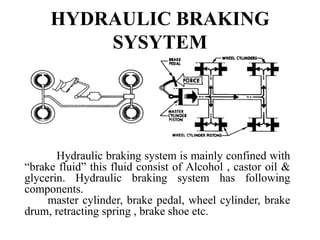
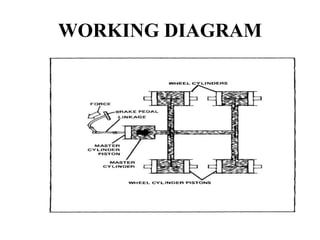
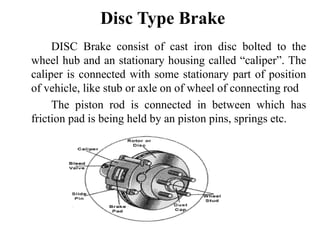
The document discusses different types of braking systems used in vehicles. It describes hydraulic, pneumatic, mechanical, disc, and anti-lock braking systems (ABS). The hydraulic system uses brake fluid to transfer pressure from the brake pedal to the wheel cylinders. ABS allows wheels to maintain traction with the road surface during braking to prevent skidding. ABS offers improved vehicle control and reduced stopping distances compared to regular brakes.