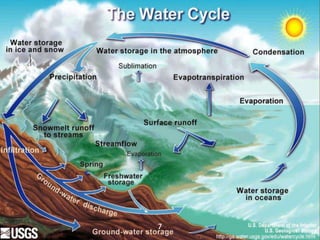
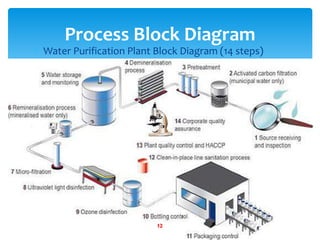
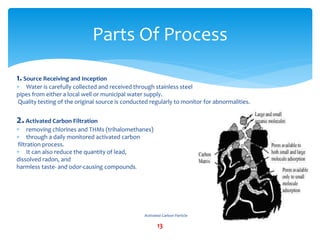
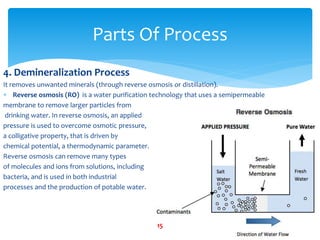
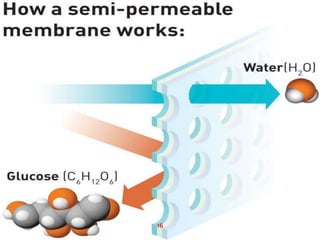
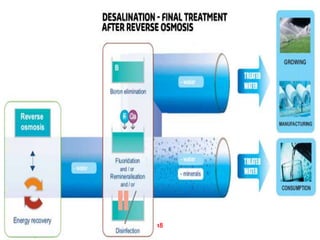
Water purification is a 14-step process that begins with water collection and ends with independent quality testing. The steps include activated carbon filtration, water softening, reverse osmosis for demineralization, remineralization by adding selected minerals, micron filtering, ultraviolet and ozone disinfection, bottling control, packaging quality assurance, line sanitation, and multiple levels of quality control and testing to produce safe drinking water.