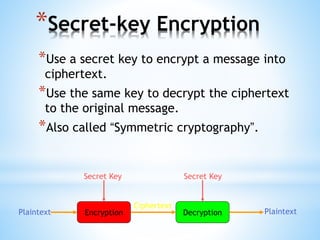
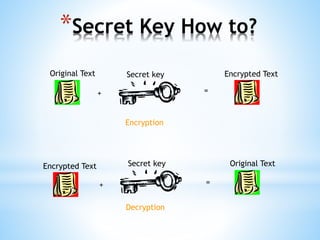
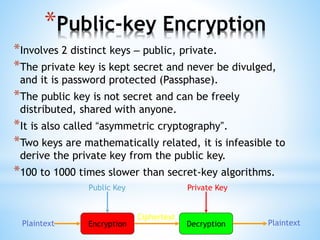
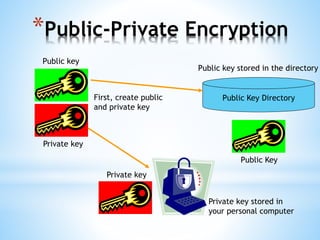
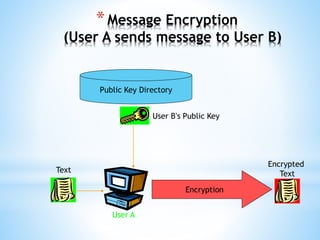
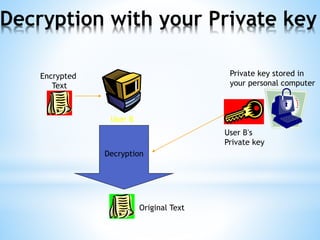
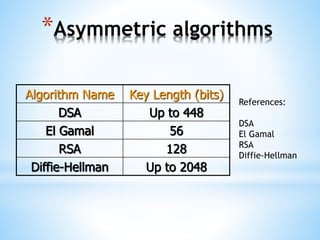
Digital signatures use asymmetric cryptography to provide authentication, integrity and non-repudiation for electronic documents and communications. A digital signature is created using a private key and can be verified by anyone using the corresponding public key. This ensures the document was not altered and the sender cannot deny sending it. Private keys are protected using devices like smart cards or hardware tokens to keep them secure.