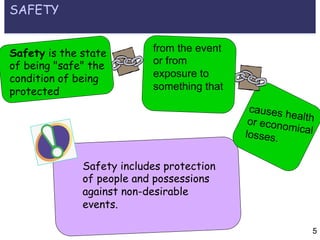
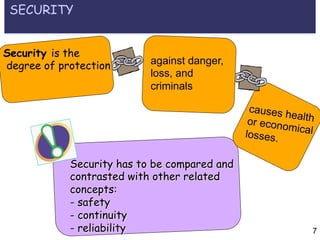
This document provides an overview of an organizational safety and security management course. The course covers key topics like defining safety and security, commonly used terminology, and distinguishing between concepts like hazards, risks, vulnerabilities, capacities, and emergencies versus disasters. It also explains differences between disaster prevention, mitigation, and preparedness approaches. The goal is to help students identify elements of definitions, explain relationships between concepts, and understand how risks can be reduced through various mitigation strategies.