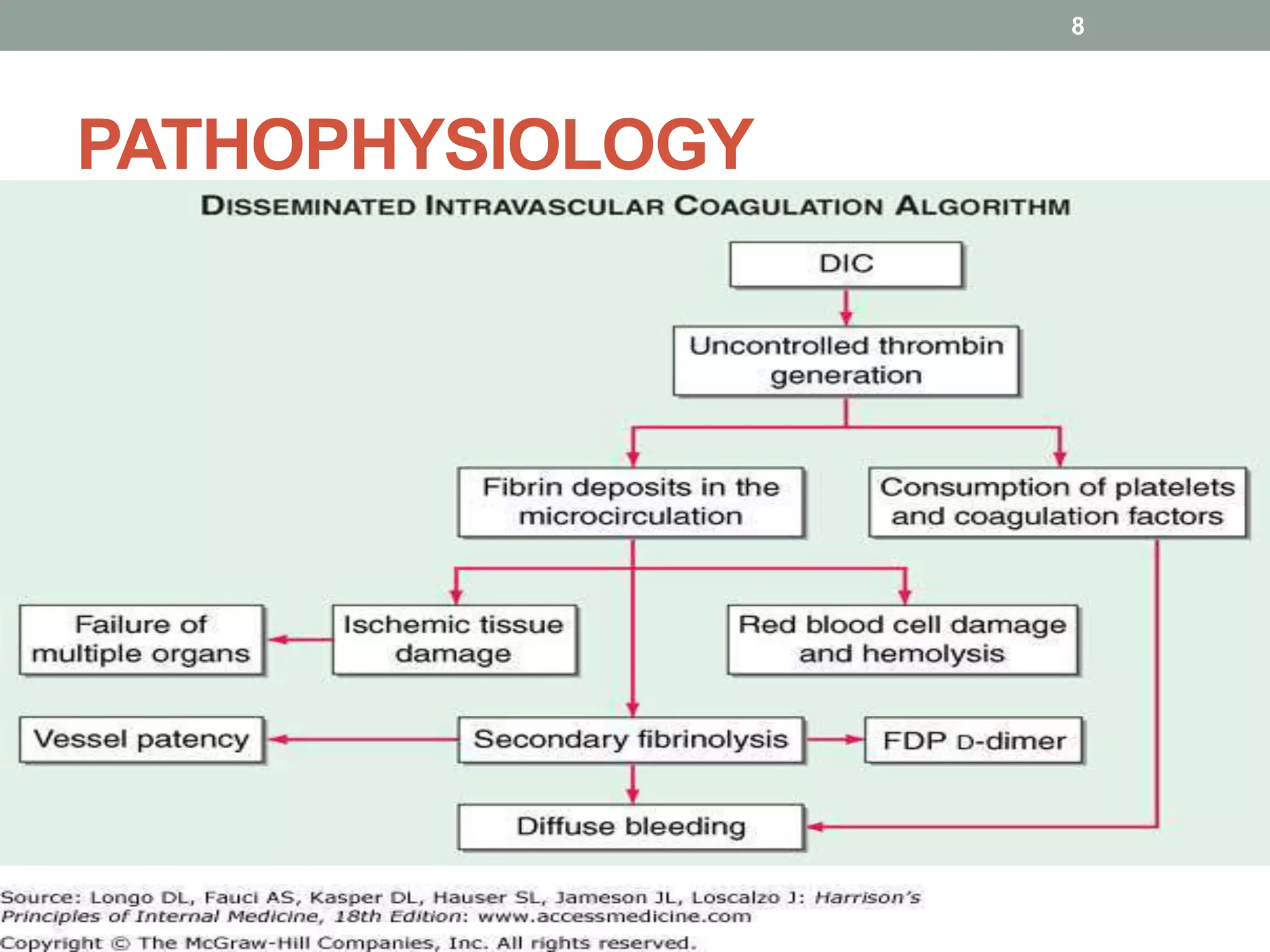
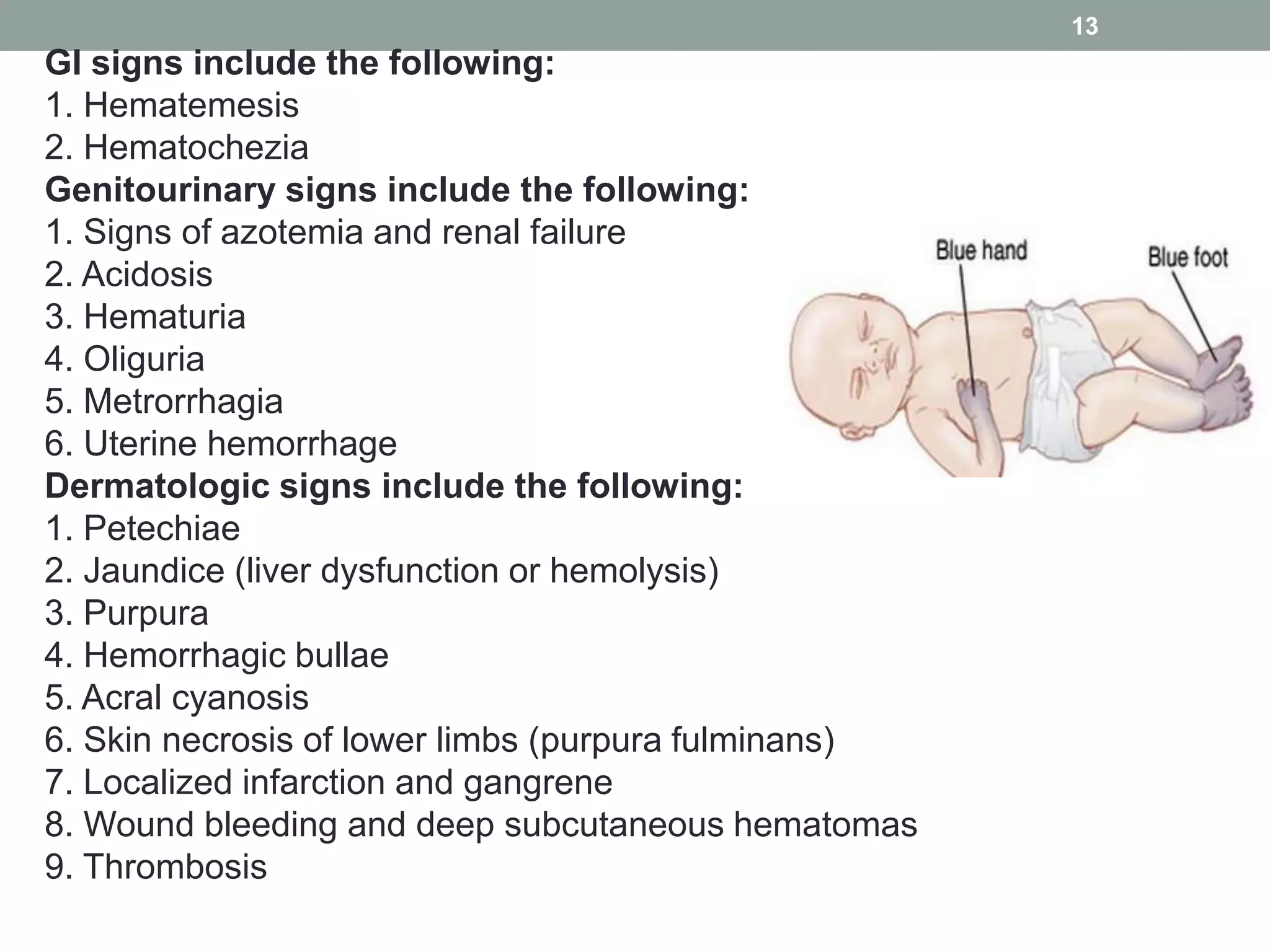
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a serious condition characterized by widespread clotting in response to excessive blood protease activity, leading to a depletion of natural anticoagulants and severe bleeding. The document outlines the types, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, differential diagnosis, diagnosis criteria, and treatment options for DIC. It emphasizes the importance of managing the underlying disorder and discusses various treatment strategies including replacement therapy, anticoagulants, and specific agents for restoration of anticoagulant pathways.











![DIAGNOSIS
•Platelet -- moderate-to-severe thrombocytopenia is
present in DIC.
•Activated partial thromboplastin time [aPTT] and
prothrombin time [PT]) are typically prolonged.
•Protein C and antithrombin are 2 natural anticoagulants
that are frequently decreased in DIC.
•Elevated levels D-dimer and FDPs
•Thrombomodulin is elevated in DIC, a marker for early
identification and monitoring of DIC.
•Chronic DIC diagnosis when the schistocytes are seen in
concert with normal coagulation values and increased D-
dimer levels.
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dic-180328193816/75/Disseminated-Intravascular-Coagulation-16-2048.jpg)