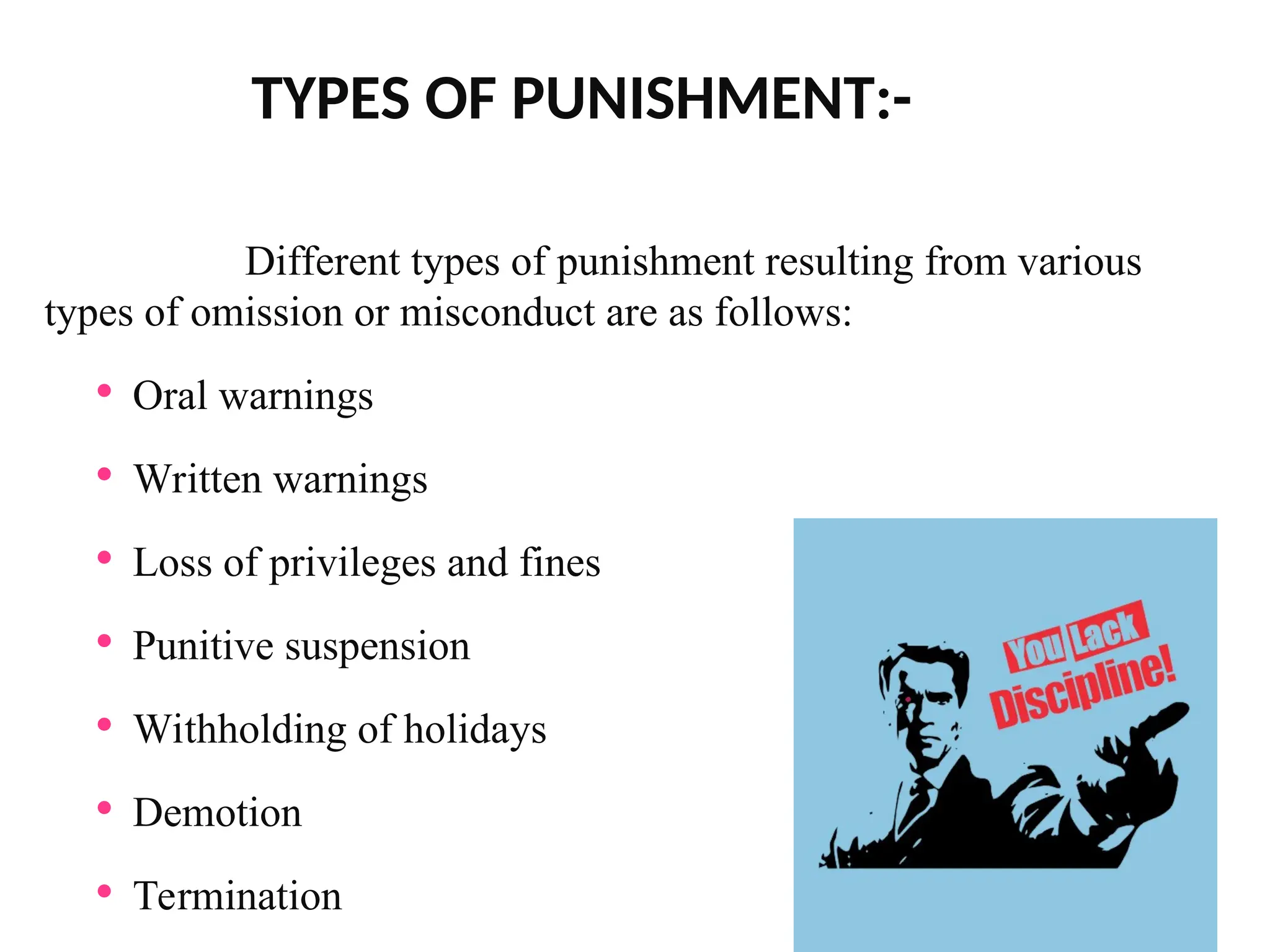
Discipline encompasses the training of mind and character to achieve desired behaviors and adherence to organizational rules and procedures. It aims to foster self-control, cooperation, and a respectful atmosphere, enhancing efficiency and morale in educational settings. Various approaches and principles outline effective disciplinary methods, emphasizing positive reinforcement, collective rule-making, and fair, consistent application of policies.