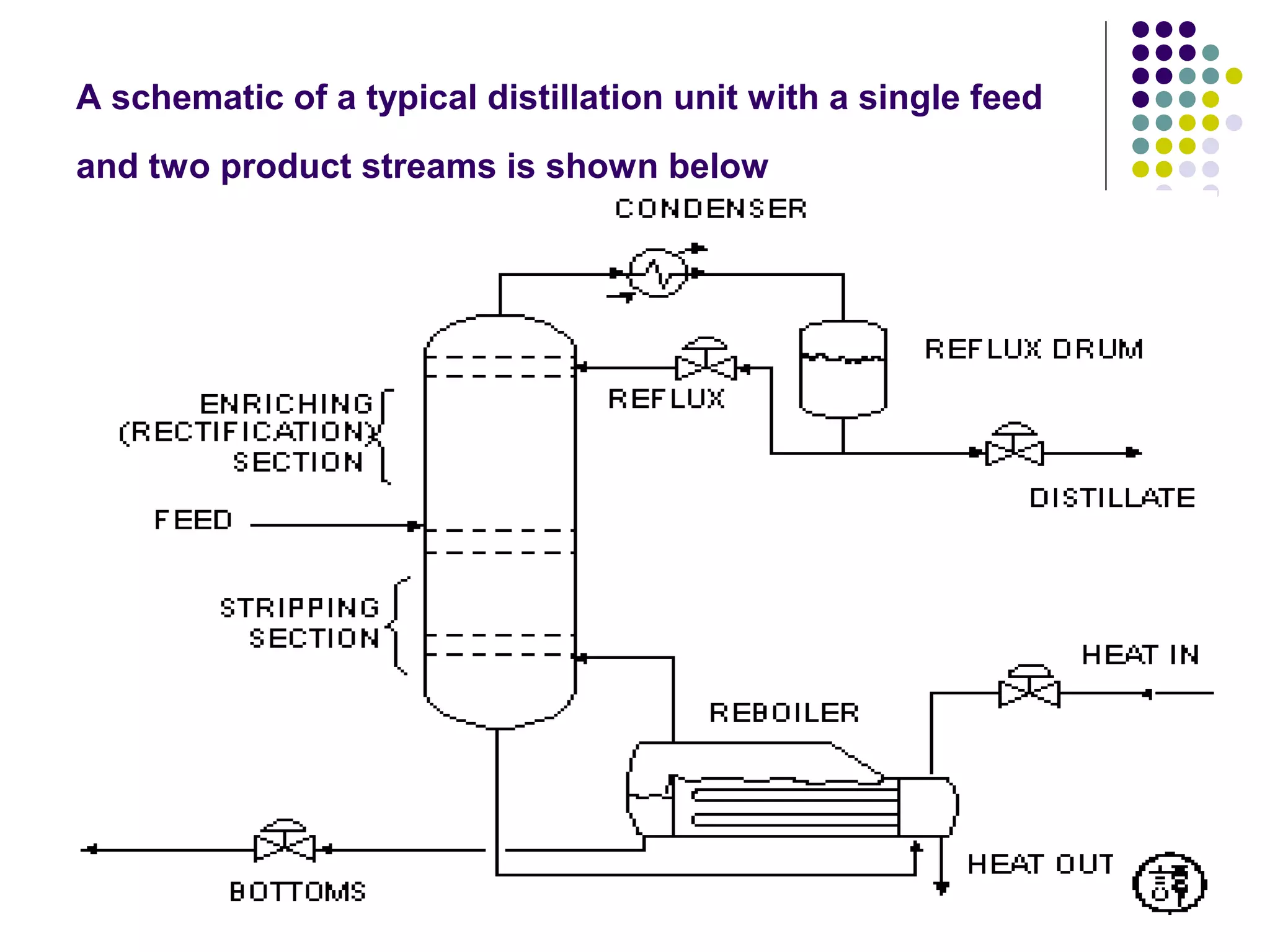
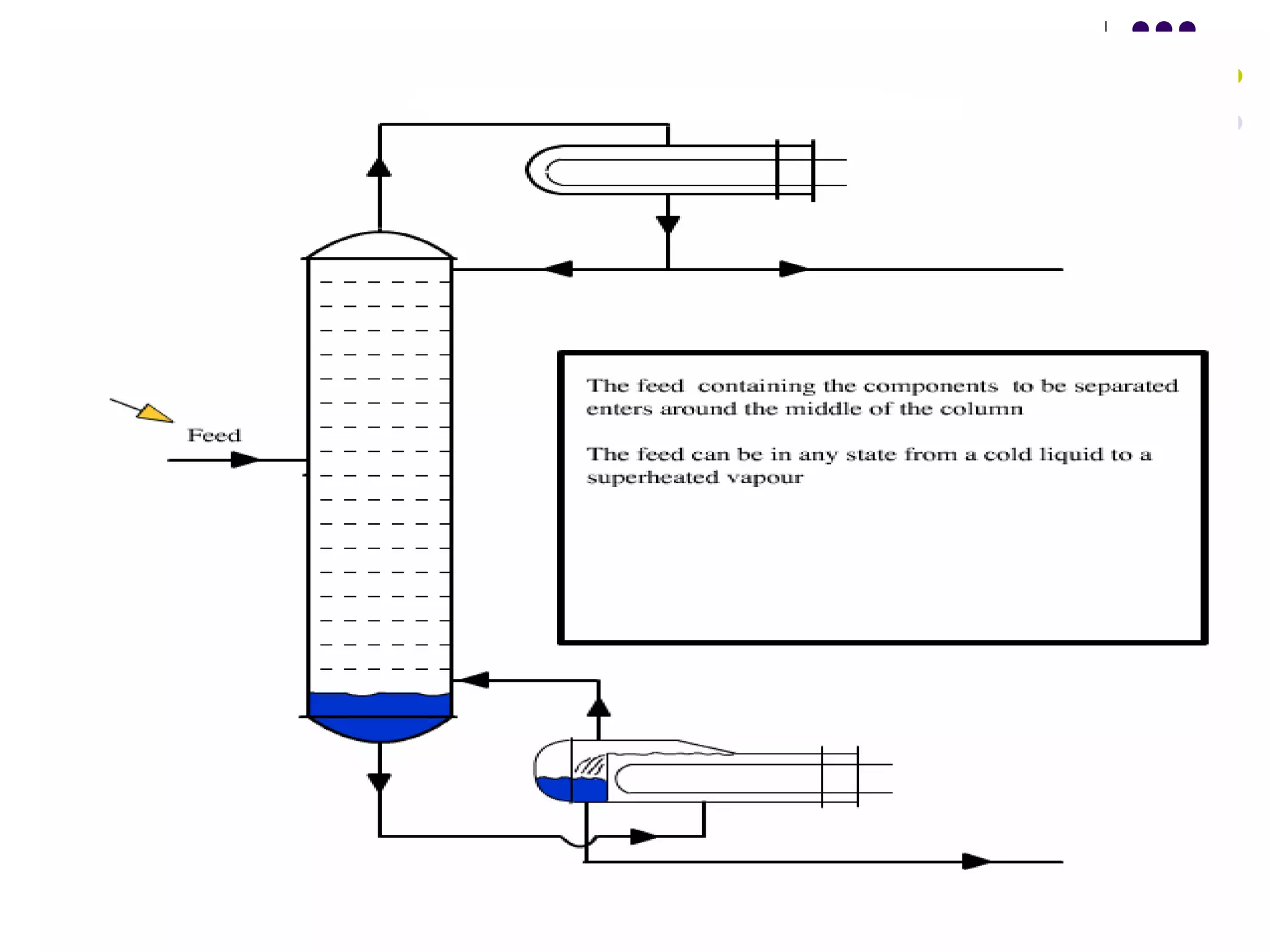
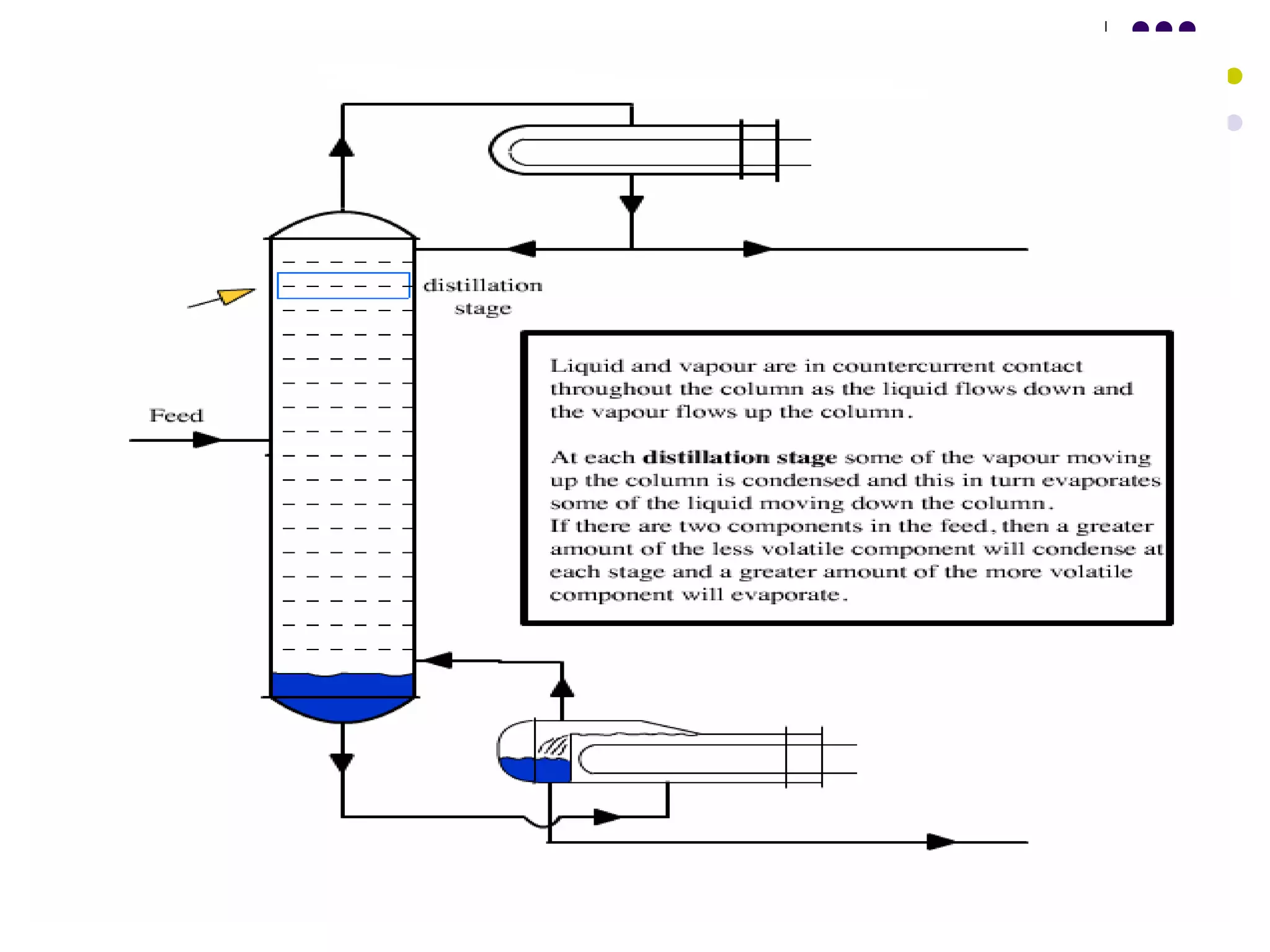
