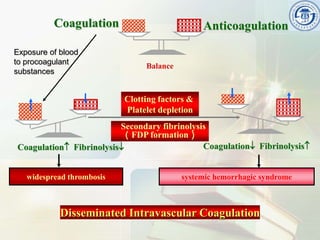
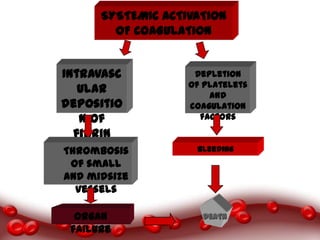
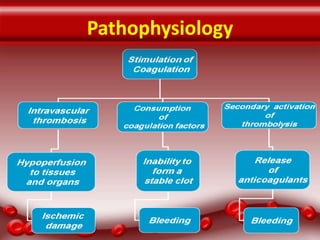
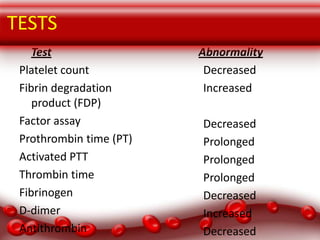
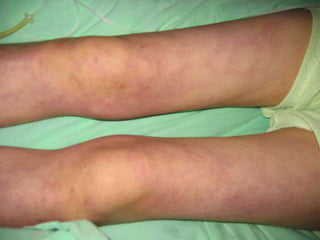
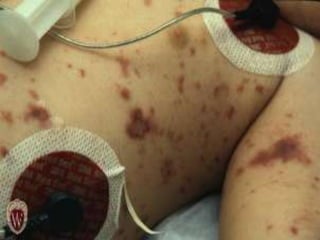
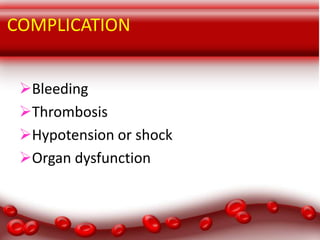
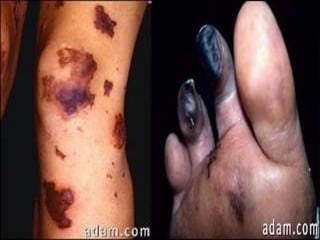
This document provides an overview of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) including its definition, pathophysiology, classification, etiology, tests, clinical manifestations, complications, treatment, and nursing process. DIC is an acquired syndrome characterized by widespread activation of coagulation and loss of localization arising from different causes that can damage microvasculature and cause organ dysfunction. It is secondary to serious illnesses like infection, cancer, obstetric complications, and tissue injury. Treatment focuses on treating the underlying cause, supportive care, and replacing depleted blood components to stop abnormal coagulation and control bleeding.