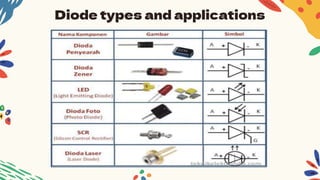
This document discusses diodes, which are semiconductor devices that allow electric current to flow in only one direction. It describes the construction of diodes using P-type and N-type semiconductors, forming a PN junction. Diodes have two characteristics - when forward biased, current can flow, and when reverse biased, little to no current flows due to the high internal resistance. Different types of diodes like power diodes, signal diodes, Zener diodes, and photo diodes are described along with their applications. The document explains that diodes work by only allowing current to flow in one direction through the PN junction.