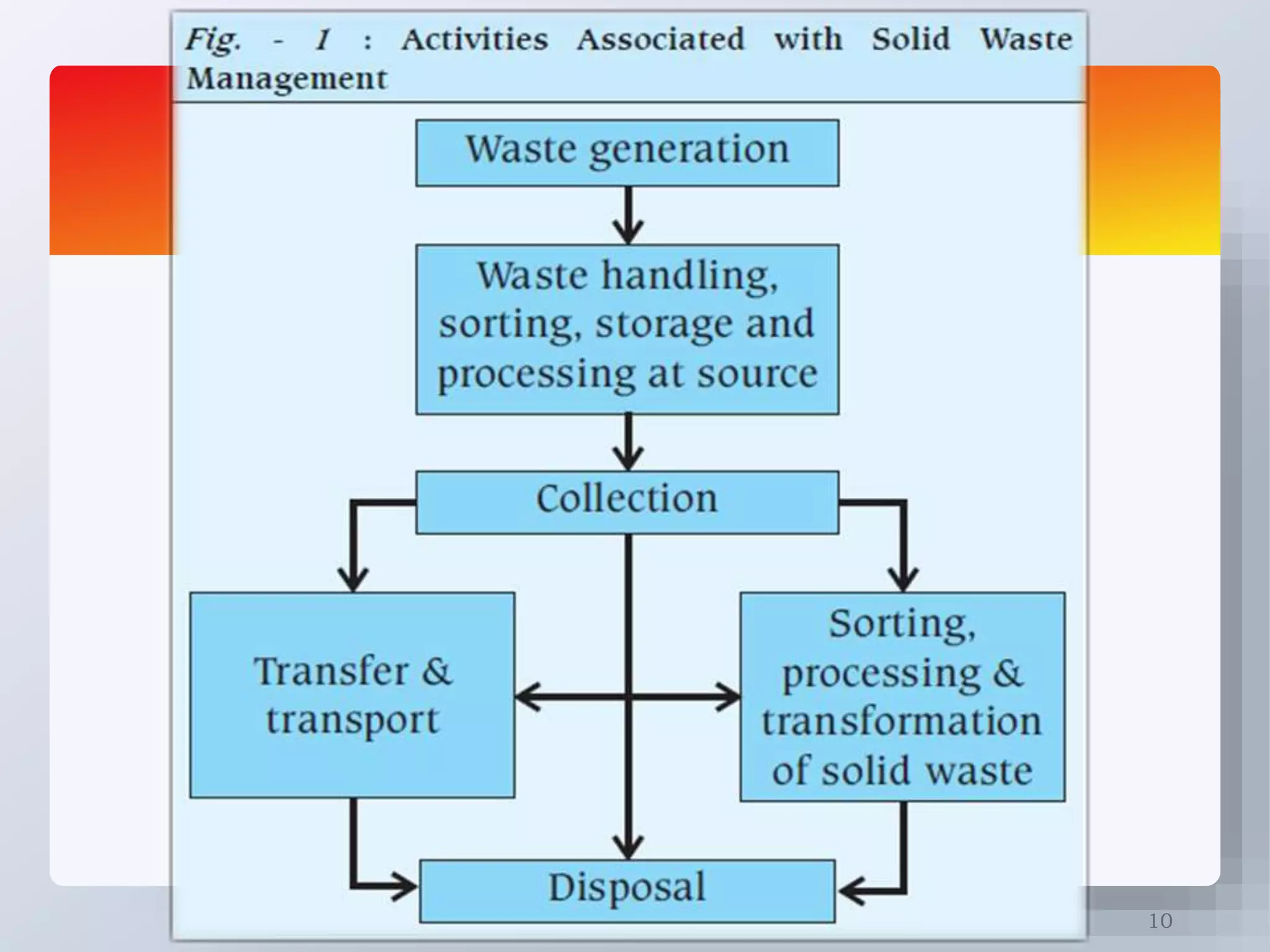
The document discusses the importance of proper solid waste disposal in promoting public health and preventing diseases. It outlines the environmental impacts of poor waste management, including contamination of water sources and the attraction of pests. Various waste disposal methods are described, including landfill, incineration, and composting, with their associated technologies and considerations.