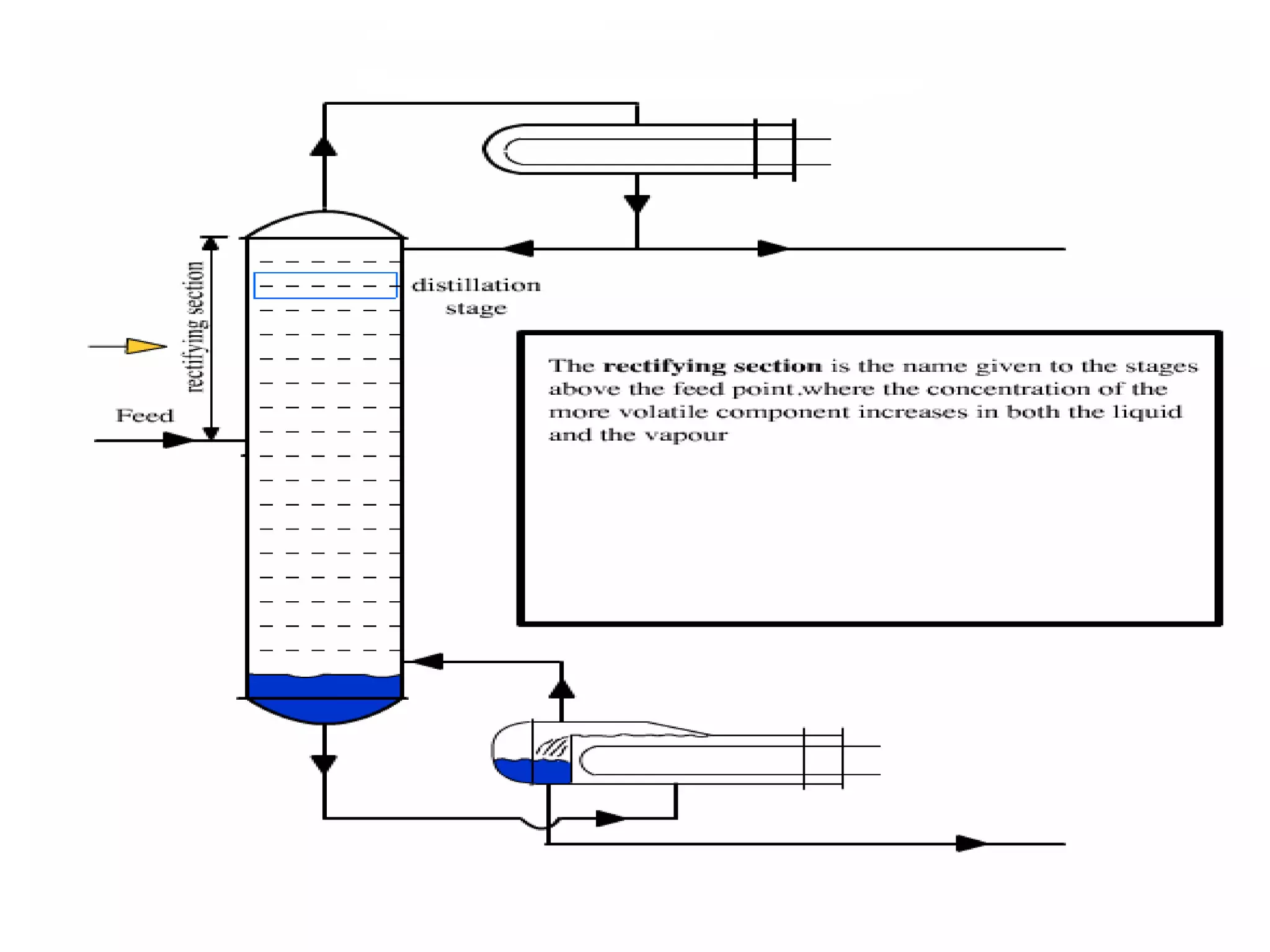
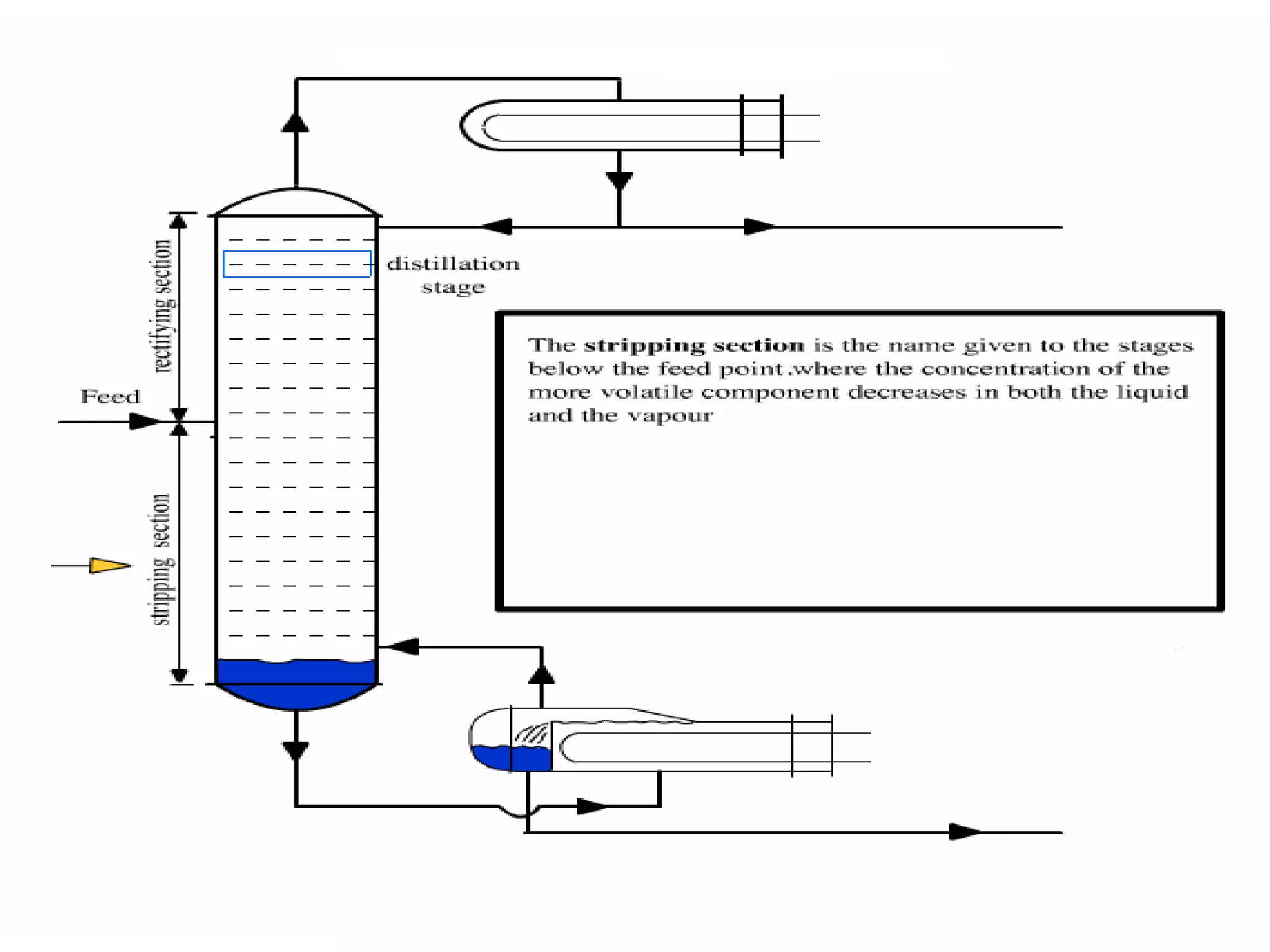
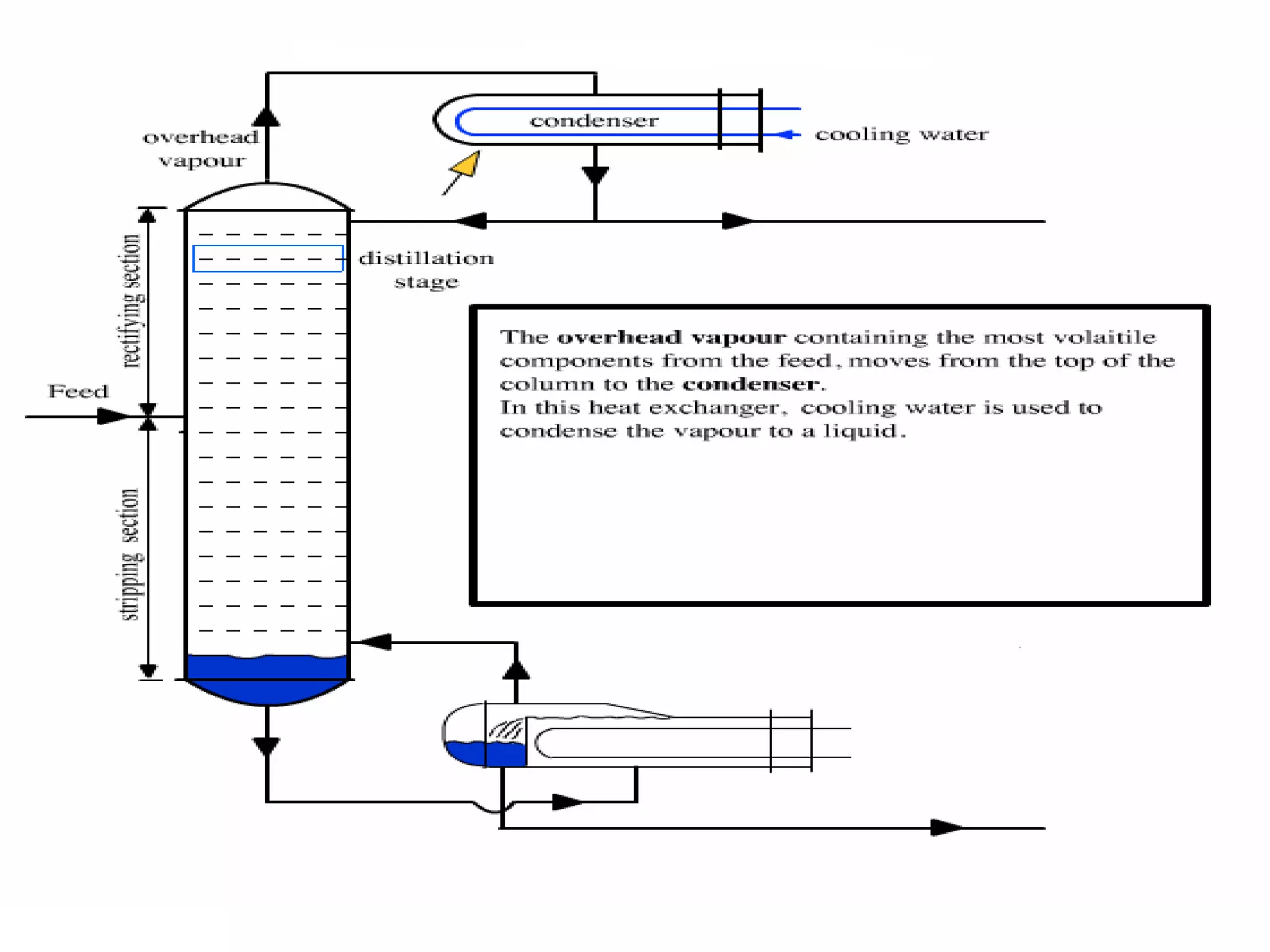
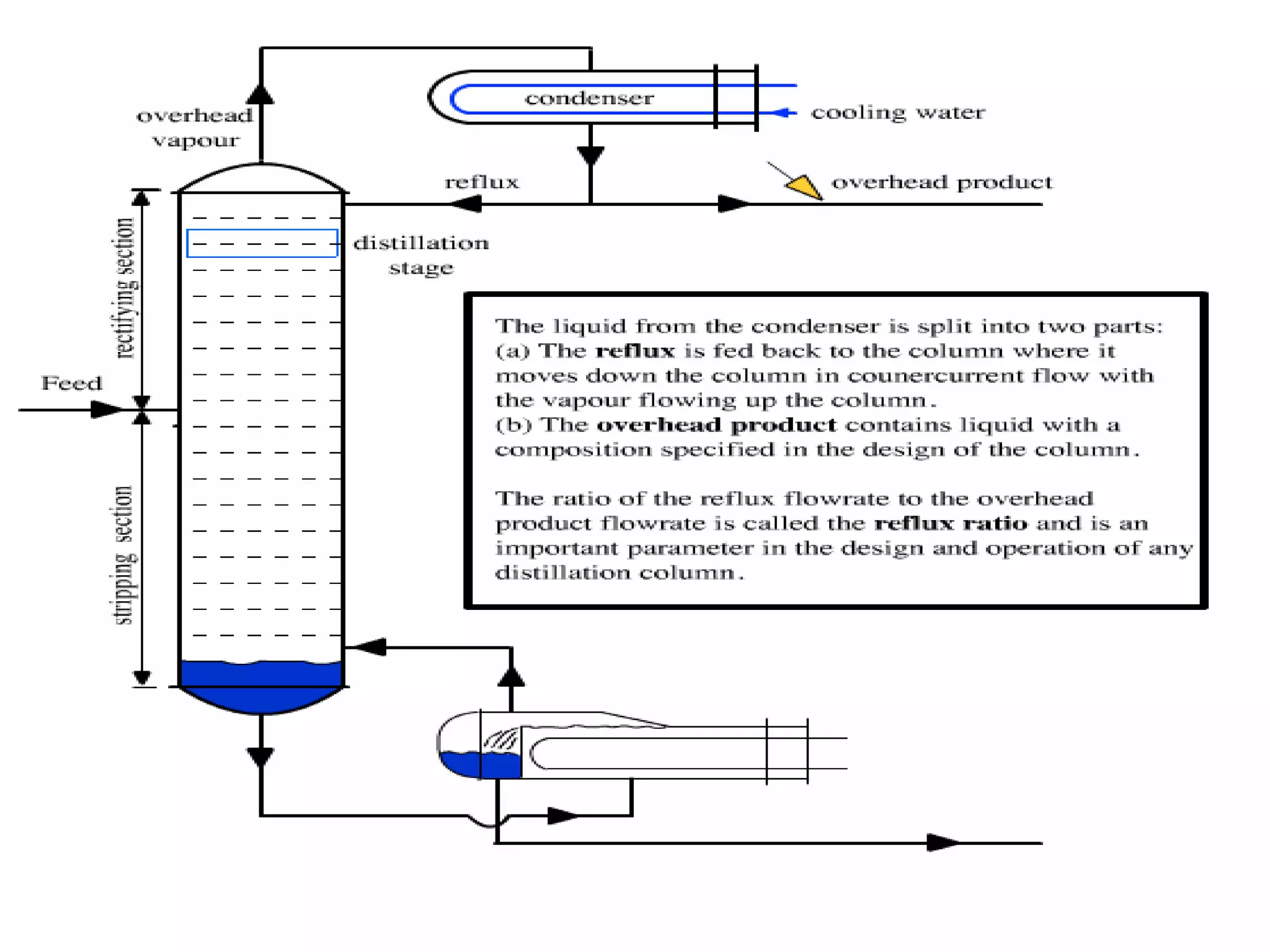
