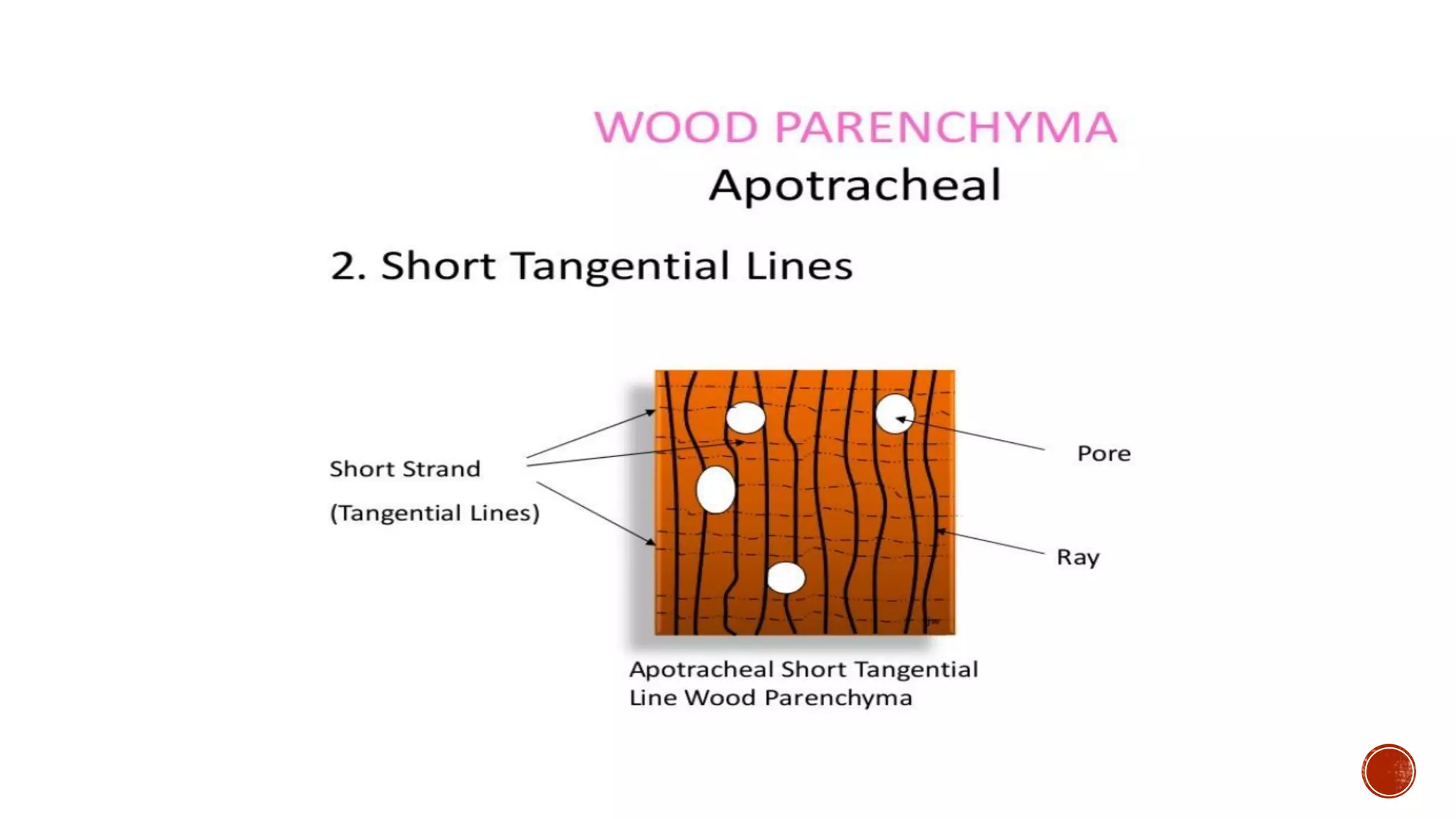
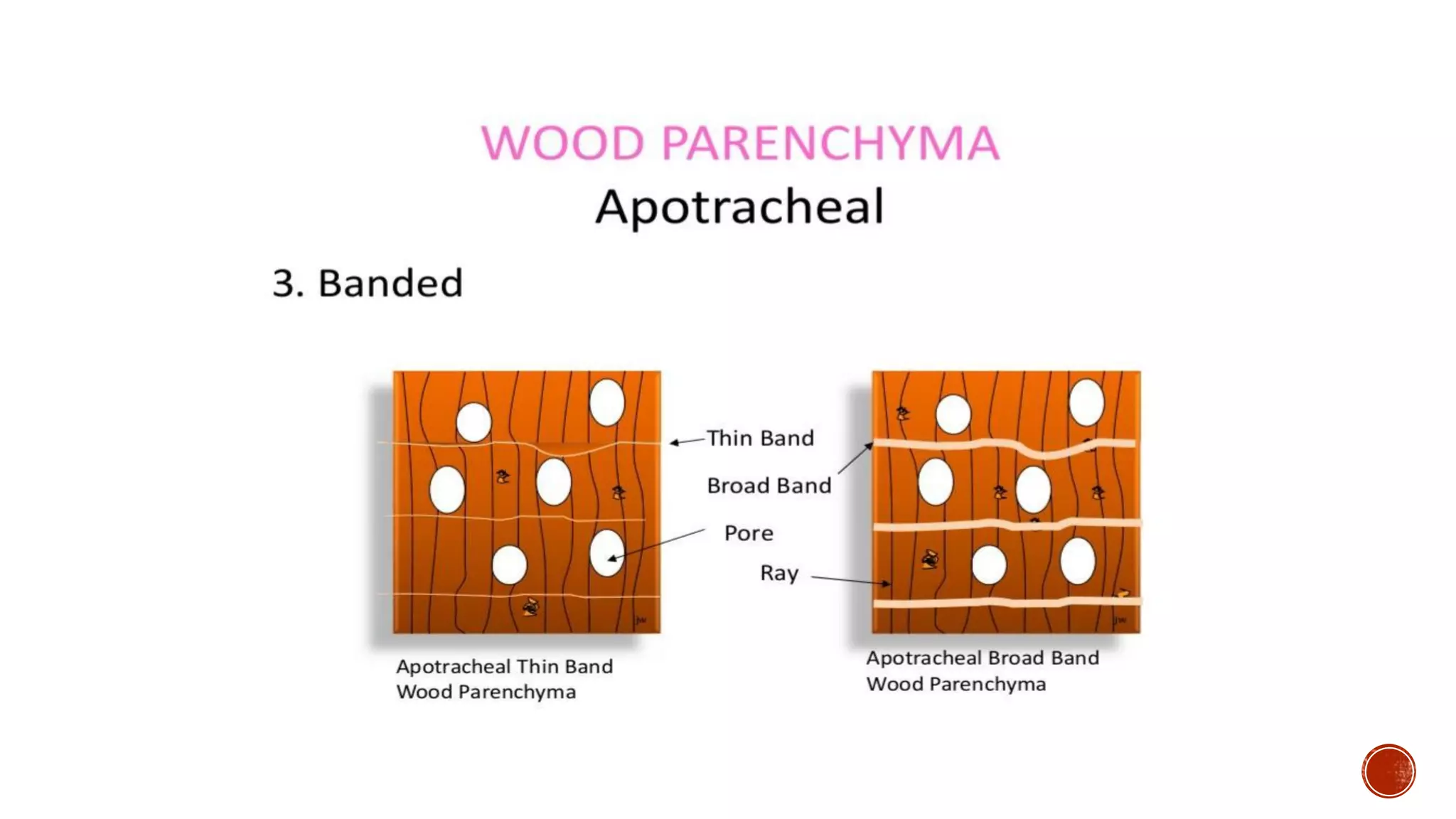
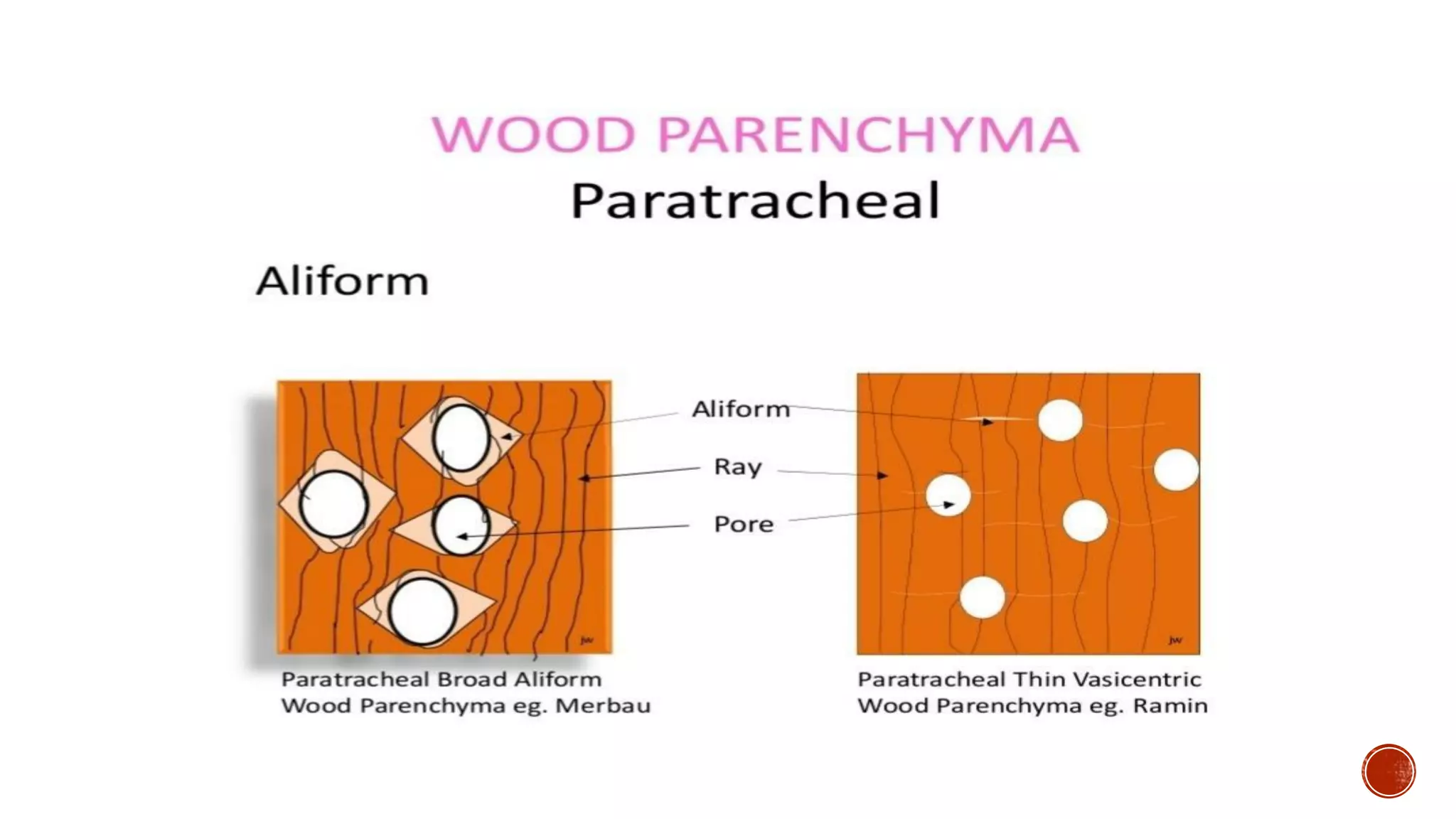
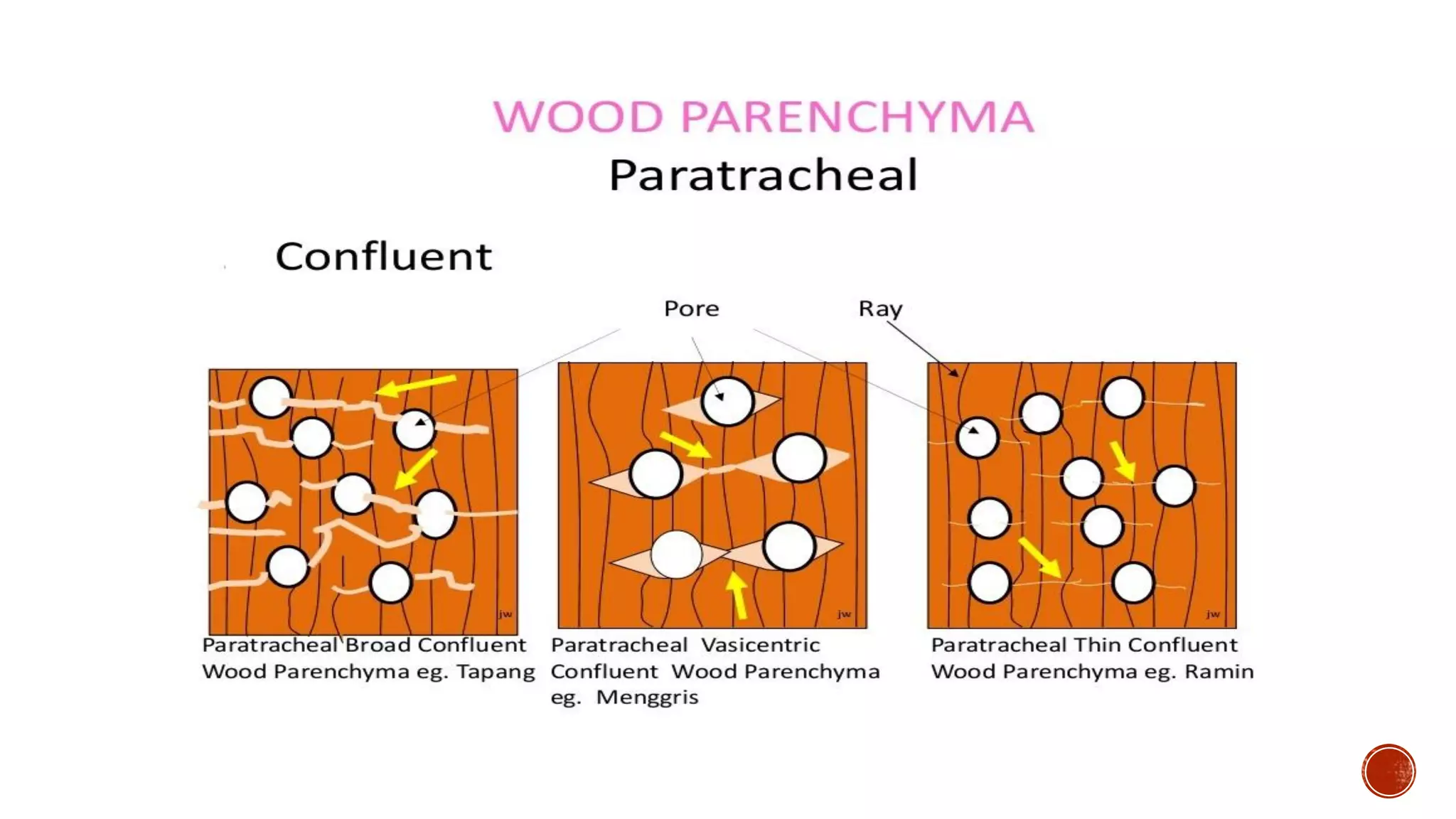
