Thrombocytopenia
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
8 likes•6,643 views
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low platelet counts. It has many potential causes, including decreased platelet production in the bone marrow due to things like cancer, viruses, medications, or liver/kidney disease. It can also be caused by increased platelet destruction, such as in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Symptoms range from bruising and bleeding to internal bleeding in severe cases. Diagnosis involves blood tests to check the platelet count and rule out underlying conditions. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include medications, splenectomy, platelet transfusions, or changing medications that are causing the low platelet count.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
Anemia Causes, Types, Symptoms, Diet, and Treatment 

https://userupload.net/0gv9ijneu7hf
Anemia is a condition that develops when your blood lacks enough healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a main part of red blood cells and binds oxygen. If you have too few or abnormal red blood cells, or your hemoglobin is abnormal or low, the cells in your body will not get enough oxygen.
Leukemia

It is a malignant disease of a blood forming organs. The common feature of leukemia is an unregulated proliferation of white blood cells (WBCs) in the bone marrow.
Thrombocytopenia

Thrombocytopenia is most frequently encountered Hematological problem in hospitalized patients. The most common causes and differential diagnosis of In-patient and Outpatient presentations of Thrombocytopenia is discussed here. Useful for Internal Medicine Boards . Archer Internal Medicine Board review lectures will be released soon.
Thrombocytopenia

When your blood has too few platelets, mild
to serious bleeding can occur. Bleeding can occur inside your body (internal
bleeding) or underneath your skin or from the surface of your skin (external
bleeding).
A normal platelet count in adults ranges
from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. A platelet count of
less than 150,000 platelets per microliter is lower than normal. If your blood
platelet count falls below normal, you have thrombocytopenia.
However, the risk for serious bleeding
doesn't occur until the count becomes very low—less than 10,000 or 20,000
platelets per microliter. Mild bleeding sometimes occurs when the count is less
than 50,000 platelets per microliter.
Many factors can cause a low platelet
count, such as:
-- The body's bone marrow doesn't make enough
platelets.
-- The bone marrow makes enough platelets, but
the body destroys them or uses them up.
-- The spleen holds on to too many platelets.
The spleen is an organ that normally stores about one-third of the body's
platelets. It also helps your body fight infection and remove unwanted cell
material.
-- A combination of the above factors.
-- How long thrombocytopenia lasts depends on
its cause. It can last from days to years.
The treatment for this condition also
depends on its cause and severity. Mild thrombocytopenia often doesn't require
treatment. If the condition causes or puts you at risk for serious bleeding,
you may need medicines or blood or
platelet transfusions. Rarely, the spleen may need to be removed.
Iron deficiency anemia.

pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment and description of condition.
thanks to mygroups members for making this ppt.
Shock

Shock, definition, types, causes, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation, diagnostic evaluation, management
Investigations in hemorrhegic disorders ppt Prashant Mune

Clinical assessment, pertinent history, and family history are good indicators for determining patient's bleeding tendencies.
The most appropriate laboratory tests performed are Routine screening tests include a complete blood cell count, platelet count, and evaluation of a peripheral blood sample, a prothrombin time, and an activated partial thromboplastin time.
More Related Content
What's hot
Anemia Causes, Types, Symptoms, Diet, and Treatment 

https://userupload.net/0gv9ijneu7hf
Anemia is a condition that develops when your blood lacks enough healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a main part of red blood cells and binds oxygen. If you have too few or abnormal red blood cells, or your hemoglobin is abnormal or low, the cells in your body will not get enough oxygen.
Leukemia

It is a malignant disease of a blood forming organs. The common feature of leukemia is an unregulated proliferation of white blood cells (WBCs) in the bone marrow.
Thrombocytopenia

Thrombocytopenia is most frequently encountered Hematological problem in hospitalized patients. The most common causes and differential diagnosis of In-patient and Outpatient presentations of Thrombocytopenia is discussed here. Useful for Internal Medicine Boards . Archer Internal Medicine Board review lectures will be released soon.
Thrombocytopenia

When your blood has too few platelets, mild
to serious bleeding can occur. Bleeding can occur inside your body (internal
bleeding) or underneath your skin or from the surface of your skin (external
bleeding).
A normal platelet count in adults ranges
from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. A platelet count of
less than 150,000 platelets per microliter is lower than normal. If your blood
platelet count falls below normal, you have thrombocytopenia.
However, the risk for serious bleeding
doesn't occur until the count becomes very low—less than 10,000 or 20,000
platelets per microliter. Mild bleeding sometimes occurs when the count is less
than 50,000 platelets per microliter.
Many factors can cause a low platelet
count, such as:
-- The body's bone marrow doesn't make enough
platelets.
-- The bone marrow makes enough platelets, but
the body destroys them or uses them up.
-- The spleen holds on to too many platelets.
The spleen is an organ that normally stores about one-third of the body's
platelets. It also helps your body fight infection and remove unwanted cell
material.
-- A combination of the above factors.
-- How long thrombocytopenia lasts depends on
its cause. It can last from days to years.
The treatment for this condition also
depends on its cause and severity. Mild thrombocytopenia often doesn't require
treatment. If the condition causes or puts you at risk for serious bleeding,
you may need medicines or blood or
platelet transfusions. Rarely, the spleen may need to be removed.
Iron deficiency anemia.

pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment and description of condition.
thanks to mygroups members for making this ppt.
Shock

