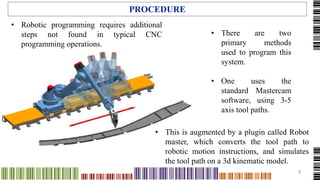
A digital fabrication lab, or fab lab, is a small workshop equipped with computer-controlled tools for creating a wide range of products through personal digital fabrication. The lab enhances educational experiences by enabling hands-on learning and interactive activities, particularly in architecture, where various advanced tools like robotic arms and CNC machines are utilized. The Taubman College fab lab exemplifies this innovation, providing state-of-the-art technology for architectural fabrication research and promoting active creation among students and professionals.