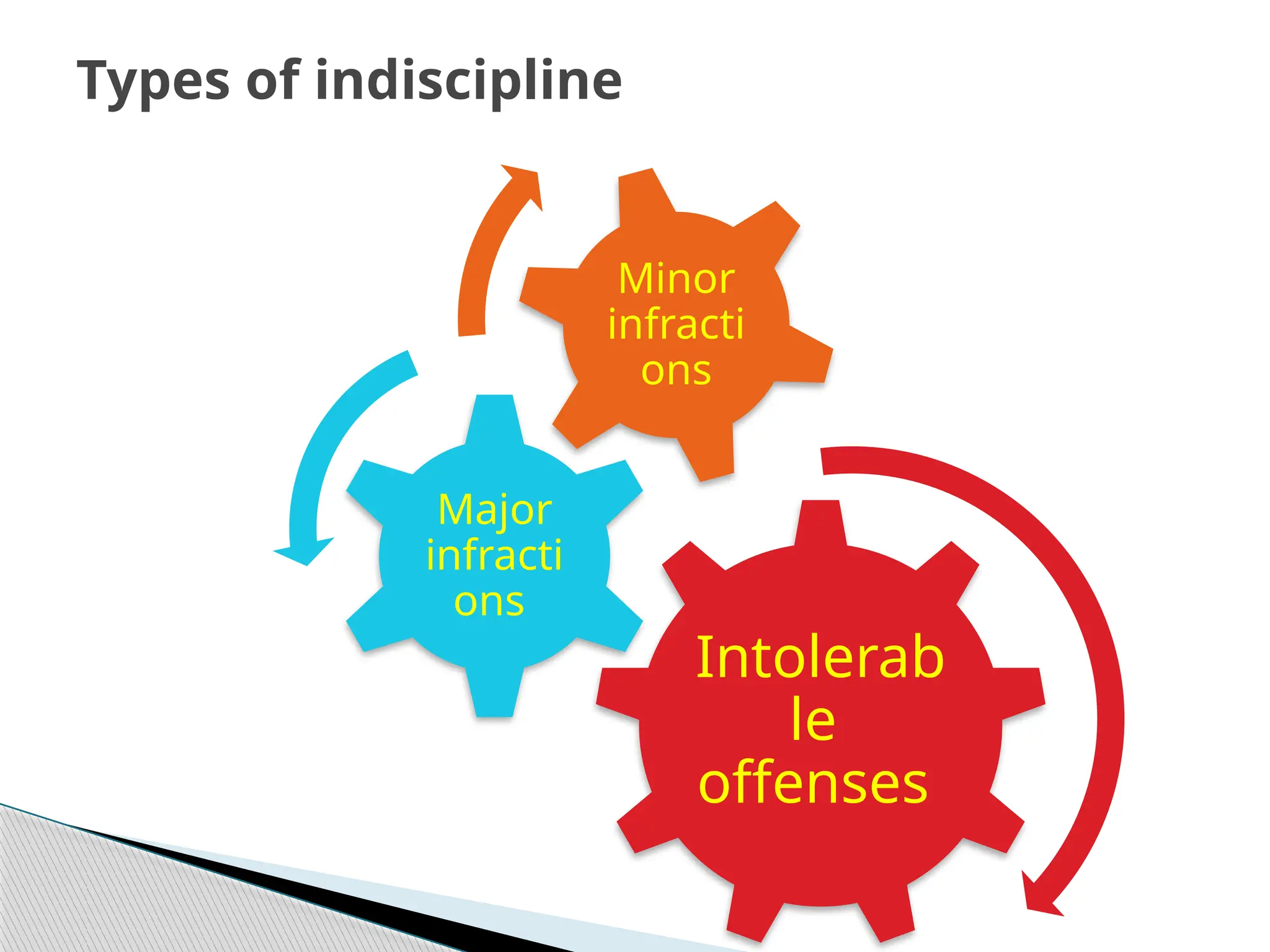
The document elaborates on the concept of discipline within educational settings, emphasizing its role in behavior control, goal attainment, and the maintenance of a conducive learning environment. It contrasts various disciplinary approaches, including assertive, democratic, and self-discipline, and discusses the principles and aims of effective disciplinary measures. Additionally, it outlines the causes of indiscipline and the consequences of various types of infractions within an organizational framework.