Shock, definition, types, causes, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation, diagnostic evaluation, management
What's hot (20)
Anemia Causes, Types, Symptoms, Diet, and Treatment 

Anemia Causes, Types, Symptoms, Diet, and Treatment
Similar to Thrombocytopenia
Investigations in hemorrhegic disorders ppt Prashant Mune

Clinical assessment, pertinent history, and family history are good indicators for determining patient's bleeding tendencies.
The most appropriate laboratory tests performed are Routine screening tests include a complete blood cell count, platelet count, and evaluation of a peripheral blood sample, a prothrombin time, and an activated partial thromboplastin time.
Thrombocytopenia during pregnancy

Thrombocytopenia during pregnancy fetal neonetal
pregnancy preeclampsia ITP gestational thrombocytopenia DIC
postpartum
Hematocrit & rbc

define hematocrit and how's the test is performed
if hematocrit is abnormal what are the symptoms
risks of getting rbc count
if rbc is abnormal what are the consequences
prepare for blood collection for hematocrit
Blood count

• Study of the formed cellular blood elements
• Blood is composed of a Liquid called Plasma & of cellular elements (RBC’S, WBC’S & Platelets)
Pseudovasculitides. Mikhail Valivach. 2015

Illustrated presentation on numerous diseaes mimicking vasculitides.
Bleeding Disorders: Classification and Diagnosis

These slides briefly tell about the bleeding disorders, their classification and diagnosis .
Similar to Thrombocytopenia (20)
Investigations in hemorrhegic disorders ppt Prashant Mune

Investigations in hemorrhegic disorders ppt Prashant Mune
More from Priya
Heart valve disease

In heart valve disease, one or more of the valves in your heart doesn't work properly.
Your heart has four valves that keep blood flowing in the correct direction. In some cases, one or more of the valves don't open or close properly. This can cause the blood flow through your heart to your body to be disrupted.
Your heart valve disease treatment depends on the heart valve affected and the type and severity of the valve disease. Sometimes heart valve disease requires surgery to repair or replace the heart valve.Your heart has four valves that keep blood flowing in the correct direction. These valves include the mitral valve, tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve and aortic valve. Each valve has flaps (leaflets or cusps) that open and close once during each heartbeat. Sometimes, the valves don't open or close properly, disrupting the blood flow through your heart to your body.
Heart valve disease may be present at birth (congenital). It can also occur in adults due to many causes and conditions, such as infections and other heart conditions.
Heart valve problems may include:
Regurgitation. In this condition, the valve flaps don't close properly, causing blood to leak backward in your heart. This commonly occurs due to valve flaps bulging back, a condition called prolapse.
Stenosis. In valve stenosis, the valve flaps become thick or stiff, and they may fuse together. This results in a narrowed valve opening and reduced blood flow through the valve.
Atresia. In this condition, the valve isn't formed, and a solid sheet of tissue blocks the blood flow between the heart chambers.Several factors can increase your risk of heart valve disease, including:
Older age
History of certain infections that can affect the heart
History of certain forms of heart disease or heart attack
High blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and other heart disease risk factors
Heart conditions present at birth (congenital heart disease)Heart valve disease can cause many complications, including:
Heart failure
Stroke
Blood clots
Heart rhythm abnormalities
Death
Arrythmia

Heart rhythm problems (heart arrhythmias) occur when the electrical impulses that coordinate your heartbeats don't work properly, causing your heart to beat too fast, too slow or irregularly.
Heart arrhythmias (uh-RITH-me-uhs) may feel like a fluttering or racing heart and may be harmless. However, some heart arrhythmias may cause bothersome — sometimes even life-threatening — signs and symptoms.
Heart arrhythmia treatment can often control or eliminate fast, slow or irregular heartbeats. In addition, because troublesome heart arrhythmias are often made worse — or are even caused — by a weak or damaged heart, you may be able to reduce your arrhythmia risk by adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle.Arrhythmias may cause you to feel premature heartbeats, or you may feel that your heart is racing or beating too slowly. Other signs and symptoms may be related to your heart not pumping effectively due to the fast or slow heartbeat. These include shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting or near fainting, and chest pain or discomfort. Seek urgent medical care if you suddenly or frequently experience any of these signs and symptoms at a time when you wouldn't expect to feel them.Ventricular fibrillation is one type of arrhythmia that can be deadly. It occurs when the heart beats with rapid, erratic electrical impulses. This causes the lower chambers in your heart (ventricles) to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood. Without an effective heartbeat, blood pressure plummets, cutting off blood supply to your vital organs.f slow heartbeats (bradycardias) don't have a cause that can be corrected, doctors often treat them with a pacemaker because there aren't any medications that can reliably speed up the heart.
A pacemaker is a small device that's usually implanted near your collarbone. One or more electrode-tipped wires run from the pacemaker through your blood vessels to your inner heart. If your heart rate is too slow or if it stops, the pacemaker sends out electrical impulses that stimulate your heart to beat at a steady rate.
Leukopenia

The terms leukopenia and neutropenia are often used interchangeably. However, they refer to slightly different conditions. Leukopenia is an umbrella term that refers to a reducation in any of the white blood cell types.
Neutropenia is a type of leukopenia but refers specifically to a decrease in neutrophils, the most common type of white blood cell. A person’s neutrophil count is an important indicator of their infection risk.
Disseminated intra vascular coagulation

