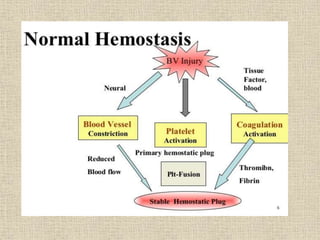
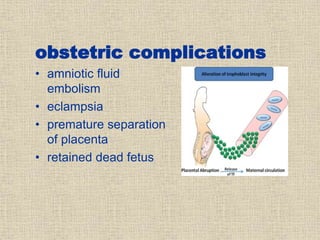
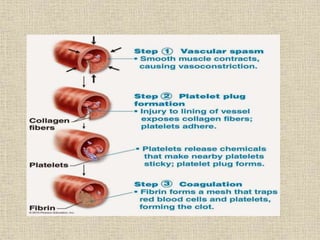
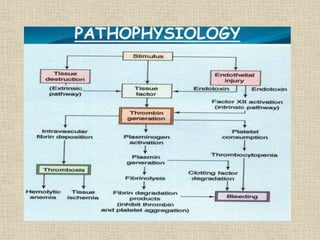
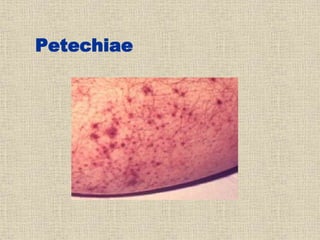
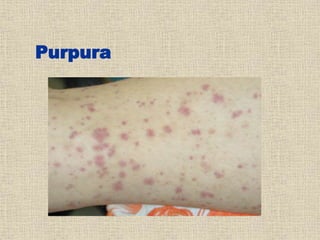
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a syndrome characterized by the activation of coagulation pathways leading to the formation of fibrin clots in small blood vessels, resulting in bleeding due to reduced coagulation factors and platelets. The document discusses various causes of DIC, including obstetric complications, malignancies, infections, and miscellaneous factors, along with methods for diagnosis and management. Management strategies include blood component therapy and anticoagulant therapy, with emphasis on nursing assessments and interventions.