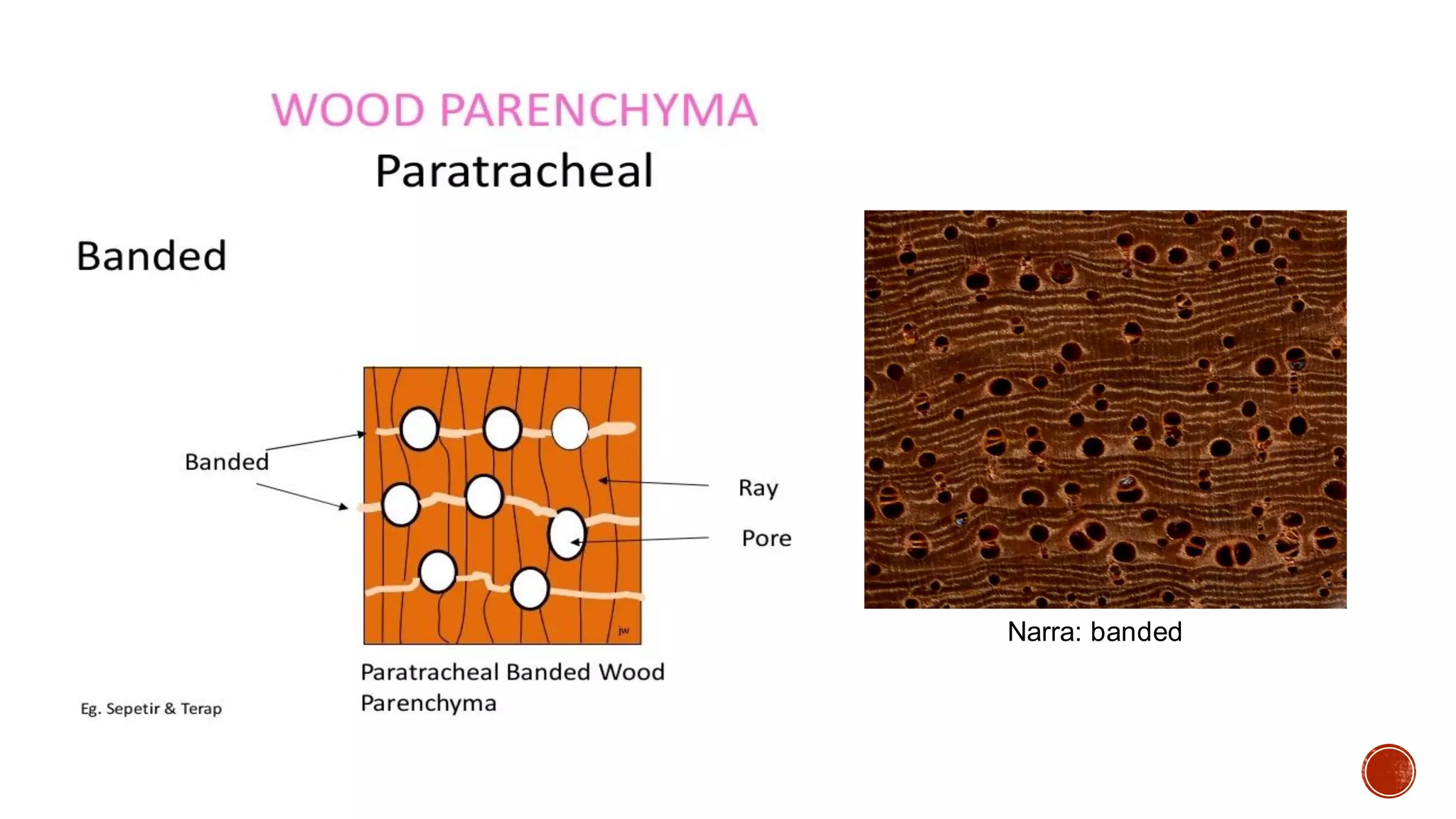
Xylem is one of the conductive tissues in plants. It is composed of various cell types that function to transport water and minerals throughout the plant. Xylem tissue is divided into primary and secondary xylem. Primary xylem develops during primary growth and consists of protoxylem and metaxylem. Secondary xylem forms during secondary growth and provides structural support through thickened cell walls. It is composed of tracheids, vessels, fibres and parenchyma cells. Vascular rays extend radially to facilitate transport between the xylem and other tissues.