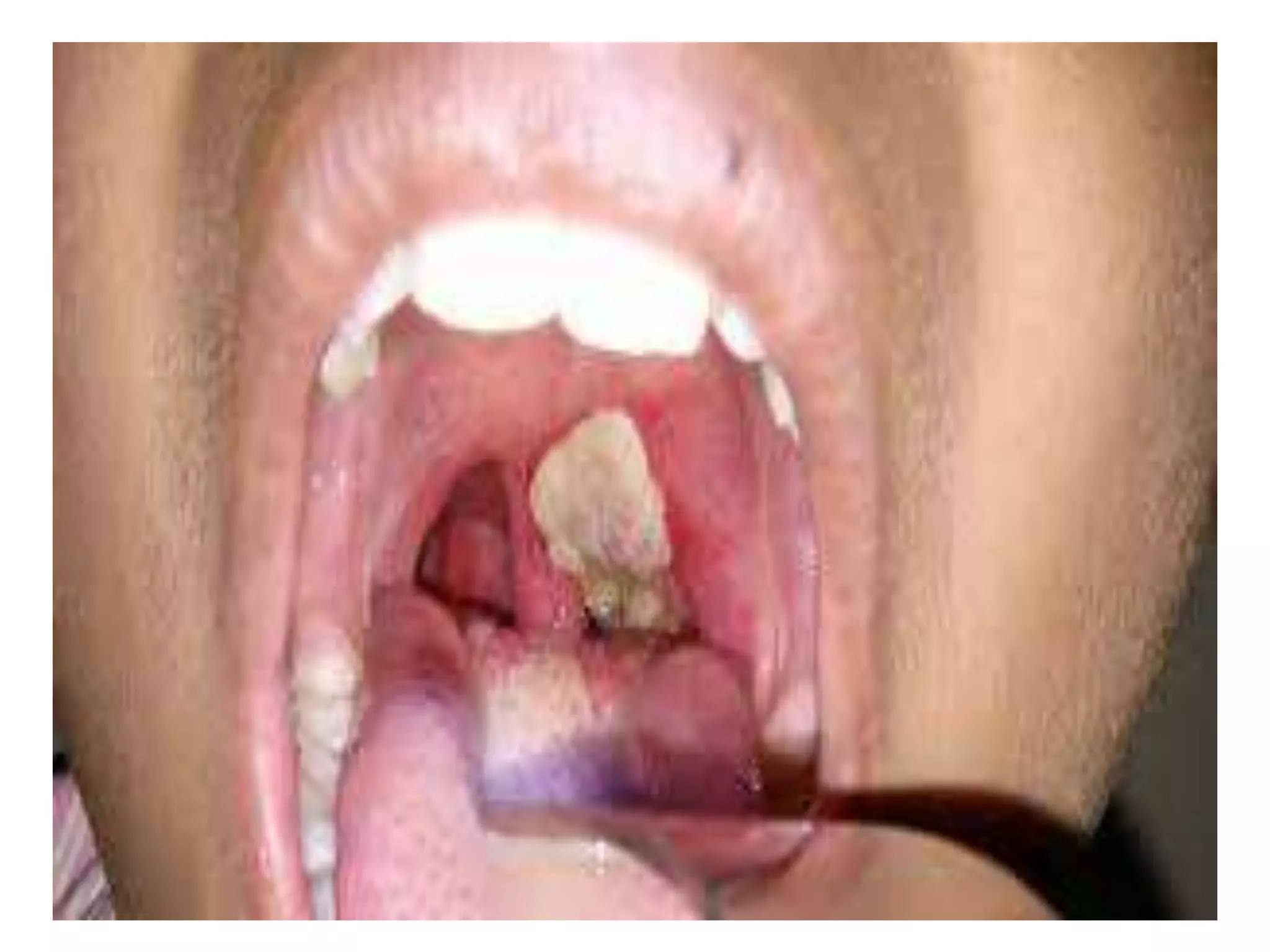
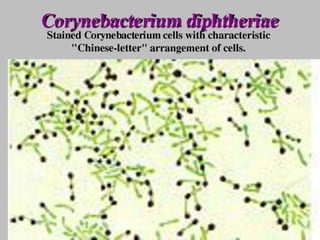
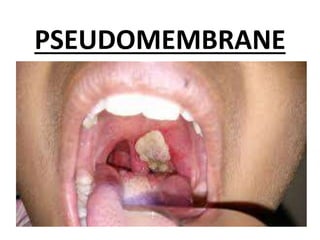
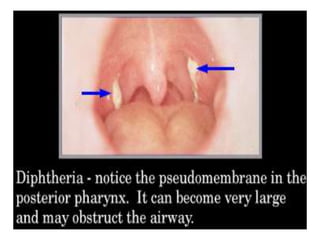
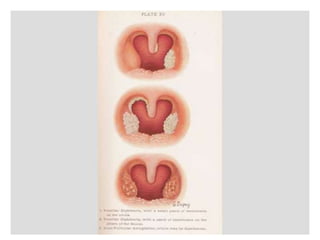
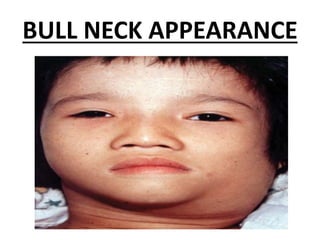
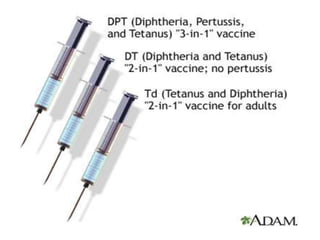
Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae which produces a toxin. It typically affects the throat and respiratory tract, causing a gray or yellow membrane that cannot be wiped away. The toxin can also damage organs like the heart. It is spread through respiratory droplets or contaminated surfaces. Immunization with DPT vaccine is the main preventive measure, with three initial doses and regular boosters recommended. Prompt treatment of cases with antitoxin and antibiotics can help control outbreaks along with isolating patients and treating carriers.