In disseminated intravascular coagulation, abnormal clumps of thickened blood (clots) form inside blood vessels. These abnormal clots use up the blood's clotting factors, which can lead to massive bleeding in other places. Causes include inflammation, infection and cancer.
Symptoms include blood clots and bleeding, possibly from many sites in the body.
The goal is to treat the underlying cause and provide supportive care through intravenous fluids and blood transfusions.
Leukocytosis

Leukocyte is another name for white blood cell (WBC). These are the cells in your blood that help your body fight infections and some diseases.
When the number of white cells in your blood is higher than normal, it’s called leukocytosis. This usually happens because you’re sick, but sometimes it’s just a sign that your body is stressed.is a condition that affects all types of white blood cells. Other illnesses, such as neutrophilia, lymphocytosis, and granulocytosis, target specific types of white blood cells. Normal white blood cell counts are 4,300-10,800 white blood cells per microliter. Leukocyte or white blood cell levels are considered elevated when they are between 15,000-20,000 per microliter. The increased number of leukocytes can occur abnormally as a result of an infection.An abnormally large number of leukocytes, as observed in acute infections, inflammation, hemorrhage, and other conditions. A white blood cell count of 10,000/mm3 (or more) usually indicates leukocytosis Most examples of leukocytosis represent a disproportionate increase in the number of cells in the neutrophilic series, and the term is frequently used synonymously with the designation neutrophilia. Leukocytosis of 15,000-25,000/mm3 is frequently observed in various pathologic conditions, and values as high as 40,000 are not unusual; occasionally, as in some examples of leukemoid reactions, white blood cell counts may range up to 100,000/mm3.Leukocytosis is usually a response to an infection or inflammation, so it’s not a cause for alarm. However, it can be caused by serious diseases such as leukemia and other cancers, so it’s important that your doctor diagnose the cause of an increased WBC when it’s found. Leukocytosis associated with pregnancy or in response to exercise is normal and nothing to worry about.
Leukemia

Leukemia is a cancer of blood-forming tissues, including bone marrow. Many types exist such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Many patients with slow-growing types of leukaemia don't have symptoms. Rapidly growing types of leukaemia may cause symptoms that include fatigue, weight loss, frequent infections, and easy bleeding or bruising.Treatment is highly variable. For slow-growing leukemias, treatment may include monitoring. For aggressive leukemias, treatment includes chemotherapy that's sometimes followed by radiation and stem-cell transplant.
Hemophiliia

Hemophilia is not one disease but rather one of a group of inherited bleeding disorders that cause abnormal or exaggerated bleeding and poor blood clotting. The term is most commonly used to refer to two specific conditions known as hemophilia A and hemophilia BHemophilia is an inherited genetic condition. This condition isn’t curable, but it can be treated to minimize symptoms and prevent future health complications.
In extremely rare cases, hemophilia can develop after birth. This is called “acquired hemophilia.” This is the case in people whose immune system forms antibodies that attack factors VIII or IX. Hemophilia A is caused by a mutation in the gene for factor VIII, so there is deficiency of this clotting factor. Hemophilia B (also called Christmas disease) results from a deficiency of factor IX due to a mutation in the corresponding gene.
A condition referred to as hemophilia C involves a deficiency of clotting factor XI. This condition is much rarer than hemophilia A and B and typically leads to mild symptoms. It is also not inherited in an X-linked manner and affects persons of both sexes.
Lymphangitis

Lymphangitis is inflammation of lymphatic channels due to infectious or noninfectious causes. Potential pathogens include bacteria, mycobacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Lymphangitis most commonly develops after cutaneous inoculation of microorganisms into the lymphatic vessels through a skin wound or a distal infection complication.
Lymphadenitis

Swollen lymph nodes usually occur as a result of infection from bacteria or viruses. Rarely, swollen lymph nodes are caused by cancer. Your lymph nodes, also called lymph glands, play a vital role in your body's ability to fight off infections. They function as filters, trapping viruses, bacteria and other causes of illnesses before they can infect other parts of your body. Common areas where you might notice swollen lymph nodes include your neck, under your chin, in your armpits and in your groin.
In some cases, the passage of time .Hard, swollen or tender lymph nodes
Itchy skin, Lump, or mass that can be felt beneath the skin, Rash
Redness, warmth or selling immune system disorders
Lupus — a chronic inflammatory disease that targets your joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart and lungs
Rheumatoid arthritis — a chronic inflammatory disease targeting the tissue that lines your joints (synovium)
Cancers
Lymphoma — cancer that originates in your lymphatic system
Leukemia — cancer of your body's blood-forming tissue, including your bone marrow and lymphatic system
Other cancers that have spread (metastasized) to lymph nodes
Lymphoma

Lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's germ-fighting network.
The lymphatic system includes the lymph nodes (lymph glands), spleen, thymus gland and bone marrow. Lymphoma can affect all those areas as well as other organs throughout the body.Being older, male, or Caucasian
Having any of the following conditions:
An inherited immune system disorder
An autoimmune disease, Use of immunosuppressant drugs following an organ transplant
High levels of exposure to certain pesticides have been found in some observational studies to slightly increase the risk of NHL in agricultural workers. The risk from low-level and/or periodic exposure to these substances is not certain.
Exposure to radiation THESEare the cause.symptoms. These can include:
night sweats
unintentional weight loss
a high temperature (fever)
a persistent cough or feeling of breathlessness
persistent itching of the skin all over the body, treat meant include like chemotherapy, radiation therapy, bone marrow transplantation, etc
Aneurysm

