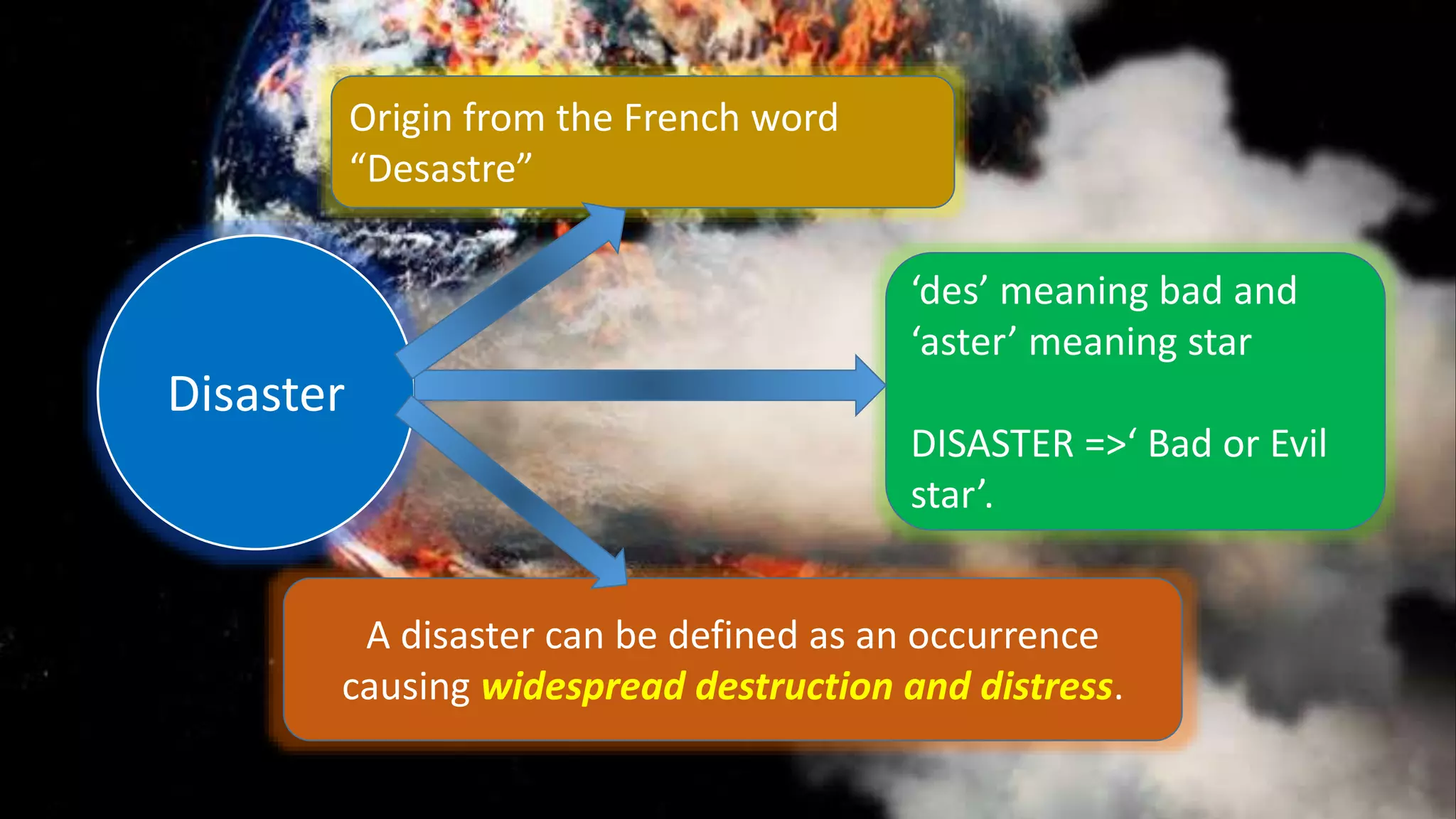
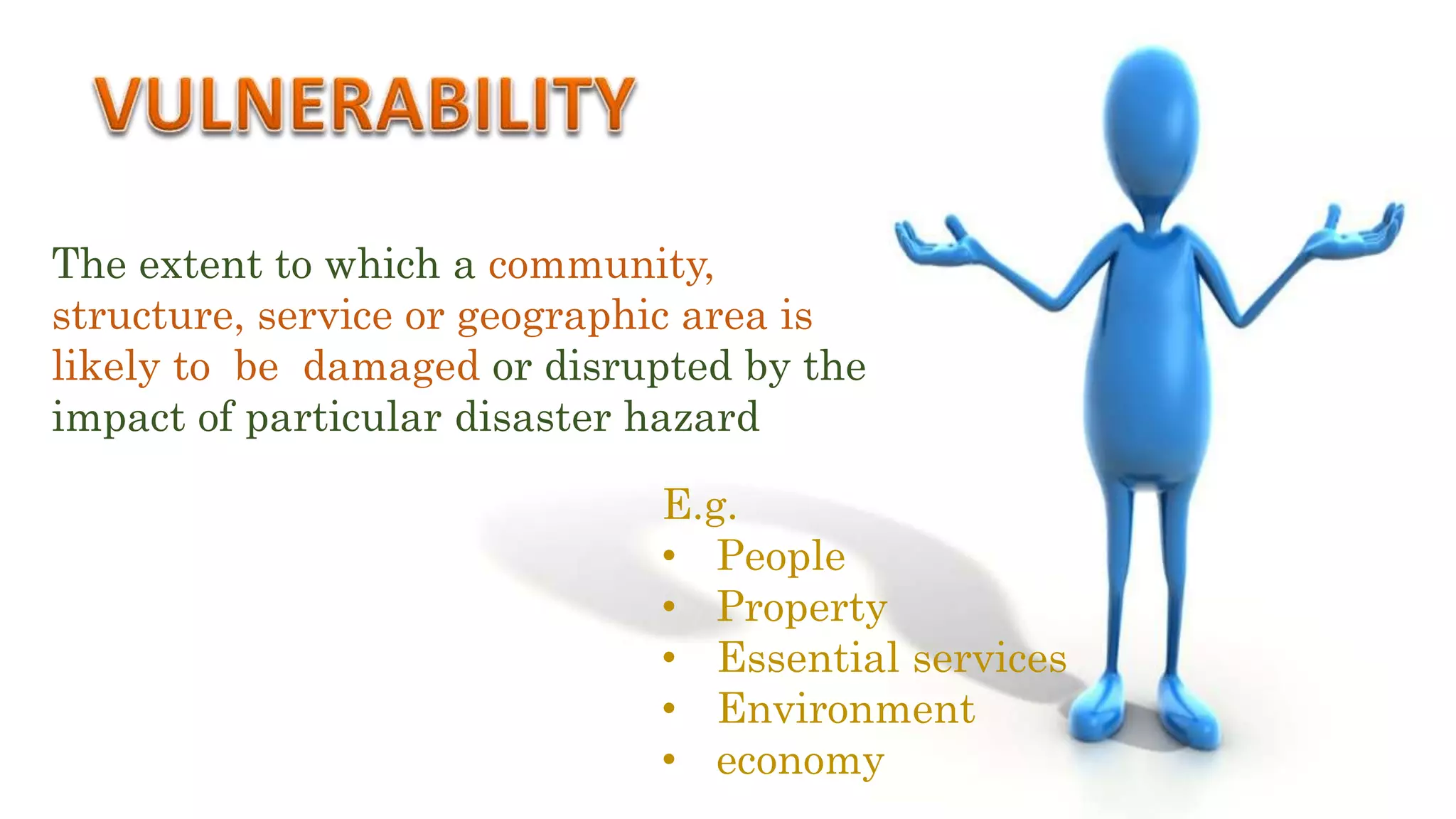
Disaster management involves preparing for, responding to, and recovering from disasters. A disaster is the result of a hazard interacting with vulnerable infrastructure or populations. Natural disasters include earthquakes, floods, droughts, volcanoes, hurricanes, and tsunamis. Disaster management has four phases: preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation. Educational institutions and teachers play an important role by providing shelter, medical care, disaster information, training, and raising awareness about hazards and preparedness. As responsible citizens, teachers should be involved in disaster preparedness efforts.