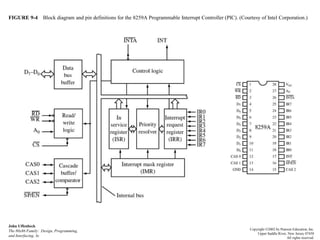
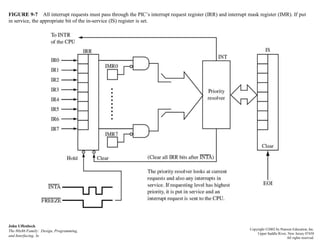
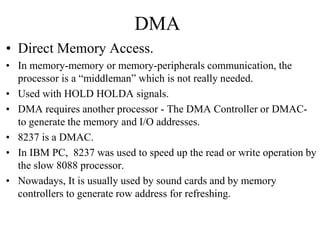
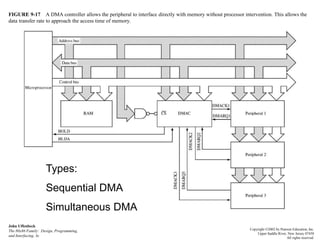
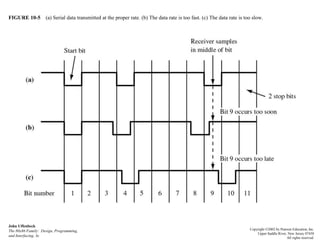
An interrupt is an event that informs the CPU it needs to service an external request. Interrupts can come from internal faults, software, or external hardware sources. When an interrupt occurs, the CPU saves its state and jumps to an interrupt service routine (ISR) to handle the interrupt before returning to its previous task. The 8259 programmable interrupt controller (PIC) is used to manage interrupt requests from peripherals by masking interrupts, assigning priorities, and directing interrupts to the CPU. Direct memory access (DMA) allows peripherals to access memory directly without CPU intervention, improving data transfer speeds. Serial communication converts parallel data to serial transmission using universal asynchronous/synchronous receiver/transmitters (UART/US