An aneurysm is an enlargement of the artery. it is divided into 3type according to action, more pathology, etc. the treatment of this is commonly surgery some of the procedures also help full for the aneurysm like shutting procedure. the prevention n of this is avoid smoking, exercise...
Raynaud’s disease

Raynauds disease is Raynaud's (ray-NOSE) disease that causes some areas of your body — such as your fingers and toes — to feel numb and cold in response to cold temperatures or stress. In Raynaud's disease, smaller arteries that supply blood to your skin become narrow, limiting blood flow to affected areas (vasospasm).This condition causes “attacks” that limit blood supply to fingers and toes, which may get pale, cold and numb. As blood returns, they may start to tingle and hurt. Except in rare cases, it’s typically not serious. There’s no cure, but there are changes you can make to your routine, dress, and diet that can help you manage symptoms. Episodes are typically triggered by cold or emotional stress. The primary treatment is avoiding the cold. Other measures include the discontinuation of nicotine or stimulant use. vaso dilator is effective .statinis effective for this condition
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction is the medical name of a heart attack. A heart attack is a life-threatening condition that occurs when blood flow to the heart muscle is abruptly cut off, causing tissue damage. This is usually the result of a blockage in one or more of the coronary arteries.Symptoms include tightness or pain in the chest, neck, back or arms, as well as fatigue, lightheadedness, abnormal heartbeat and anxiety. Women are more likely to have atypical symptoms than men.
Treatment ranges from lifestyle changes and cardiac rehabilitation to medication, stents, and bypass surgery.
Cellulitis

Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue. It is most commonly caused by S. pyogenes and S. aureus.5 Bacteria may gain access to the dermis via a break in the skin barrier in healthy adults, whereas the hematogenous route is more common in immunocompromised patients.
The affected skin is usually erythematous, swollen, painful, and warm to the touch. Severe cellulitis can be complicated by bullae, pustules, or necrotic tissue. Damage to lymphatic vessels can lead to recurrent episodes of cellulitis.6 In areas of the world endemic for lymphatic filariasis, it is important to rule out this disease in cases of recurrent bouts of lower-extremity cellulitis and lymphangitis.
Hypertension

high blood pressure (hypertension) is a common condition in which the long-term force of the blood against your artery walls is high enough that it may eventually cause health problems, such as heart disease.
Blood pressure is determined both by the amount of blood your heart pumps and the amount of resistance to blood flow in your arteries. The more blood your heart pumps and the narrower your arteries, the higher your blood pressure. A blood pressure reading is given in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). It has two numbers. The top number (systolic pressure). The first, or upper, number measures the pressure in your arteries when your heartbeats.
Bottom number (diastolic pressure). The second, or lower, number measures the pressure in your arteries between beats.For most adults, there's no identifiable cause of high blood pressure. This type of high blood pressure, called primary (essential) hypertension, tends to develop gradually over many yearsSome people have high blood pressure caused by an underlying condition. This type of high blood pressure, called secondary hypertension, tends to appear suddenly and cause higher blood pressure than does primary hypertension. Various conditions and medications can lead to secondary hypertension, including: Obstructive sleep apnea
Kidney disease
Adrenal gland tumors
Thyroid problems
Certain defects you're born with (congenital) in blood vessels
Certain medications, such as birth control pills, cold remedies, decongestants, over-the-counter pain relievers and some prescription drugs
Illegal drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines. The risk of high blood pressure increases as you age. Until about age 64, high blood pressure is more common in men. Women are more likely to develop high blood pressure after age 65.
Race. High blood pressure is particularly common among people of African heritage, often developing at an earlier age than it does in whites. Serious complications, such as stroke, heart attack and kidney failure, also are more common in people of African heritage.Weakened and narrowed blood vessels in your kidneys. This can prevent these organs from functioning normally.
Thickened, narrowed, or torn blood vessels in the eyes. This can result in vision loss.
Varicose vein

Varicose veins are dilated, often palpable subcutaneous veins with reversed blood flow. They are most commonly found in the legs. Estimates of the prevalence of varicose veins vary. Visible varicose veins in the lower limbs are estimated to affect at least a third of the population. Varicose veins are swollen, twisted veins that you can see just under the skin. They usually occur in the legs, but also can form in other parts of the body. Hemorrhoids are a type of varicose vein.
Your veins have one-way valves that help keep blood flowing toward your heart. If the valves are weak or damaged, blood can back up and pool in your veins. This causes the veins to swell, which can lead to varicose veins.
Varicose veins are very common. You are more at risk if you are older, are female, have obesity, don't exercise, or have a family history of varicose veins. They can also be more common in pregnancy. Visible Blue, Red, or Purple veins in legs. May even bulge
Pain in legs while standing and sitting, Leg cramps, Legs feeling heavy, burning, Radiating pain Numb legs and Bleeding.
Treatment involves compression stockings, exercise, or procedures to close or remove the veins home treatments for varicose veins · 1. Exercise · 2. Compression stockings · 3. Plant extracts · 4. Dietary changes · 5. Eat more flavonoids · 6. Herbal remedies.
Deep vein thrombosis

