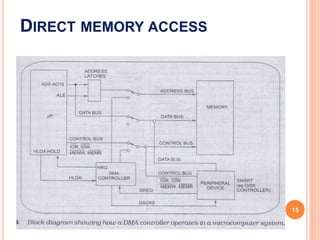
Direct Memory Access (DMA) is a process that allows external devices to transfer data directly to and from memory, bypassing the CPU to increase efficiency. The DMA controller manages this process by temporarily taking control of the system buses, which significantly reduces the time required for data transfers compared to traditional CPU-mediated methods. This mechanism is especially useful for high-speed data transfers between mass storage devices and memory, enabling faster operations in computer systems.