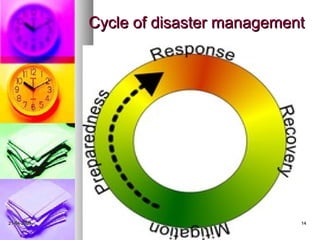
The document discusses key concepts in disaster management including:
1. Disaster management aims to avoid risks by preparing for disasters, responding to disasters, and supporting rebuilding after disasters.
2. It is defined as a continuous process managed at the individual, group, and community levels based on risk perception and integrated government and private plans.
3. The "golden hour" is critical for saving lives after a disaster and requires an integrated rescue plan with trained teams, equipment, and swift evacuation measures.