Deep vein thrombosis is a blood clotting disorder. causes of this is age above 60 yrs. cancer , obesity, prolonged standing etc. diagnostic evaluation of this doppler study, CT, MRI, etc. medical management of this blood thinner, like aspirin, stockings etc
Disseminated intra vascular coagulation

disseminated intravascular coagulation is an abnormal blood clot in the blood vessels called dic. causes of this are any infection, cancer, liver disease, abnormal pregnancy, etc. signs and symptoms of this fever, petechiae, purpura, etc .treatment of this id anticoagulant agent like aspirin, plasma transfusion, etc
Rheumatoid heart disease

Rheumatoid heart disease is a disease. rheumatic fever, rheumatoid heart disease. cause of this is group A hemolytic streptococci infectfection., any autoimmune disease, etc. symptoms of this are fever tiredness, vomiting, chorea, etc treatment of this is in penicillin. surgical manage meant of this valvuloplasty
Endocarditis

ENDOCARDITIS is the internal inflammation of the endocardium. and some value or has affected causes of this infection and noninfective endocarditis, management of the valve replacement medical management is antibiotic.
More from Priya (20)
Recently uploaded
Pulmonary Thromboembolism - etilogy, types, medical- Surgical and nursing man...

Disruption of blood supply to lung alveoli due to blockage of one or more pulmonary blood vessels is called as Pulmonary thromboembolism. In this presentation we will discuss its causes, types and its management in depth.
The Normal Electrocardiogram - Part I of II

These lecture slides, by Dr Sidra Arshad, offer a quick overview of physiological basis of a normal electrocardiogram.
Learning objectives:
1. Define an electrocardiogram (ECG) and electrocardiography
2. Describe how dipoles generated by the heart produce the waveforms of the ECG
3. Describe the components of a normal electrocardiogram of a typical bipolar leads (limb II)
4. Differentiate between intervals and segments
5. Enlist some common indications for obtaining an ECG
Study Resources:
1. Chapter 11, Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th edition
2. Chapter 9, Human Physiology - From Cells to Systems, Lauralee Sherwood, 9th edition
3. Chapter 29, Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition
4. Electrocardiogram, StatPearls - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549803/
5. ECG in Medical Practice by ABM Abdullah, 4th edition
6. ECG Basics, http://www.nataliescasebook.com/tag/e-c-g-basics
263778731218 Abortion Clinic /Pills In Harare ,

263778731218 Abortion Clinic /Pills In Harare ,ABORTION WOMEN’S CLINIC +27730423979 IN women clinic we believe that every woman should be able to make choices in her pregnancy. Our job is to provide compassionate care, safety,affordable and confidential services. That’s why we have won the trust from all generations of women all over the world. we use non surgical method(Abortion pills) to terminate…Dr.LISA +27730423979women Clinic is committed to providing the highest quality of obstetrical and gynecological care to women of all ages. Our dedicated staff aim to treat each patient and her health concerns with compassion and respect.Our dedicated group ABORTION WOMEN’S CLINIC +27730423979 IN women clinic we believe that every woman should be able to make choices in her pregnancy. Our job is to provide compassionate care, safety,affordable and confidential services. That’s why we have won the trust from all generations of women all over the world. we use non surgical method(Abortion pills) to terminate…Dr.LISA +27730423979women Clinic is committed to providing the highest quality of obstetrical and gynecological care to women of all ages. Our dedicated staff aim to treat each patient and her health concerns with compassion and respect.Our dedicated group of receptionists, nurses, and physicians have worked together as a teamof receptionists, nurses, and physicians have worked together as a team wwww.lisywomensclinic.co.za/
Tom Selleck Health: A Comprehensive Look at the Iconic Actor’s Wellness Journey

Tom Selleck, an enduring figure in Hollywood. has captivated audiences for decades with his rugged charm, iconic moustache. and memorable roles in television and film. From his breakout role as Thomas Magnum in Magnum P.I. to his current portrayal of Frank Reagan in Blue Bloods. Selleck's career has spanned over 50 years. But beyond his professional achievements. fans have often been curious about Tom Selleck Health. especially as he has aged in the public eye.
Follow us on: Pinterest
Introduction
Many have been interested in Tom Selleck health. not only because of his enduring presence on screen but also because of the challenges. and lifestyle choices he has faced and made over the years. This article delves into the various aspects of Tom Selleck health. exploring his fitness regimen, diet, mental health. and the challenges he has encountered as he ages. We'll look at how he maintains his well-being. the health issues he has faced, and his approach to ageing .
Early Life and Career
Childhood and Athletic Beginnings
Tom Selleck was born on January 29, 1945, in Detroit, Michigan, and grew up in Sherman Oaks, California. From an early age, he was involved in sports, particularly basketball. which played a significant role in his physical development. His athletic pursuits continued into college. where he attended the University of Southern California (USC) on a basketball scholarship. This early involvement in sports laid a strong foundation for his physical health and disciplined lifestyle.
Transition to Acting
Selleck's transition from an athlete to an actor came with its physical demands. His first significant role in "Magnum P.I." required him to perform various stunts and maintain a fit appearance. This role, which he played from 1980 to 1988. necessitated a rigorous fitness routine to meet the show's demands. setting the stage for his long-term commitment to health and wellness.
Fitness Regimen
Workout Routine
Tom Selleck health and fitness regimen has evolved. adapting to his changing roles and age. During his "Magnum, P.I." days. Selleck's workouts were intense and focused on building and maintaining muscle mass. His routine included weightlifting, cardiovascular exercises. and specific training for the stunts he performed on the show.
Selleck adjusted his fitness routine as he aged to suit his body's needs. Today, his workouts focus on maintaining flexibility, strength, and cardiovascular health. He incorporates low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, and light weightlifting. This balanced approach helps him stay fit without putting undue strain on his joints and muscles.
Importance of Flexibility and Mobility
In recent years, Selleck has emphasized the importance of flexibility and mobility in his fitness regimen. Understanding the natural decline in muscle mass and joint flexibility with age. he includes stretching and yoga in his routine. These practices help prevent injuries, improve posture, and maintain mobilit
Hemodialysis: Chapter 3, Dialysis Water Unit - Dr.Gawad

