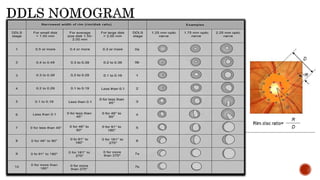
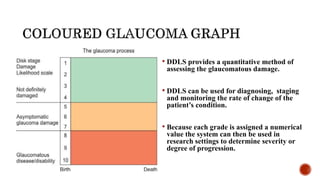
Glaucoma is a chronic optic neuropathy and a leading cause of blindness worldwide. Structural changes to the optic disc can be detected earlier than functional vision loss, so assessing the disc is crucial. The Disc Damage Likelihood Scale (DDLS) was developed to incorporate disc size and focal rim width into grading glaucomatous damage. The DDLS provides a quantitative method for diagnosing, staging, and monitoring glaucoma progression. While it has limitations for some disc types, the DDLS correlates well with visual field loss when used properly.