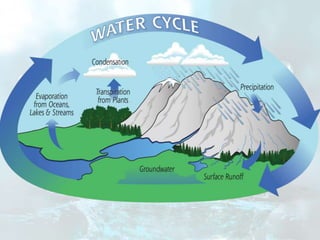
This document discusses various sources of water and methods of water purification. It describes the three main sources of water as rain, surface water, and ground water. Surface water sources include rivers, reservoirs, lakes and seas. Ground water sources include shallow wells, deep wells, and springs. The document then discusses various methods used to purify water, including storage, filtration, and disinfection. It provides details on storage, slow sand filtration, and rapid sand filtration as common purification techniques.