- Video recording of this lecture in English language: https://youtu.be/lK81BzxMqdo
- Video recording of this lecture in Arabic language: https://youtu.be/Ve4P0COk9OI
- Link to download the book free: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/nephrotube-nephrology-books.html
- Link to NephroTube website: www.NephroTube.com
- Link to NephroTube social media accounts: https://nephrotube.blogspot.com/p/join-nephrotube-on-social-media.html
Phone Us ❤85270-49040❤ #ℂall #gIRLS In Surat By Surat @ℂall @Girls Hotel With...

Phone Us ❤85270-49040❤ #ℂall #gIRLS In Surat By Surat @ℂall @Girls Hotel With 100% Satisfaction
Alcohol_Dr. Jeenal Mistry MD Pharmacology.pdf

Ethanol (CH3CH2OH), or beverage alcohol, is a two-carbon alcohol
that is rapidly distributed in the body and brain. Ethanol alters many
neurochemical systems and has rewarding and addictive properties. It
is the oldest recreational drug and likely contributes to more morbidity,
mortality, and public health costs than all illicit drugs combined. The
5th edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
(DSM-5) integrates alcohol abuse and alcohol dependence into a single
disorder called alcohol use disorder (AUD), with mild, moderate,
and severe subclassifications (American Psychiatric Association, 2013).
In the DSM-5, all types of substance abuse and dependence have been
combined into a single substance use disorder (SUD) on a continuum
from mild to severe. A diagnosis of AUD requires that at least two of
the 11 DSM-5 behaviors be present within a 12-month period (mild
AUD: 2–3 criteria; moderate AUD: 4–5 criteria; severe AUD: 6–11 criteria).
The four main behavioral effects of AUD are impaired control over
drinking, negative social consequences, risky use, and altered physiological
effects (tolerance, withdrawal). This chapter presents an overview
of the prevalence and harmful consequences of AUD in the U.S.,
the systemic nature of the disease, neurocircuitry and stages of AUD,
comorbidities, fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, genetic risk factors, and
pharmacotherapies for AUD.
New Drug Discovery and Development .....

The "New Drug Discovery and Development" process involves the identification, design, testing, and manufacturing of novel pharmaceutical compounds with the aim of introducing new and improved treatments for various medical conditions. This comprehensive endeavor encompasses various stages, including target identification, preclinical studies, clinical trials, regulatory approval, and post-market surveillance. It involves multidisciplinary collaboration among scientists, researchers, clinicians, regulatory experts, and pharmaceutical companies to bring innovative therapies to market and address unmet medical needs.
Non-respiratory Functions of the Lungs.pdf

These simplified slides by Dr. Sidra Arshad present an overview of the non-respiratory functions of the respiratory tract.
Learning objectives:
1. Enlist the non-respiratory functions of the respiratory tract
2. Briefly explain how these functions are carried out
3. Discuss the significance of dead space
4. Differentiate between minute ventilation and alveolar ventilation
5. Describe the cough and sneeze reflexes
Study Resources:
1. Chapter 39, Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th edition
2. Chapter 34, Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition
3. Chapter 17, Human Physiology by Lauralee Sherwood, 9th edition
4. Non-respiratory functions of the lungs https://academic.oup.com/bjaed/article/13/3/98/278874
KDIGO 2024 guidelines for diabetologists

KDIGO guidelines 2024 for evaluation and management of CKD, related to diabetes and management of diabetic kidney disease
BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA.BPH. BPHpdf

The prostate is an exocrine gland of the male mammalian reproductive system
It is a walnut-sized gland that forms part of the male reproductive system and is located in front of the rectum and just below the urinary bladder
Function is to store and secrete a clear, slightly alkaline fluid that constitutes 10-30% of the volume of the seminal fluid that along with the spermatozoa, constitutes semen
A healthy human prostate measures (4cm-vertical, by 3cm-horizontal, 2cm ant-post ).
It surrounds the urethra just below the urinary bladder. It has anterior, median, posterior and two lateral lobes
It’s work is regulated by androgens which are responsible for male sex characteristics
Generalised disease of the prostate due to hormonal derangement which leads to non malignant enlargement of the gland (increase in the number of epithelial cells and stromal tissue)to cause compression of the urethra leading to symptoms (LUTS
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE IN HEALTHCARE.pdf

Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. It encompasses tasks such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding. AI technologies are revolutionizing various fields, from healthcare to finance, by enabling machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
Physiology of Chemical Sensation of smell.pdf