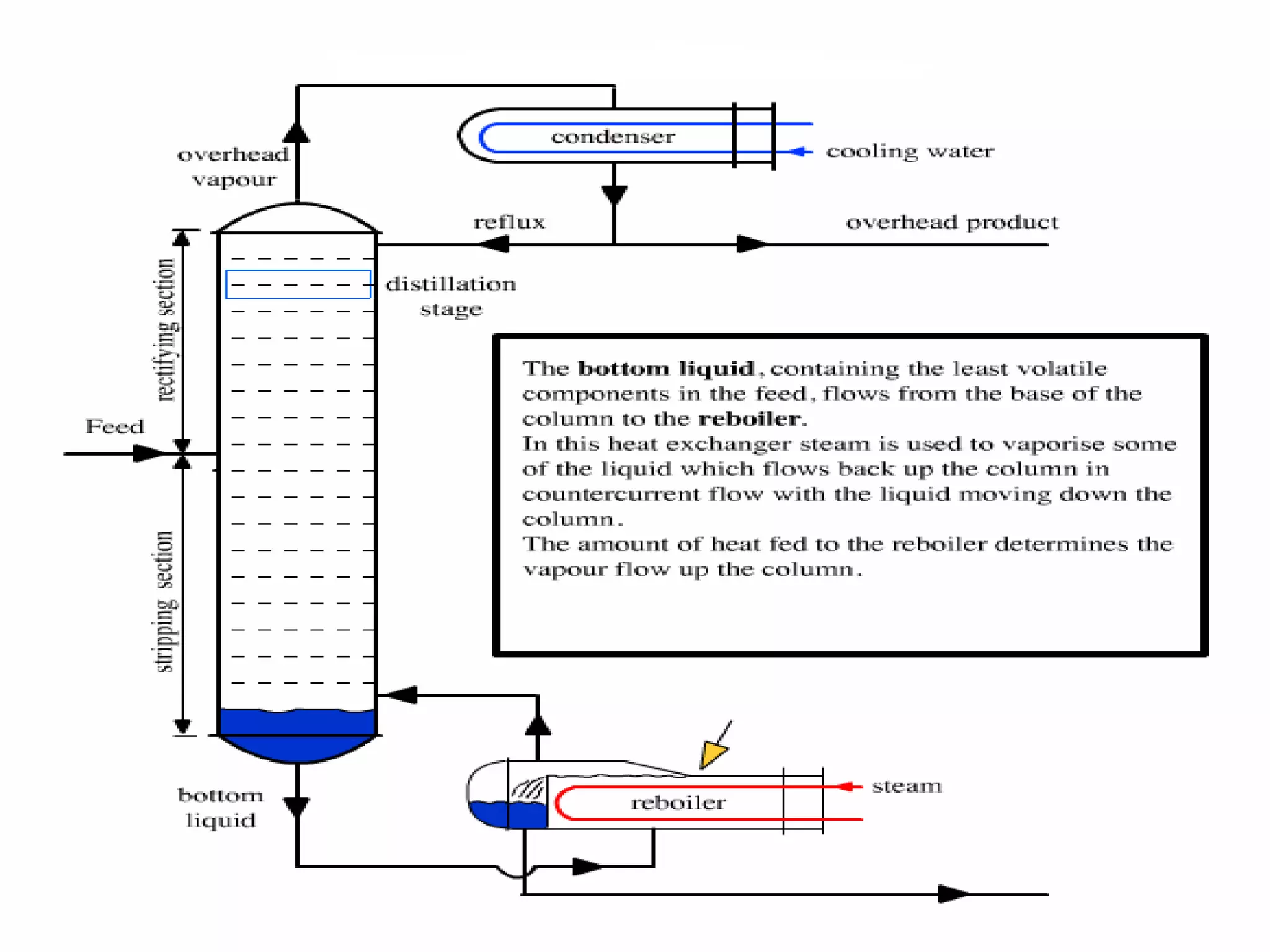
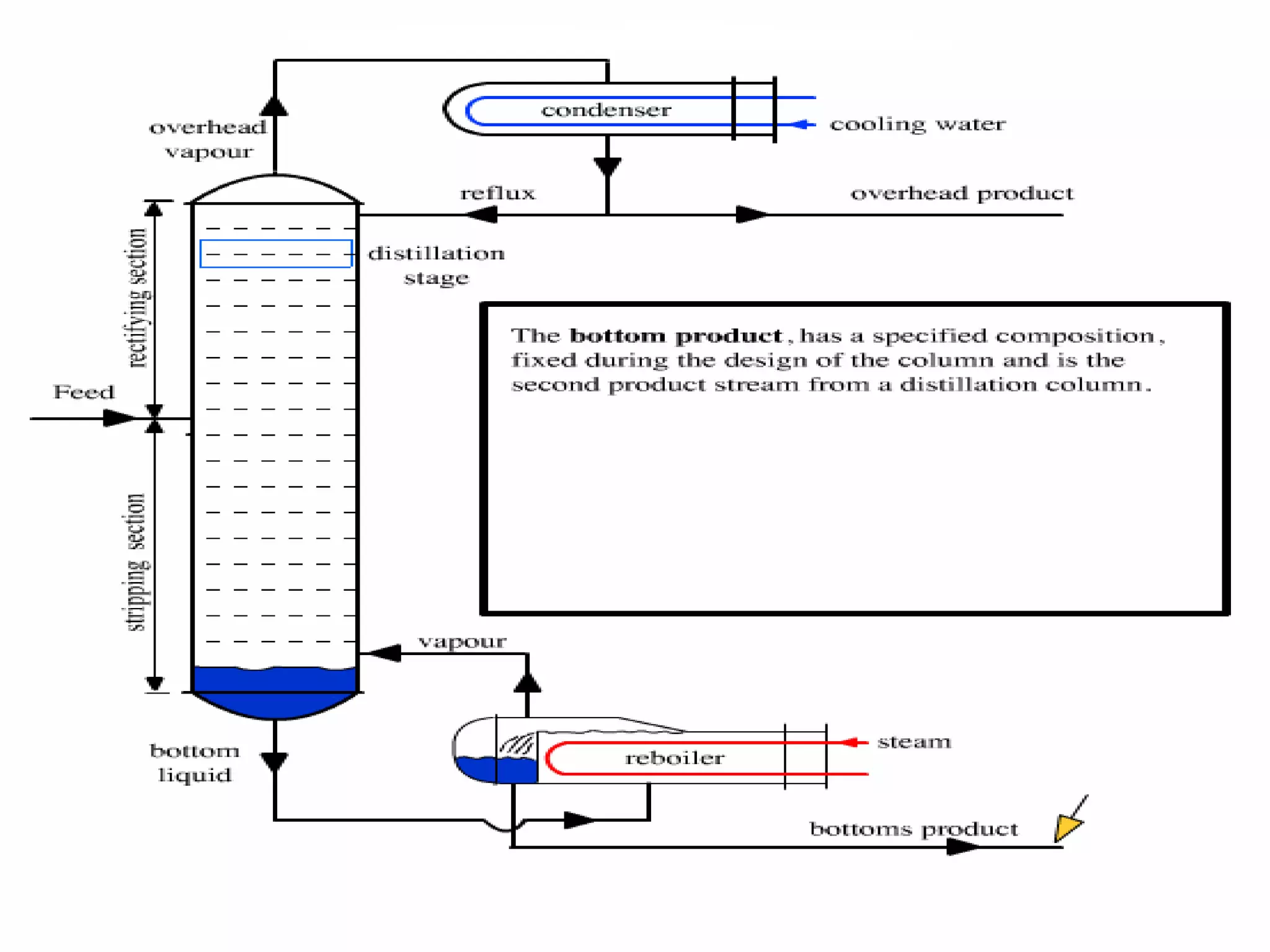
Distillation is a process that separates liquid mixtures into individual fractions based on differences in boiling points. It works by heating the mixture to vaporize components with lower boiling points, which are separated from higher-boiling components as vapors rise and condense. Distillation columns continuously process feed streams and are the most common type, while batch columns introduce feed in discrete batches. Distillation units have components like trays or packings for enhanced separation, a reboiler for vaporization, a condenser to condense vapors, and a reflux drum to collect condensed liquids and return some to the column. Separation depends on differences in vapor pressure and relative volatility between mixture components.