Title: Sense of Smell
Presenter: Dr. Faiza, Assistant Professor of Physiology
Qualifications:
MBBS (Best Graduate, AIMC Lahore)
FCPS Physiology
ICMT, CHPE, DHPE (STMU)
MPH (GC University, Faisalabad)
MBA (Virtual University of Pakistan)
Learning Objectives:
Describe the primary categories of smells and the concept of odor blindness.
Explain the structure and location of the olfactory membrane and mucosa, including the types and roles of cells involved in olfaction.
Describe the pathway and mechanisms of olfactory signal transmission from the olfactory receptors to the brain.
Illustrate the biochemical cascade triggered by odorant binding to olfactory receptors, including the role of G-proteins and second messengers in generating an action potential.
Identify different types of olfactory disorders such as anosmia, hyposmia, hyperosmia, and dysosmia, including their potential causes.
Key Topics:
Olfactory Genes:
3% of the human genome accounts for olfactory genes.
400 genes for odorant receptors.
Olfactory Membrane:
Located in the superior part of the nasal cavity.
Medially: Folds downward along the superior septum.
Laterally: Folds over the superior turbinate and upper surface of the middle turbinate.
Total surface area: 5-10 square centimeters.
Olfactory Mucosa:
Olfactory Cells: Bipolar nerve cells derived from the CNS (100 million), with 4-25 olfactory cilia per cell.
Sustentacular Cells: Produce mucus and maintain ionic and molecular environment.
Basal Cells: Replace worn-out olfactory cells with an average lifespan of 1-2 months.
Bowman’s Gland: Secretes mucus.
Stimulation of Olfactory Cells:
Odorant dissolves in mucus and attaches to receptors on olfactory cilia.
Involves a cascade effect through G-proteins and second messengers, leading to depolarization and action potential generation in the olfactory nerve.
Quality of a Good Odorant:
Small (3-20 Carbon atoms), volatile, water-soluble, and lipid-soluble.
Facilitated by odorant-binding proteins in mucus.
Membrane Potential and Action Potential:
Resting membrane potential: -55mV.
Action potential frequency in the olfactory nerve increases with odorant strength.
Adaptation Towards the Sense of Smell:
Rapid adaptation within the first second, with further slow adaptation.
Psychological adaptation greater than receptor adaptation, involving feedback inhibition from the central nervous system.
Primary Sensations of Smell:
Camphoraceous, Musky, Floral, Pepperminty, Ethereal, Pungent, Putrid.
Odor Detection Threshold:
Examples: Hydrogen sulfide (0.0005 ppm), Methyl-mercaptan (0.002 ppm).
Some toxic substances are odorless at lethal concentrations.
Characteristics of Smell:
Odor blindness for single substances due to lack of appropriate receptor protein.
Behavioral and emotional influences of smell.
Transmission of Olfactory Signals:
From olfactory cells to glomeruli in the olfactory bulb, involving lateral inhibition.
Primitive, less old, and new olfactory systems with different path
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF URINARY SYSTEM.pptx

Valuable Content of Human Anatomy and Physiology of Urinary system as per PCI Syllabus for Pharmacy and PharmD Students.
TEST BANK for Operations Management, 14th Edition by William J. Stevenson, Ve...

TEST BANK for Operations Management, 14th Edition by William J. Stevenson, Verified Chapters 1 - 19, Complete Newest Version.pdf
TEST BANK for Operations Management, 14th Edition by William J. Stevenson, Verified Chapters 1 - 19, Complete Newest Version.pdf
Ozempic: Preoperative Management of Patients on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists 

Preoperative Management of Patients on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists like Ozempic and Semiglutide
ASA GUIDELINE
NYSORA Guideline
2 Case Reports of Gastric Ultrasound
Recently uploaded (20)
Pulmonary Thromboembolism - etilogy, types, medical- Surgical and nursing man...

Pulmonary Thromboembolism - etilogy, types, medical- Surgical and nursing man...
Tom Selleck Health: A Comprehensive Look at the Iconic Actor’s Wellness Journey

Tom Selleck Health: A Comprehensive Look at the Iconic Actor’s Wellness Journey
Hemodialysis: Chapter 3, Dialysis Water Unit - Dr.Gawad

Hemodialysis: Chapter 3, Dialysis Water Unit - Dr.Gawad
Phone Us ❤85270-49040❤ #ℂall #gIRLS In Surat By Surat @ℂall @Girls Hotel With...

Phone Us ❤85270-49040❤ #ℂall #gIRLS In Surat By Surat @ℂall @Girls Hotel With...
Triangles of Neck and Clinical Correlation by Dr. RIG.pptx

Triangles of Neck and Clinical Correlation by Dr. RIG.pptx
TEST BANK for Operations Management, 14th Edition by William J. Stevenson, Ve...

TEST BANK for Operations Management, 14th Edition by William J. Stevenson, Ve...
Ozempic: Preoperative Management of Patients on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists 

Ozempic: Preoperative Management of Patients on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Thrombocytopenia
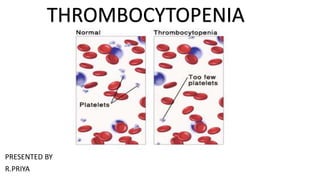
- 2. INTRODUCTION The estimated prevalence of thrombocytopenia in MDS, defined as a platelet count of <100,000/mcL, ranges from 40% to 65%. A retrospective review of patients referred to the MD Anderson Cancer Center identified 1605 of 2410 (67%) patients with thrombocytopenia at referral. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000 per microliter
- 3. DEFINITION Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets , also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in 20% of medical patients and a third of surgical patients.
- 4. CAUSES Decreased production of platelets Platelets are produced in your bone marrow. Factors that can decrease platelet production include: •Leukemia and other cancers •Some types of anemia •Viral infections, such as hepatitis C or HIV •Chemotherapy drugs and radiation therapy •Heavy alcohol consumption •Dehydration, Vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency •Leukaemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, or aplastic anaemia •Decreased production of thrombo poietin by the liver in liver failure •Sepsis, systemic viral or bacterial infection •Leptospirosis •Hereditary syndromes[14] • ACTN1-related thrombocytopenia • A megakaryocytic thrombocytopenia with radio-ulnar synostosis • ANKRD26 related thrombocytopenia
- 5. CAUSES Increased breakdown of platelets Abnormally high rates of platelet destruction may be due to immune or nonimmune conditions, including:[15] •Immune thrombocytopenic purpura •Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura •Hemolytic–uremic syndrome •Disseminated intravascular coagulation •Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria •Antiphospholipid syndrome •Systemic lupus erythematosus •Post-transfusion purpura •Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia •Hypersplenism •Dengue fever •Gaucher's disease •Zika virus
- 6. CAUSES Some conditions can cause your body to use up or destroy platelets faster than they're produced, leading to a shortage of platelets in your bloodstream. Examples of such conditions include: •Pregnancy. Thrombocytopenia caused by pregnancy is usually mild and improves soon after childbirth. •Immune thrombocytopenia. Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, cause this type. The body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys platelets. If the exact cause of this condition isn't known, it's called idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. This type more often affects children. •Bacteria in the blood. Severe bacterial infections involving the blood (bacteremia) can destroy platelets. •Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. This is a rare condition that occurs when small blood clots suddenly form throughout your body, using up large numbers of platelets. •Hemolytic uremic syndrome. This rare disorder causes a sharp drop in platelets, destruction of red blood cells and impairs kidney function. Medication-induced These medications can induce thrombocytopenia through direct myelosuppression: •Valproic acid •Methotrexate •Carboplatin •Interferon •Isotretinoin •Panobinostat •H2 blockers and proton-pump inhibitors •. Certain medications can reduce the number of platelets in your blood. Sometimes a drug confuses the immune system and causes it to destroy platelets. Examples include heparin, quinine, sulfa-containing antibiotics and anticonvulsants.
- 7. CAUSES Other causes •Lab error, possibly due to the anticoagulant EDTA in CBC specimen tubes;[citation needed] a citrated platelet count is a useful follow-up study •Snakebite •Niacin toxicity •Lyme disease •Thrombocytapheresis (also called plateletpheresis)[citation needed] •Niemann–Pick disease
- 9. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS •red, purple, or brown bruises, which are called purpura •a rash with small red or purple dots called petechiae •nosebleeds •bleeding gums •bleeding from wounds that lasts for a prolonged period or doesn’t stop on its own •heavy menstrual bleeding •bleeding from the rectum •blood in your stool •blood in your urine In more serious cases, you may bleed internally. Symptoms of internal bleeding include: •blood in the urine •blood in the stool •bloody or very dark vomit
- 10. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION Blood tests To diagnose this condition, your doctor needs to do a complete blood count test. This test looks at the amount of blood cells in your blood. It’ll tell your doctor if your platelet count is lower than it should be. A typical platelet count will range between 150,000 and 450,000 platelets per mL blood. Your doctor may also wish to have your blood tested for platelet antibodies. These are proteins that destroy platelets. Platelet antibodies can be produced as a side effect to certain drugs, such as heparin, or for unknown reasons. Your doctor may also order blood-clotting tests, which includes partial thromboplastin time and prothrombin time. These tests simply require a sample of your blood. Certain chemicals will be added to the sample to determine how long it takes your blood to clot. Ultrasound If your doctor suspects that your spleen is enlarged, they may order an ultrasound. This test will use sound waves to make a picture of your spleen. It can help your doctor determine if your spleen is the proper size. Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy If your doctor suspects that there’s a problem in your bone marrow, they may order a bone marrow aspiration. During an aspiration, your doctor will use a needle to remove a small amount of bone marrow from one of your bones. A bone marrow biopsy may also be ordered. Your doctor will use a needle to take a sample of your core bone marrow, usually from the hipbone. It may be performed at the same time as a bone marrow aspiration. liver enzymes, kidney function, vitamin B12 levels, folic acid levels, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and peripheral blood smear. If the cause for the low platelet count remains unclear, a bone marrow biopsy is usually recommended to differentiate cases of decreased platelet production from cases of peripheral platelet destruction.
- 11. MANAGEMENT •blood or platelet transfusions •changing medications that are causing a low platelet count •steroids •immune globulin •corticosteroids to block platelet antibodies •drugs that suppress your immune system •spleen removal surgery • Lithium carbonate or folate may also be used to stimulate platelet production in the bone marrow. • Discontinuation of heparin is critical in a case of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). Beyond that, however, clinicians generally treat to avoid thrombosis. Treatment may include a direct thrombin inhibitor, such as lepirudin or argatroban. Other blood thinners sometimes used in this setting include bivalirudin and fondaparinux. Platelet transfusions are not routinely used to treat HIT because thrombosis, not bleeding, is the primary problem. Warfarin is not recommended until platelets have normalized.
- 12. THANK YOU